RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Tenses
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 English Grammar Tenses Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 English Grammar Tenses
Tenses का अध्ययन तभी सम्भव है जबकि एक वाक्य के विभिन्न भागों व उसके आदर्श प्रारूप का ज्ञान हमारे पास हो। ऐसा इसलिए है कि Tense (काल) विभिन्न प्रकार के वाक्यों के लिए कार्यक्षेत्र का कार्य करता है। किसी भी अंग्रेजी के साधारण व आदर्श वाक्य की रचना निम्न नियम पर आधारित होती है -
Subject (s) + Verb (v) + Complement (c) उपरोक्त प्रारूप ही अंग्रेजी भाषा का मूलाधार है। इसी प्रारूप अर्थात् नियम में विभिन्न परिवर्तन करके विभिन्न रचनाओं का निर्माण होता है।
उपरोक्त नियम की विभिन्न इकाइयों/अवयवों का ज्ञान होना अति आवश्यक है।
(1) Subject (tral) : A subject is the agency of conductance of an action or the performer of an action.
कर्ता किसी कार्य या गतिविधि की सम्पन्नता का माध्यम होता है या किसी कार्य का संपादन करने वाला कर्ता कहलाता है। सामान्यत: Noun (संज्ञा), Pronoun (सर्वनाम) या Adjective (विशेषण)
किसी क्रिया के कर्ता होते हैं। वचन की दृष्टि से कर्ता Singular या Plural हो सकता है। किसी वाक्य में कर्ता की भूमिका ठीक उसी तरह से होती है जैसे कि किसी परिवार में मुखिया की या किसी रेलगाड़ी में इंजन की। दूसरे शब्दों में, कर्ता वाक्य में प्रयुक्त होने वाली क्रिया या सहायक क्रिया का निर्धारण करता है। किसी भी वाक्य से "कौन" या "किसने" का प्रश्न करने पर उत्तर में जो प्राप्त हो वही उस वाक्य की क्रिया का कर्ता होता है। यही प्रश्न अंग्रेजी में “Who' की सहायता से पूछा जाता है।

(2) Verb (क्रिया) : Those words which are symbolic of some action or moment are called verbs. किसी कार्य या गतिविधि के परिचायक शब्द क्रिया कहलाते हैं। किसी वाक्य से "क्या करता है", "क्या कर रहा'' या "क्या किया" आदि प्रश्न करने पर उत्तर में जो प्राप्त हो वही किसी वाक्य का सबसे महत्वपूर्ण अंग होता है। बिना क्रिया के किसी भी वाक्य का अस्तित्व सम्भव नहीं है। क्रिया के सबसे महत्वपूर्ण होने का कारण इसका परिवर्तनशीलता (changeability) का गुण होता है। इसी गुण के कारण क्रिया का विभिन्न वाक्यों में विभिन्न रूपों में अस्तित्व सम्भव है। भाषा की उत्कृष्टता के लिए भी क्रिया का यही गुण जिम्मेदार होता है।
Kinds of Verbs (क्रिया के प्रकार) : क्रियाओं को कई आधारों पर कई समूहों में बाँटा जा सकता है
(1) Basis of Utility (उपयोगिता का आधार) - क्रिया को उपयोगिता के आधार