RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 7 Changing Cultural Traditions
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 7 Changing Cultural Traditions Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 History Important Questions Chapter 7 Changing Cultural Traditions
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Changing Cultural Traditions Class 11 Extra Questions Question 1.
What is the meaning of Renaissance ? Where did this term emerge ?
Answer:
The meaning of Renaissance is Rebirth. This term originated in Italy first of all.
Changing Cultural Traditions Class 11 Important Questions Question 2.
Write any two reasons which gave birth to the Renaissance.
Answer:
(i) Fall of Feudalism.
(ii) Growth of Middle Class.
(iii) Growth of Printing Press and Literature.
Class 11 History Chapter 7 Extra Questions And Answers Question 3.
What is Renaissance ?
Answer:
The word Renaissance is taken from a French word, which means Rebirth. It gave a new dimension to art and architecture and created awareness among the people.

Changing Cultural Traditions Class 11 Questions And Answers Question 4.
How did the invention of Printing Press support the Renaissance ?
Answer:
(i) It provided intellectual knowledge.
(ii) It awared the people about new literature.
(iii) It awkened the people politically.
Changing Cultural Traditions Class 11 Extra Questions And Answers Question 5.
Name any four Italian provinces. Where did the towns begin to emerge first ?
Answer:
The four Italian provinces were :
(i) Venice
(ii) Florence
(iii) Genoa
(iv) Padua
The town first began to develop in Italy.
Class 11 Changing Cultural Traditions Extra Questions Question 6.
Name any four writers who contributed a lot in bringing Renaissance.
Answer:
(i) Dante,
(ii) Petrarch,
(iii) Thomas Moore,
(iv) Erasmus.
Changing Cultural Traditions Extra Questions Question 7.
Who was Petrarch ?
Answer:
He was a great poet and a historian of Italy. He criticised the drawbacks of the society. Through his poetry he tries to awake the people. He is regarded as the ‘Father of Humanism’ in world history.
Changing Cultural Traditions Class 11 Important Questions And Answers Question 8.
Write in short about the contribution of Michelangelo.
Answer:
Michelangelo was a great artist of Renaissance. His creation, “The Fall of the Man and “The Last Judgement” are considered to be the masterpiece of art throughout the world. His paintings gave deep interpretation to human life and humanity.

कक्षा 11 इतिहास पाठ 7 के प्रश्न उत्तर Question 9.
What do you mean by the term ‘Renaissance Man’ ?
Answer:
The term ‘Renaissance Man’ means, an individual who has many interests, innovations and skills. There were many individuals in the Renaissance period who had deep interest in arts. For example, a person could be a scholar, dioplomat, theologist and artist even a historian.
Class 11 History Chapter 7 Questions And Answers Question 10.
Write any three features of humanist thought.
Answer:
Following were the main features of humanist thought :
(i) Stress on physical pleasures or material pleasures for humans.
(ii) Freedom of the individual and inalienable rights of the individual.
(iii) Ideal life for humans.
Class 11 History Ch 7 Extra Questions Question 11.
Describe any three significant consequences of the discovery of new lands.
Answer:
(i) The priests began to preach Christianity in the new colonies, as a result of which Christianity became greatest religion of the world.
(ii) Europeans began to trade in America, Africa and Asia after they discovered new sea routes.
(iii) Sale and purchase of slaves started.
Class 11 History Changing Cultural Traditions Questions And Answers Question 12.
Which two persons gave the greatest contribution to the popularity of Florence ?
Answer:
Dante Alighieri (1265-1321), a layman who wrote on religious themes, and Giotto (1267-1337), an artist who painted lifelike portraits, very different from the stiff figures done by earlier artists. From then it developed as the most exicting intellectual city in Italy and as a centre of artistic creativity.

Class 11 History Chapter Changing Cultural Traditions Question Answer Question 13.
Why did humanists name the beginning of the fifteenth century as new age or modern age ?
Answer:
Humanists named the beginning of the fifteenth century as new age or modern age in order to differentiate it from medieval age or middle age.
History Class 11 Chapter 7 Question Answer Question 14.
Who was Andreas Vesalius ?
Answer:
Andreas Vesalius (1514-64) was a professor of medicine at the University of Padua. He dissected the human body. It led to the beginning of modern physiology.
Ch 7 History Class 11 Important Questions Question 15.
Write a comparative details of Italian architecture of this period with the Islamic architecture in brief.
Answer:
Magnificent buildings were constructed in both the Italian and Islamic architectures. Magnificent cathedrals and monasteries were constructed in Italian architecture, whereas large mosques were built in Islamic architecture. Great care was taken about decoration of these buildings. Arch and pillars were salient features of these buildings.
Class 11 History Ch 7 Important Questions Question 16.
Who was Ibn Rushd ?
Answer:
Ibn Rushd was an Arab philosopher of Spain who tried to resolve the contradiction between philosophical knowledge and religious beliefs.
Class 11 History Changing Cultural Traditions Extra Questions And Answers Question 17.
Which two things played a significant role in transmitting humanist ideas to people ?
Answer:
(i) Humanist subjects began to be taught in schools and colleges.
(ii) Art, architecture and literature also played an effective role in transmitting humanist ideas.
Class 11 History Chapter 7 Important Questions Question 18.
What is the subject-matter of Ptolemy’s Almagest ?
Answer:
Ptolemy’s Almagest was a work on astronomy. It was written in Greek before 140 CE and later it was translated into Arabic. It carries the Arabic definite article ‘al’, which brings out the Arabic connection.

Changing Culture And Traditions Class 11 Question Answer Question 19.
To whom were Europeans indebted for the development of printing technology in Europe in the sixteenth century and why ?
Answer:
In sixteenth century, revolutionary printing technology developed in Europe. For this, Europeans were indebted to the Chinese and Mongol rulers. It was so because European traders and diplomats visited to the courts of Chinese and Mongol rulers and they had become familiar with it.
Class 11 History Chapter 7 Question 20.
What was Realism ?
Answer:
Anatomy, Physics, Geometry and a strong sense of beautifulness gave a new form to Italian art. Later it came to be known as realism.
Changing Cultural Traditions Question Answer Question 21.
Write any two effects of humanist culture on human life.
Answer:
(i) It weakened the control of religion over human life.
(ii) Italians were strongly affected to material wealth, power and glory.
Class 11 History Ch 7 Question Answer Question 22.
Who was Michael Angelo Buonarotti ? What was his contribution in the field of Italian art ?
Answer:
Michael Angelo Buonarotti was a skilled painter, sculptor and an architect. He painted for the Pope in the Sistine Chapel and made a sculpture called ‘The Pieta’. He also prepared the design of the dome of St. Peter’s Church. All these extraordinary pieces of art are in Rome.
Question 23.
Name any two humanist writers. Also tell what views they expressed. Write one point of each.
Answer:
Two humanist writers were Francesco Barbaro and Lorenzo Valla.
(i) Francesco Barbaro : Francesco Barbaro defended acquisition of wealth as virtue in one of his pamphlets.

(ii) Lorenzo Valla : In ‘On Pleasure’, Lorenzo Valla criticised the Christian injunction against pleasure.

Question 24.
Why was the Renaissance considered as the beginning of the modem age ? State two reasons.
Answer:
(i) The modem age began with the Renaissance. Ancient and medieval assumptions started to abolish in this age. Almost all the aspects of human life saw changes in this age.
(ii) A number of new scientific inventions were made and new ideologies came into being in the fields of art and literature.

Question 25.
What were the effects of the growth of trade and commerce ?
Answer:
(i) It made European nations economically prosperous.
(ii) It also helped to discover new lands for their colonies and used them as markets.
Question 26.
Describe in brief the consequences of the discovery of new lands.
Answer:
(i) Sale and purchase of slaves came into limelight.
(ii) The priests began to spread Christianity as a result Christianity religion became the world’s greatest religion.
Question 27.
Write any two real motivating factors behind voyages discoveries.
Answer:
(i) To enslave people.
(ii) To encourage trade and earning money.
(iii) To earn name and fame.
Question 28.
What were the results of the Protestant Reformation Movement ? Write any two.
Answer:
(i) People’s attitude towards religion changed and Christianity got divided into two parts.
(ii) The Pope himself came to know about his weaknesses and save his position by the Counter Reformation.
Question 29.
What do you understand by the term ‘Protestant Reformation’ ?
Answer:
(i) Disparity, injustice, corruption in churches forced people to do without the priests and religion.
(ii) They left themselves to superstitions and misconceptions.
(iii) The period of Renaissance brought light of truth and facts to them and helped them to reform their life style.
(iv) Those who believed in scientific approach and protested against Catholic religious blindness were called as Protestants and efforts in this direction were collectively known as “Protestant Reformation’.
Question 30.
Write three points of success of Nation-States.
Answer:
(i) The nation-states brought an end to all forms slavery.
(ii) Agriculture, industry and trade progressed.
(iii) The nation states helped in the establishment of constitutional form of governments in many countries.
(iv) Despotism became a weak force.

Question 31.
Who was believed to be the inventor of the Printing Press ? Which was the first printed book in Europe ?
Answer:
Gutenberg and Castar are the inventors of printing press in mid 15th century. Their first book was Bible which was printed in Europe. It helped to increase the impetus of Renaissance in the 15th century.
Question 32.
How did the development of Nation-States become possible ?
Answer:
(i) End of Feudalism : With the end of feudalism, the powerful kings became strong in their nation states.
(ii) Middle Class : The middle class became strong. They got a firm hold in trade and business.
(iii) Discovery of Gun Powder : It increased the power of kings. They did not need the help of feudal lords for their safety.
Question 33.
What do you know about concept Humanism ?
Answer:
Humanism means the service of humanity irrespective of caste, religion, colour or cread. This thought took up root from Padua University in 1300 CE and became popular by 15th century.
Question 34.
Why were humanist thought first expressed in Italian cities ?
Answere:
(i) University and new cities first came up on Italian landscape.
(ii) Due to Renaissance, the writers of Italy wrote many books on it.
Question 35.
Write any four causes of the origin of nation-States.
Answer:
(i) Decline of feudalism.
(ii) Growth of trade
(iii) Growth of national language.
(iv) Invention of Printing Press.
(v) Invention of gun-powder.

Question 36.
Mention any three results of the Reformation Movement.
Answer:
(i) It divided the church into Catholic Chruch and Protestant Church.
(ii) Rise of mutual conflict between Catholic and Protestant Monarch.
(iii) Rise of Nation as a State.
Question 37.
Discuss the contribution of Renaissance to the development of Modern Science.
Answer:
(i) The developing of towns by common man provided opportunity to think freely. Copernicus, Galileo and Kepler changed the concept of universe while others like Vesalius and William Harvey thoroughly worked out the structure and functioning of human body.
(ii) Others like Leonardo-da-Vinci, Gioto, Michael Angelo created masterpieces of art and literature to understand the religion and truth in better way.
Question 38.
The Europeans in the Middle Ages believed that the earth was the centre of the universe. What was the change that the Renaissance scientists brought about in this view ? Mention the names of two scientists in this connection.
Answer:
(i) Copernicus and Galileo contributed tremendously in the field of astronomy by inventing new tools and implements to verify astronomical events.
(ii) Galileo was the first to develop the first telescope to watch the stars.
(iii) Copernicus was the first to declare that Earth is not flat and is not the centre of universe and it revolves around the sun.
(iv) Later on German scientist Kepler searched out other members of‘solar system’.

Question 39.
Discuss the discoveries of Copernicus and Galileo on Man’s Conception of the Universe.
Answer:
(i) The observations of Copernicus regarding earth were not in accordance with what was given in the Holy Bible about earth. So very soon it became a controversial matter and people were afraid of accepting his views against religion.
(ii) The concept of Copernicus was scientifically supported by Galileo’s Telescope which forced people to believe the theory of Copernicus.
Question 40.
Mention the evil practices of the Catholic Church that led to the movement against them.
Answer:
(i) The Catholics remained closely associated with king and power for many centuries.
(ii) They preferred to live in luxury and away from the common man.
(iii) The Catholics were empowered the extract taxes and fines so they became the representatives of the kings than the representative of the God.
(iv) Such unchallenged powers made them immoral, corrupt and indignified which finally led to revolt by the common man against the church.
Question 41.
Who was Rapheal ? Write about his contribution in brief.
Answer:
Raphael was a great artist of Italy He did his paintings in the times of the Renaissance in Italy. He is counted among the best artists of the world. His most famous work is the painting of “Madonna”.
Question 42.
Who was Leonardo-da-Vinci ?
Answer:
Leonardo-da-Vinci was a great artist of Italy. He was a man of multiple talents. He was a poet, singer, painter, sculptor, philosopher, scientist and engineer. He knew many languages also. He painted many pictures during the Renaissance period. His two paintings i.e. “The Last Supper” and “Mona Lisa” are still admired throughout the world.
Question 43.
What do you know about Thomas Moore ?
Answer:
Thomas Moore was a great writer and scholar of England of the Renaissance period. His literary masterpiece called “Utopia”. In this book he has ridiculed the bad practices of the contemporary society.
Question 44.
Who was Machiavelli ?
Answer:
Machiavelli was a famous historian of Florence. He is regarded as the “Father of the Modem Political Science”. In his notable book “The Prince” he painted the picture of an imaginary state. He was in favour of keeping separate, the politics and religion.

Question 45.
Write a short note on Gutenberg’s achievements.
Answer:
Gutenberg was a great scholar of Germany. He invented the printing press during the Renaissance period. The Bible of Gutenberg was probably the first book which was printed in Europe. His invention of the printing press proved very much helpful in the spread of education and knowledge in Europe.
Question 46.
Who was Martin Luther? What is his movement against the Catholic Church known as?
Answer:
Martin Luther was the founder of the Reformation Movement in Germany. He was strongly opposed to the Pope and the Catholic Church, as they were badly exploiting the people. Moreover, they had become very corrupt.
Question 47.
Name an English reformer who was unhappy to see corruption in Roman Catholic Church.
Answer:
Wycliffe was an English reformer who was not happy to see corruption in the Roman Catholic Church. He condemned the interference of church into religious affairs.
Question 48.
Who was Dante ?
Answer:
Dante was a great poet of Italy. He wrote many poems. In his famous epic of poem ‘The Divine Comedy’ he ridiculed the religious beliefs and practices of his age. He is considered as the greatest poet among Renaissance poets.
Question 49.
What is the meaning of the concept ‘Heretics’ and the Protestant Reformation ?
Answer:
Heretics : This concept refers to all those persons who criticised the corrupt and objectionable practices of the Roman Catholic Church.
Protestant Reformation : This reformation movement was started by a German clergyman Martin Luther against the corrupt practices of the Roman Catholic Church. As a result of this movement Christianity divided between Roman Catholics and the Protestant churches.
Question 50.
Define the concept Humanism.
Answer:
Humanism : It is a philosophy of life. It stressed the importance of man and his sentiments rather than the religious matters. During the Renaissance period the influence of Humanism was much evident in art, science and literature. The exponents of Humanism believed that the worldly problems of man should be solved first and then man should think about God, Heaven etc.
Question 51.
What do you know about Counter Reformation ?
Answer:
Counter Reformation : This movement was started by the Roman Catholic Church to counter the effects of the Protestant Reformation, which was spreading very rapidly. According to this movement the Catholic Church tried to reform itself of some of its objectionable practices. For example now the Bishops were appointed on the basis of ability. This movement tried to recover the last influence of the Roman Church.
Question 52.
Define the concept Nation States.
Answer:
Nation-States : The nation-states were established in the Renaissance period. These states were governed by a strong political ruler. These states used to keep themselves free from all kinds of foreign interference, political or religious. The nationstates used to have common language and common philosophy. They were governed by a uniform code of laws.
Question 53.
What is Mercantilism ?
Answer:
Mercantilism : It is a theory of economics which measured the wealth of a country according to the amount of precious metals, particularly gold. The exponents of this theory insist that a country should export the maximum quantity of goods and should restrict its import in order to maintain the balance of trade and to increase her gold reserves.

Question 54.
What is the meaning of concept ‘despotism ?
Answer:
The concept ‘despotism’ means arbitrary rule. Under despotism, the despot’s will be supreme.
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
State the major demerits of the Nation-States.
Answer:
The Nation-States provide both useful and harmful effect to the nation. The demirits of nation-states are as follows :
(i) Monarchial Attitude of King : The despotic rulers kept their self interest in mind. The Pope and feudal lords could not force them to work in the interest of the state and its people.
(ii) National-Interest : The establishment of nation-states made the states selfish and individualistic. The international interests were overlooked. Sometimes the interests of different nations clashed and created an atmosphere of tussle and conflict.
(iii) Hatred for other State-Nations : Being nationalistic, the people developed an attitude of selfishness. This caused hatred in their minds for the people of other Nation-States.
Question 2.
State the features of humanistic thought.
Answer:
This educational programme implied that there was much to be learnt that religious teachings alone could not provide. This was the culture which historians in the nineteenth century were to label ‘humanism’. By the early fifteenth century, the term ‘humanist’ was used for masters who taught grammar, rhetoric, poetry, history and moral philosophy.
The Latin word humanitas, from which ‘humanities’ was derived had been used many centuries ago by the Roman lawyers and essayist Cicero (106-43 BCE), a contemporary of Julius Caesar, to mean culture. These subjects were not drawn from or connected with religion, and emphasised skills developed by individuals through discussion and debate.
Question 3.
Explain the changes that helped in the revival of Italian culture after the fall of Western Homan Empire.
Answer:
Political and cultural centres in Italy destroyed after the fall of Western Roman Empire. There was no unified government during those time. Pope was not quite strong in European politics although he was sovereign in his own state. For a long time, regions of Western Europe were reshaped by feudal relations and were unified under the Latin church.
Changes were being brought in Eastern Europe under the Byzantine Empire. Islam was creating a common civilisation in west. Italy was a divided and weak country. These changes helped in the revival of Italian culture.

Question 4.
Compare details of Italian architecture of this period with Islamic architecture.
Answer:
With the expansion of trade between the Byzantine Empire and the Islamic countries, the ports on the Italian coast revived. While western Europe was being reshaped by feudal bonds and unified under the Latin church, and eastern Europe under the Byzantine Empire, and Islam was creating a common civilisation further west, Italy was weak and divided. However, it was these very developments that helped in the revival of Italian culture.
From the twelfth century, as the Mongols opened up trade with China via the Silk Route and as trade with Western Europe countries also increased, Italian towns played a central role. They no longer say themselves as part of a powerful empirely but as independent city-states.
Question 5.
How was the wprld appeared different to seventeenth century Europeans ?
Answer:
The world had entered the modem age in seventeenth century. So it had taken a new shape which was different from the earlier world in the following ways :
(i) New distinct urban culture was developed. Towns people began to think of themselves as more ‘civilised’ than rural people.
(ii) Towns were growing in many countries of Europe.
(iii) Towns - particularly Florence, Venice and Rome had become centres of art and learning.
(iv) Artists and writers were patronised by the rich and the aristocrates.
(v) The invention of printing made books and prints available to many people.
(vi) Asense of history developed in Europe. People contrasted their modem world with the ancient one of the Greeks and Romans.
Question 6.
Why were Italian towns the first to experience the ideas of humanism ?
Answer:
The Roman and Greek scholars composed a large number of classic books. These books were not-read as there was no spread of education. But education spread in Italy by the thirteenth and the fourteenth centuries. That is why these books were translated.
The humanist views and ideas were introduced to the Italian people by these books and commentaries. First of all the subjects of humanism were taught in the schools and colleges of Italy. The subjects include Anthropology, Natural science, Astronomy, Medicine and Mathematics. These subjects centred people thought at men and comforts.

Question 7.
State the reformers’ objection against the Roman Catholic Church and churchmen of 15th and 16th centuries.
Answer:
(i) They raised objection against the luxurious and immoral life of the churchmen.
(ii) They objected against the practice of selling the offices of the church to inefficient, immoral and corrupt persons.
(iii) The reformers also objected the undesirable methods of extracting money from common man.
(iv) They protested the Pope’s authority to raise such taxes and fees as would make the Pope and his Bishops to live in luxury.
Question 8.
Give some major causes about the Renaissance in Western Europe.
Answer:
(i) The Spread of Islam : During the Middle Ages, a new religion-Islam spread rapidly. In 1493 the Turks conquered Constantinople. As a result most of the Christian scholars fled from Constantinople to Italy and some of other places. They spread among the people the spirit of reasoning, enquiry and free thinking which led to the Renaissance Movement.
(ii) The Crusades : During the crusades many fanatic lords and barons had died. Moreover, the people came in contact with the developed culture of the Arabs. The new ideas inspired them to think freely. They started learning the superstitions and narrow mindedness which proved helpful in bringing the Renaissance.
(iii) Growth of Cities and Towns: The decline of feudalism promoted the growth of free cities where trade, commerce and industry grew quite rapidly, the trading class became rich and it set up many schools and colleges.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Renaissance ? Discuss its main characteristics.
Answer:
The term ‘Renaissance’ means rebirth. The Rennaissance was in fact a movement as a result of which western nations came out of darkness of medieval age and saw the light of modem age. They were influenced by the ideas and styles of modem age. Man began to think freely, which set new standards.
Main Characteristics :
(i) City-states of Italy became the first centres of the Renaissance.
(ii) Architecture and literature developed.
(iii) A new-style emerged.
(iv) Emergence of several new towns.
(v) Free thoughts and humanism developed in man.
Question 10.
Describe some causes and consequences of the Renaissance.
Or
Discuss the causes of Renaissance in Europe.
Answer:
Causes :
(i) At the end of the middle age, new towns emerged. There was a free atmosphere in these towns and people were prosperous. Such atmosphere gave the ideas of the Renaissance.
(ii) Constantinople was occupied by the Turks. So scholars migrated to Italy. Besides, printing press was invented. These things strengthened Renaissance.
Consequences :
(i) New geographical discoveries were made. Countries like America and India were discovered.
(ii) Humanism was given preference in artistic and literary works because of the Renaissance.
(iii) In science, compass, telescope and other things were invented.
Question 11.
Write a short note on brilliance of Leonardo-da-Vinci.
Answer:
Leonardo-da-Vinci was the greatest personalities of the Renaissance Age. He was born in 1452. He was a painter, sculptor, engineer, scientist, poet and singer.

Although his paintings are a few, they are marvellous. Among these paintings, the ‘Mona Lisa’ and ‘Virgin of the Rocks’ are extra-ordinary. ‘The Last Supper’ painted in Milan’s church is counted in artistic wonders of the world. He also designed a flying machine, on the basis of which he wanted to make such machines. Such a man of multidimensional brilliance perhaps has never born in the world.

Question 12.
Which elements of Greek and Roman cultural traditions were revived in the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries ?
Answer:
The archaeological and literary recovery of Roman culture create a great admiration of that civilisation. But technological and skills in Asia had moved for ahead of what the Greeks and Romans had known. Much more of the world had become connected and the new techniques of navigation enabled people to sail much further than had been possible earlier.
The expansion of Islam and Mongol conquests had linked Asia and North Africa with Europe, not politically but in terms of trade and of learning skills. The Europeans learned not just from the Greeks and Romans, but from India, from Arabia, from Iran, Central Asia and China.
Question 13.
Why did Renaissance start in Italy ? Write any three reasons to justify.
Answer:
The Renaissance started in Italy because :
(i) The people of Italy honoured scholars who had settled their.
(ii) There was freedom of expression in Italy.
(iii) First cities and university were set-up there (in Italy) to enlighten the people.
(iv) The turks got control over Constantinople in 1453. The scholars were tortured by them. So, scholars found themselves safe in Italy.
Question 14.
What were the achievements of nation states ?
Answer:
Achievements of a nation states:
(i) Freedom of serfs due to fall of feudal system.
(ii) Establishment of constitutional governments.
(iii) Unification of small states into nation state or empire.
(iv) Spread of common language and literature.
(v) Beginning of planned agriculture, trade and industries.
Question 15.
Write any four impacts of Glourious Revolution 1688.
Or
Describe the impact of Glorious Revolution which occurred in England in 1688.
Answer:
Impacts of Glorious Revolution of 1688.
(i) It put an end to the despotic rule of the Stuart King.
(ii) It laid the formation of nation state in England.
(iii) It laid down the foundation of the independent judiciary.
(iv) It established democracy.
(v) It marks the victory of Protestant.
Question 16.
Describe any four developments of nation states as a step forward in man’s progress.
Answer:
(i) The nation-states united the people belonging to a common culture. These states were able to promote the spirit of nationalism by releasing their people from the clutches of the Pope and the priests.
(ii) The nation-states had also struck a death blow to the feudal system.
(iii) Humanism was established.
(iv) The nation-states had many achievements as they led the people on their way to social, economic and political growth and progress.

Question 17.
Describe the political system that developed in nation-states in Europe.
Answer:
(i) Absolute Monarchy: The kings were despotic monarchs. The kings were treated as God’s representatives on earth. They ruled on God’s behalf.
(ii) Supporters of the King : The rich middle classes financed, supported and strengthened the king.
(iii) Courts of Appeal : The powerful monarchies had strong courts of appeal. The courts could challenge and condemn the decisions of the feudal lords.
(iv) Independent Kings : Now the king was free from the intervention of the Pope and the feudal lords.
Question 18.
Briefly discuss the Arab's contribution to Science and Philosophy.
Answer:
Through the middle ages, monks and clergymen were familiar with most of the writings of the Greeks and RomAnswer:But they did not spread these writings widely. In the 14th century, many writers read the translated works of Plato andAristotle. These translations were a contribution of Arab translators who had carefully preserved and translated ancient manuscripts.
Ptolemy’s Almagest carries the Arabic definite article ‘al’ which brings out the Arabic connection. Among the muslim writers who were regarded as ‘men of wisdom’ in the Italian world were Ibn Sina, who was an Arab physician and a philosopher of Bukhara in Central Asia, Al-Razi who an author of a medical encyclopaedia. Ibn Rushd, who was an Arab philosopher of Spain, tried to find solution of tension between religious beliefs and philosophical knowledge. Christian thinkers also adopted his method.
Question 19.
The humanists made distinction between middle age and modern age. How ?
Answer:
(a) The humanists believed that after the collapse of the Roman Empire, the dark age had begun. Later on, scholars followed them and assumed that ‘a new age’ had begun in Europe from 14th century.
(b) After the fall of the Roman Empire, they used the term ‘Middle Age’ for one thousand years.
(c) They argued that in the middle age, the church had such complete control over men's minds that all the learning of the Greeks and Romans had been blotted out.
(d) The humanists used the word ‘modem’ for the period from the 15th century.
Periodisation used by humanists and later scholars
5th-14th century - The Middle Ages
5th-9th century - The Dark Ages
9th-11th century - The Early Middle Ages
11th-14th century - The Late Middle Ages
15th century onwards - The Modem Age

Question 20.
Which values indicate the growth/development of cultural traditions during the period of Renaissance ?
Answer:
(i) Growth of literature.
(ii) Growth and development in the field of fine art.
(iii) Discovery of scientific inventions.
(iv) Discovery of new lands.
(v) Development of education.
Question 21.
Write any three values associated with the economy during the period of Renaissance.
Answer:
(i) Growth of trade.
(ii) Beginning of clonial era.
(iii) Development/Growth of industrial capitalism.
Question 22.
Which political values were depicted by the period of Renaissance ?
Answer:
Political values depicted by the period of Renaissance were :
(i) Rise of monarchial system.
(ii) Fall of feudal system.
(iii) Development of new modes of warfare.
Long Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
Elaborate the contribution of any five writers whose thoughts and works contributed to the emergence of Renaissance.
Answer:
(i) Dante: He was the greatest poet among the Renaissance poet. He belonged to Italy and wrote an epic of poem named ‘The Divine Comedy’. In it he criticise the religious beliefs and practices of his age.
(ii) Erasmus: He was a great Dutch poet. He wrote a book named ‘The Praise of Folly’. In it he rediculed the corrupt practices prevalent in the church of his times.
(iii) Thomas Moore : He was a greatest scholar of his time. He belongs to England. He wrote a book named ‘Utopia’. In this book he criticised the social evils prevailing in the society at that time. He also condemned the malpractices of the society.
(iv) Petrarch: He was a greatest poet and a historian. He was an Italian. He is regarded as the father of ‘Humanism’. He criticised the contemporary society and its systems.
(e) Francis Bacon : He was a greatest scholar and an author of England of the Renaissance Age. He wrote many scholarly essays on the topic of contemporary interest. He enlighted the people with his writings.
Question 2.
What do you understand by the term 'Renaissance'? Analyse the role of the printing press in Renaissance and the rapid spread of humanist culture of Italy.
Answer:
Renaissance means 'rebirth'. It occurred in Italy in the fifteenth century. A new movement of knowledge started in Europe after a long dark age of ignorance. The people of Europe again began to take interest in European ancient culture and civilisation.
By 1500 CE a number of classical texts had been printed in Italy and most of them in Latin language. Now students had not to depend solely on lecture notes because printed books were easily available. Ideas, opinions, etc., spread more widely and more rapidly than ever before. A printed book with new ideas could quickly reach thousand of readers. Now every reader could purchase books from market and read them. This developed the reading habit among people and greatly spread humanist ideas.
Humanism and the Renaissance and print Literature : Humanism also greatly influenced writers like Shakespeare. Scholars like Dante made man, not God, the topic of their works. They thoroughly discussed man's sentiments, capabilities and weakness. Famous literary works of this period include Utopia, Hamlet, Divine Comedy, etc.
Humanism cast a special influence on art of the Renaissance Age. Though the paintings of Raphael and Michelangelo concerned with wealth, their basis was man. In their paintings, they depicted Jesus as a child and Mary as an affectionate mother. Other humanist works of this age include Mona Lisa, Madonna, etc., which are world famous.

Question 3.
Why did Renaissance appear Italy first of all ? What changes did it bring about in the contemporary life of the people ?
Answer:
Renaissance first appeared in Italy because of following reasons :
(i) Fall of Constantinople : After the fall of Constantinople the learned Christian scholars were persecuted by the Turks and forced to flee to Italy the seat of Pope. These scholars had reached Italy via Greece and brought good literary idea with them. This helped them to share knowledge.
(ii) Fall of Feudalism : The fall of feudalism helped in the emergence of new towns and cities.
(iii) Topographic Location of Italy : Italy is situated on the half way between the western Europe and Middle East. The Italian cities were the centres of the prosperous trade and commerce and were encouraged by Greek scholars.
Changes brought by Renaissance :
(i) The cold age of superstitions and evil practices came to an end.
(ii) New ideas, rational outlook and scientific beliefs were adopted.
(iii) It also preached Humanism.
(iv) It also inspired the contemporary writers, artists and philosophers to take up man as their main subject.
(v) People discarded the old values.
(vi) People began to adopt new scientific outlook.
(vii) Education and knowledge begun to spread quickly.
(viii) Many new universities were established.
Question 4.
Describe any five key features of Renaissance.
Answer:
Features of Renaissance :
(i) Rise of Nation States : The main feature was the development of idea of nation state. It paved the way for national security and growth of common culture, language, humanism, literature etc. It helped in bring the modem age and scientific knowledge also.
(ii) The Discovery of New Lands : The great sailors like Vasco-da-Gama and Columbus discovered many new lands like India and America. As a result, people of one country began to mix freely with the people of the rest of the world. And there was free exchange of ideas. Thus the discovery of new lands also helped in bringing the modem age.
(iii) The Reforms made by the Reformers : Many reformers attacked and criticised the church and the feudal system, the two main pillars of the Middle Ages. The reformers like Martin Luther of Germany, criticised and opposed the corrupt practices of the clergy. He started a new movement i.e. the Protestant Movement against the Roman Catholic Church. His movement proved helpful in promoting free thinking among the people. Now they gave up blind faith and useless dogmas and thus stepped towards the modern age.
(iv) Humanism : Humanism was a philosophy which had faith and confidence, in the unlimited capacities of man to develop himself. The exponents of his philosophy said that man should be honoured and all efforts should be directed to promote his welfare. All problems that face us as human beings should be solved without reference to God and religion etc.
(v) The Rise of the Middle Class : During the Middle Ages the clergy and the feudal lords were in all in the society. But with the growth of trade and commerce, the rise of new cities and towns and the discovery of new lands, a new class of society known as the middle class emerged. The class was not prepared to how before the pleasure seeking nobility and corrupt clergy. Due to the help of the middle class the common people also became courageous to challenge the special rights and privileges of the so called upper class of the contemporary society.

Question 5.
Write an account of the Renaissance Movement in the field of literature.
Answer:
Renaissance in Literature : Literature was dominated by religion. The Renaissance writers wrote about man, his interests and nature. They became interested in this world rather than in future life as the scholars of the Middle Ages had been.
(i) Literature in England : English literature reached the height of its glory in the Renaissance era. Chaucer was the father of English poetry. “The Canterbury Tale” is his outstanding work.

Thomas More was the author of ‘Utopia’. It was written in Latin and contained the criticism of the society and government of the day. Francis Bacon was a famous essay writer. Shakespeare’s works have never been excelled in any language. ‘Paradise Lost’ is an immortal work of Milton. Spencer is the author of the graceful poem named ‘Faerie Queene’.
(ii) Literature in Italy: Machiavelli was the great political writer of Italy. He developed political ideas and expressed them in his chief work ‘The Prince’ which served as a guide for the rulers. Dante’s ‘Divine Comedy’ is an epic poem. Though its theme is the state of the soul after death, yet it reveals human love, love of country and a desire for a free and united Italian nation. It helps us to understand the religious and social life of the day. Petrarch, a great scholar and writer, has been called ‘the father of humanism’.
His sonnets and lyrics made Italy supreme in European literature. His poems dealt with the economic, social and political aspects of man’s life. He collected allthe classics of Rome and roused the interests of people in the writing of Livy, Virgil and Cicero. Ariosto and Tasso were also famous poets of Italy. They composed “Orlando Furiosa’ and ‘Jerusalem Delivered’ respectively. Boccaccio was the father of Italian prose. His greatest work was ‘Decameron’, a collection of 100 short stories which is considered as one of the world’s greatest books.
(iii) Literature in France : Francois Rabelais and Michael De Montaigne were strong and vigorous poets and essay-writers of France.
(iv) Literature in Spain and Portugal: Cervantez was the most important Renaissance writer in Spain. He gave to the world his mighty work ‘Don Quixole’ in which he had made fun of old chivalry. Lope de Vega was the famous dramatics and Calderon was the greatest Spanish poet of Renaissance. Portuguese writer Camoens has described the wonderful voyages of Vasco-De-Gama in his immortal epic Lusiads.
(v) Literature in Germany : Martin Luther made great contribution-to the German literature through his translation of the Bible.
(vi) Literature in Holland : Erasmus was the greatest Renaissance scholar of Holland and ‘The Praise of Folly’ is a his immortal work. In it he has condemned the evils of the church and atrocities of the clergymen.

Question 6.
Discuss the rise of Protestant Reformation Movement launched in Europe in the 16th and 17th century,
Answer:
Reformation Movement was launched by Martin Luther of Germany against the prevailing wrong practices in the Roman Church. Supporters of this movement abolished corrupt practices and tried to establish an improved practice. They separated themselves from the Roman Church and set-up a new Protestant Church.
Thus the followers of Christianity got divided into two groups - Catholics and Protestants. From Germany the Reformation Movement expanded to other European countries also. It was developed by Zwingli in Switzerland and Calvin in France.
Causes :
(i) In the medieval age, the Roman Catholic Church dominated western Europe. It was leading all the Christians of Europe. As the church enjoyed abundant powers, several evils had crept into it. The Renaissance created a commonsense and rataionality. Now people were losing their faith in the church. They began to criticise worship and organisation of the church.
(ii) King’s power increased with the rise of nation-states. They wanted to put a check on the Pope’s international rights. So the kings accelerated the Reformation Movement.
(iii) The Pope enjoyed absolute powers. He appointed clergymen in different countries. The church had its court of justice. The church officials were free from state laws. The Pope could interfere with the state functions. So kings were waiting for a chance to get themselves free from the Pope.
Question 7.
Describe the progress made by Renaissance Movement in the field of Art.
Answer:
(i) Art of Painting: Artists focussed on realism and their concern to be accurate was helped by the work of scientists. Artists focussed on making figures of perfectly proportioned men and women. Donatello, for example broke a new ground with his life like statues. To study bone structures, artists went to the laboratories of medical schools. Painters painted as realistically as possible.
They found that a knowledge of geometry helped them understand perspective and that by noting the changing quality of light, their pictures acquired a three dimensional quality. The use of oil as a medium for painting also gave a great richness of colour to paintings than before. Thus anatomy, geometry, physics as well as a strong sense of what was beautiful gave a new quality to Italian art, which was to be called ‘realism’ and which continued till the 19th century.
(ii) Renaissance in Architecture : Popes, wealthy merchants and aristocrats employed architects who were familiar with classical architecture. Artists and sculptors were also to decorate buildings with paintings, sculptures and reliefs. Michelangelo Buonarroti, painted for the Pope in the Sistine Chapel, the scripture called ‘The Pieta’ and his design of the dome of St. Peter's Church, all in Rome. Another remarkable change was that artists came to be known individually and not as members of a group or guild.
Question 8.
Discuss in brief the Calvinism.
Answer:
Luther was the propounder of Reformation Movement. But Calvin achieved more success than Luther in religion. He was the first reformer who tried to establish such a holy sect as had influence not in single country but in the whole world.
(i) Calvin was born in 1509 CE in France. His parents wanted him to be a clergy. On the Church’s scholarship he made a thorough study of religion and literature in Paris. But later on his father advised him to be a barister. Consequently, he was engaged in studying law. One day a new change came in him. He realised that he had not been here in this world for reforming the Catholic Church but for setting up a new and holy sect.
For this, he had to wage a successful opposition against the Catholic Church. He firmly believed that he could succeed in his motive only by his firm reasoning. He separated himself from the Catholic Church and began to preach his ideas amongst people. As a result, his followers increased day by day. Seeing his popularity, the French ruler Francis wanted to put restrictions on him. So he fled to Switzerland.
(ii) In Switzerland, Calvin came in contact with Zwingli. There he composed the ‘Institute of Christian Religion’, in which he propounded the doctrines of the Protestant Church. This book was dedicated to Emperor Francis. Calvin wanted to go back to France to present his book to the emperor and influence him with his arguments. But it did not happen. This book greatly influenced people and soon opponents of the church began to unite.

(iii) In 1536 CE, Calvin visited Genoa. With his strange power of organisation, he organised people of Genoa and made them able to get political and religious freedom. Soon Genoa became a religion-dominated city state, whose supreme leader was Calvin. He introduced a moral system in the city. Calvin himself led a simple life and strongly followed the rules of morality.
Soon he became famous all over Europe and people from far and wide came to him to be his followers. He got the Bible translated into French, opened many schools and made University of Genoa a great centre of learning. As a result he became as influential in people as the Pope was. Now he was called the ‘Protestant Pope’.
Question 9.
Describe the effects of the Renaissance.
Answer:
Effects of the Renaissance :
(i) Political Effects : People were tired of the tyrannies of feudalism and the chaos and anarchy created by it. Renaissance did not usher in an era of democracy but it promoted nationalism and led to the rise of strong and powerful monarchies which ensured peace, security, political stability and economic prosperity and happy life.
(ii) Church was Weakened : In the Middle Ages the church had influence in all the spheres of life. Its authority was supreme and unchallengable. It had enslaved the mind of a man. But the Renaissance created the spirit of enquiry. People began to question the authority of the church and refused to follow blindly the dogmas which did not appeal to reason. This greatly weakened the authority of the church.
(iii) Scientific Outlook : People of the Middle Ages believed in superstitions, supernaturalism and mysteries. They accepted theories without verifying or investigating them. But Renaissance encouraged original thinking and the spirit of enquiry and scientific investigation. It developed a critical outlook. It freed man from the mental slavery of the church.
(iv) Development of Humanism : The study of theological subjects occupied the time and energy of man in the Middle Ages. They were more interested in future life. But Renaissance widened the outlook and created an interest in man, his interests, his nature and his life in this world. It developed humanism and encouraged the study of humanities.
(v) Spread of Education and Literature : The invention of printing press helped in bringing out cheap books in large number. Schools, colleges, universities were opened at various places which helped a lot in spreading education and knowledge. It also led to the growth of vernacular languages and vernacular literature of high order. It thus enriched European civilisation and culture.
(vi) Development of Trade and Industry : The geographical discoveries and contact with, the eastern countries promoted trade and industry with the European countries. Their national income increased and they began to lead a happy and prosperous life. It also resulted in the rise of a powerful middle class and gave a fatal blow to feudalism.
(vii) Reformation : Church was supreme in religious matters and its authority could not be challenged. But with the growth of the spirit of enquiry and development of critical attitude, people began to question the authority and supremacy of the church. They now raised a strong voice against the evils that had penetrated in it. This led to the Reformation movement in Europe.
Question 10.
What was the main reason that the humanist culture of Italy spread more rapidly across the Alps from the end of 15th century ?
Answer:
(i) This was because of the greatest revolution of the sixteenth century-the mastery of the technology of printing. For this, Europeans were indebted to other peoples - the Chinese, for printing technology, and to Mongol rulers because European traders and diplomats had become familiar with it during visits to their courts. (This was also the case with three other important innovations - firearms, the compass and the abacus.)

(ii) Earlier, texts existed in a few hand-written copies.
(iii) By 1500, many classical texts, nearly all in Latin, had been printed in Italy. As
printed books became available, it was possible to buy them, and students did not have to depend solely on lecture-notes. Ideas, opinions and information moved more widely and more rapidly than ever before.
(iv) A printed book promoting new ideas could quickly reach hundreds of readers. This also made it possible for individuals to read books, since it was possible to buy copies for oneself. This developed the reading habit among people.
(v) The chief reason that the humanist culture of Italy spread more rapidly across the Alps from the end of the fifteenth century is that printed books were circulating. This also explains why earlier intellectual movements had been limited to particular regions.

Question 11.
Describe the position of the women in the society during the 14th and 15th century.
Answer:
(i) The new ideal of individuality and citizenship excluded women. Men from aristocratic families dominated public life and were the decision-makers in their families. Women generally had no say in how their husbands should run their business. Obviously, the public role of women was limited and they were looked upon as keepers of the households.
(ii) The position of women in the families of merchants, however, was somewhat different. In families of merchants and bankers, wives looked after the businesses when the male members were away on work. The early death of a merchant compelled his widow to perform a large public role than was the case in aristocratic families.
(iii) A few women were intellectually very creative and sensitive about the importance of a humanist education. ‘Even though the study of letters promises and offers no reward for women and no dignity’, wrote the Venetian Cassandra Fedele (1465-1558), ‘every woman ought to seek and embrace these studies’. She was one of a handful of women who questioned the idea that women were incapable of achieving the qualities of a humanist scholar. Fedele was known for her proficiency in Greek and Latin,and was invited to give orations at the University of Padua.
(iv) Fedele’s writing bring into focus the general regard for education in that age. She was one of many Venetian women writers who criticised the republic ‘for creating a highly limited definition of freedom that favoured the desires of men over those of women’. Another remarkable woman was the Marchesa of Mantua, Isabella d’Este (1474-1539).
Question 12.
Discuss the causes of protest against the Catholic Church. Describe in short the role of Martin Luther in it.
Answer:
(i) In 1517, a young German monk called Martin Luther (1483-1546) launched a campaign against the Catholic Church and argued that a person did not need priests to establish contact with God. He asked his followers to have complete faith in God, for faith alone could guide them to the right life and entry into heaven.
This movement-called the Protestant Reformation-led to the churches in Germany and Switzerland breaking their connection with the Pope and Catholic Church. In Switzerland, Luther’s ideas were popularised by Ulrich Zwingli (1484-1531) and later by Jean Calvin (1509-64). Backed by merchants, the reformers had greater popular appeal in towns, while in rural areas the Catholic Church managed to retain its influence.
(ii) Other German reformers, like the Anabaptists, were even more radical: they blended the idea of salvation with the end of all forms of social oppression. They said that since God had created all people as equal, they were not expected to pay taxes and had the right to choose their priest. This appealed to peasants oppressed by feudalism.
(iii) Luther did not support radicalism. He called upon German rulers to suppress the peasants’ rebellion, which they did in 1525. But radicalism survived, and merged with the resistance of Protestants in France, who persecuted by the Catholic rulers, started claiming the right of a people to remove an oppressive ruler and to choose someone of their own liking.
(iv) Eventually, in France, as in many other parts of Europe, the Catholic Church allowed Protestants to worship as they chose. In England, the rulers ended the connection with the Pope. The king/queen was from then onwards the head of the Church.
(v) The Catholic Church itself did not escape the impact of these ideas, and began to reform itself from within. In Spain and in Italy, churchmen emphasised the need for a simple life and service to the poor.

Question 13.
What do you know about ‘the Copernican Revolution ?
Answer:
(i) Christians had believed that the earth was a sinful place and the heavy burden of sin made it immobile. The earth stood at the centre of the universe around which moved the celestial planets.
(ii) Copernicus asserted that the planets, including the earth, rotate around the sun. A devout Christian, Copernicus was afraid of the possible reaction to his theory by traditionalist clergy-men. For this reason, he did not want his manuscript, De revolutionibus (the Rotation) to be printed. On his deathbed, he gave it to his follower, Joachim Rheticus.

(iii) It look time for people to accept this idea. It was much later - more than half a century later, in fact - that the difference between ‘heaven’ and earth was bridged through the writings of astronomers like Johannes Kepler (1571-1630) and Galileo Galilei (1564-1642).
(iv) The theory of the earth as part of a sun-centred system was made popular by Kepler’s Cosmographical Mystery, which demonstrated that the planets move around the sun not in circles but in ellipses. Galileo confirmed the notion of the dynamic world in his work The Motion. This revolution in science reached its climax with Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation.
Question 14.
Was there a European ‘Renaissance’ in the 14th century ?
Answer:
(i) Recent writers, like Peter Burke of England, have suggested that Burckhardt was exaggerating the sharp difference between this period and the one that preceded it, by using the term ‘Renaissance’, which implies that the Greek and Roman civilisations were reborn at this time, and that scholars and artists of this period substituted the pre-Christian world-view for the Christian one. Both arguments were exaggerated. Scholars in earlier centuries had been familiar with Greek and Roman cultures, and religion continued to be a very important part of people’s lives.
(ii) To contrast the Renaissance as a period of dynamism and artistic creativity, and the Middle Ages as a period of gloom and lack of development is an over-simplification. Many elements associated with the Renaissance in Italy can be traced back to the twelfth and thirteenth centuries. It has been suggested by some historians that in the ninth century in France, there had been similar literary and artistic blossoming.
(iii) Much more of the world had become connected, and the new techniques of navigation enabled people to sail much further than had been possible earlier. The expansion of Islam and the Mongol conquests had linked Asia and North Africa with Europe, not politically but in terms of trade and of learning skills. The Europeans learned not just from the Greeks and Romans, but from India, from Arabia, from Iran, from Central Asia and China. These debts were not acknowledged for a long time because when the history of this period started to be written, historians saw it from a Europe-centred viewpoint.
(iv) An important change that did happen in this, period was that gradually the ‘private’ and the ‘public’ spheres of life began to become separate: the ‘public’ sphere meant the area of government and of formal religion; the ‘private’ sphere included the family and personal religion.
The individual had a private as well as a public role. He was not simply a member of one of the ‘three orders’; he was also a person in his own right. An artist was not just a member of a guild, he was known for himself. In the eighteenth century, this sense of the individual would be expressed in a political form, in the belief that all individuals had equal political rights.
(v) Another development was that the different regions of Europe started to have their separate sense of identity, based on language. Europe, earlier united partly by the Roman Empire and later by Latin and Christianity, was now dissolving into states, each united by a common language.

Question 15.
What do you understand by Humanism ? Give examples of humanism in art and literature of the Renaissance Age.
Answer:
Before the Renaissance, philosophers used to think over results of after life and consider the existing life as a preparation for Heaven. The Renaissance changed this approach. Now thinkers began to think over the existing problems of man. This approach of man is called ‘Humanism’. The historian Petrarch is regarded as the Father of Humanism. Humanist writers took man as a central point and tried to depict him.
Humanism and the Renaissance Art: Humanism cast a special influence on art of the Renaissance Age. Though the paintings of Raphel and Machael Angelo concerned with wealth, their basis was man. In their paintings, they depicted Jesus as a child and Mary as an affectionate mother. Other humanist works of this age include Mona Lisa, Medona, etc., which are world-famous.
Humanism and the Renaissance Literature : Humanism also greatly influenced writers like Shakespeare. Scholars like Dante made man, not God, the topic of their works. They thoroughly discussed man’s sentiments, capabilities and weaknesses. Famous literary works of this period include Utopia, Hamlet, Divine Comedy, etc.
Question 16.
Why is it said that the Renaissance started a new age ?
Answer:
The Renaissance undoubtedly started a new age.
Following were its main reasons :
(i) The Renaissance ended conservative assumptions of anicient and medieval societies. Now people began to discuss their problems.
(ii) It broke the feudal bonds and established nation-states.
(iii) Before the Renaissance people had blind faith in principles of the Church. But now they began to doubt the truthfulness of these principles and examined everything on the test of logic. Consequently, an age of scientific thinking started.
(iv) The Renaissance originated many new ideologies in art and literature. Many writers wrote satirical essays and painters attached on polluted society and politics in their paintings. All the things indicated the modem age.
Source Based Questions
1. Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow :
Niccolo Machiavelli wrote about human nature in the fifteenth chapter of his book, The Prince (1513). ‘So, leaving aside imaginary things, and referring only to those which truly exist, I say that whenever men are discussed (and especially princes, who are more exposed to view), they are noted for various qualities which earn them either praise or condemnation. Some, for example, are held to be generous, and others miserly.
Some are held to be benefactors, others are called grasping, some cruel, some compassionate; one man faithless, another faithful; one man effeminate and cowardly, another fierce and courageous; one man courteous, another proud; one man lascivious, another pure; one guileless, another crafty; one stubborn, another flexible; one grave, another frivolous; one religious, another sceptical; and so forth.’ Machiavelli believed that ‘all men are bad and ever ready to display their vicious nature partly because of the fact that human desires are insatiable’. The most powerful motive Machiavelli saw as the incentive for every human action is selfinterest.

(i) Name the book written by Machiavelli.
Answer:
‘The Prince’.
(ii) Which works of Machiavelli known as Bible of the kings ?
Answer:
The book written by him ‘The Prince’.
(iii) Which one important value did it depicts ?
Answer:
The human nature.
(iv) What did he believe ?
Answer:
He believed that “All men are bad and ever ready to display their vicious nature partly because of the fact their desires are insatiable.
2. Read the given passage and answer the questions that follow :
William Tyndale (1494-1536), an English Lutheran who translated the Bible into English in 1506, defended Protestantism thus : ‘In this they be all agreed, to drive you from the knowledge of the scripture, and that ye shall not have the text thereof in the mother-tongue, and to keep the world still in darkness, to the intent they might sit in the consciences of the people, through vain superstition and false doctrine, to satisfy their proud ambition and insatiable convetousness, and to exalt their own honour above king and emperor, yea, and above God himself.
Which thing only moved me to translate the New Testament. Because I had perceived by experience, how that it was impossible to establish the lay-people in any truth, except the scripture were plainly laid before their eyes in their mother-tongue, that they might see the process, order, and meaning of the text.’
(i) Who was William Tyndale ?
Answer:
He was an English Lutheran who translated Bible into English.
(ii) What did he defend ?
Answer:
Protestantism.
(iii) What is New Testament ?
Answer:
It is a section of the Bible, which deal with the life and teaching of the Christ and his early followers.
(iv) Who set-up Society of Jesus and when ?
Answer:
Ignatius Loyala set up the Society of Jesus in 1540 in Spain.

Map Question
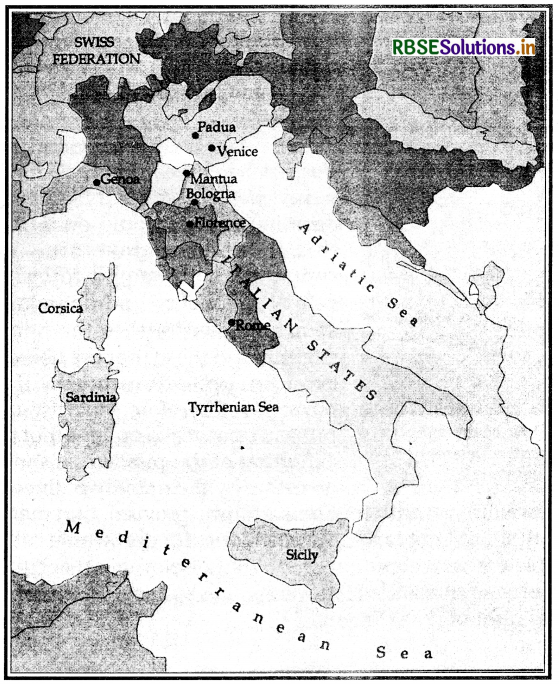
Question 1.
On the map mark and locate the following Italian states :
(i) Rome,
(ii) Sicily,
(iii) Florence,
(iv) Venice,
(v) Padua,
(vi) Mantua
Answer:
Choose the Correct Option:
Question 1.
When did town culture begin to develop ?
(а) From 14 to 17 century
(b) From 19 to 20 century
(c) None of the above
(d) In contemporary era
Answer:
(a) From 14 to 17 century.
Question 2.
The historians used to began the concept ‘Renaissance’ from ........................
(a) 16th century
(b) 14th century
(c) 19th century
(d) 18th century
Answer:
(c) 19th century.

Question 3.
Which of these towns began to develop as centres of art and learning ?
(a) Florence
(b) Venice
(c) Rome
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 4.
What is the literally meaning of the concept ‘Renaissance’ ?
(a) Re-generate
(b) Rebirth
(c) Reborn
(d) Rethink
Answer:
(b) Rebirth.
Question 5.
Jacob Burckhardt was a Swiss scholar. He complete his education from University of Baste. Where is this university ?
(a) Switzerland
(b) Ireland
(c) New Zeland
(d) England
Answer:
(a) Switzerland.

Question 6.
The earlier universities of Europe were set up in ...................
(a) German cities
(b) Italian cities
(c) French cities
(d) England
Answer:
(b) Italian Cities.
Question 7.
Which of these statement is false about Cicero ?
(a) He was Roman laywer
(b) He was Roman essayist
(c) He was contemporary to Julius Ceasar
(d) He was a British officer
Answer:
(d) He was a British officer.
Question 8.
Who was regarded as Father of Humanism ?
(a) Francesco Robert
(b) Francesco Petrarch
(c) Joseph Conard
(d) Cicero
Answer:
(b) Francesco Petrarch.
Question 9.
Who wrote the famous debate “On the Dignity of Man” ?
(a) Francesco Petrarch
(b) Mirandala
(c) Vinci
(d) Galileo
Answer:
(b) Mirandala.
Question 10.
Who was Giotto ?
(a) A scholar
(b) Humanist
(c) Historian
(d) Artist
Answer:
(d) Artist.
Question 11.
The term Renaissance Man’ used to describe a person who ...............
(a) Has many interests
(b) Has no interest in development
(c) Has many interests and skills
(d) Has technical knowledge
Answer:
(c) Has many interests and skills.
Question 12.
The period from 11 to 14th century is called:
(а) Dark Age
(b) The Early Medieval Period
(c) The Middle Ages
(d) The Later Medieval Period
Answer:
(c) The Middle Ages.

Question 13.
Which of the following book is written by Niccolo-Machiavelli ?
(a) The State
(b) The Kinship
(c) The Prince
(d) The Kingdom
Answer:
(c) The Prince.
Question 14.
Who wrote 95 thesis ?
(a) Martin Luther
(b) Martin Killar
(c) Ulrich Zwingli
(D) Jean Calvin
Answer:
(a) Martin Luther.
Question 15.
Who popularised Luther’s idea in Switzerland ?
(а) Martin Kullar
(b) Ulrich Zwingli
(c) Jean Calvin
(d) Both Zwingli and Calvin
Answer:
(d) Both Zwingli and Calvin.
Question 16.
Where did Renaissance originate?
(a) France
(b) Germany
(c) Italy
(d) England
Answer:
(c) Italy.
Question 17.
Which of these documents was issued by church ?
(a) Indulgences
(b) Luther’s theses
(c) Stamp papers
(d) Legal documents
Answer:
(a) Indulgences.

Question 18.
With the decline of .......... modern age began.
(а) Feudal system
(b) Monarchy
(c) Slave System
(d) Chinch’s influence
Answer:
(a) Feudal system.
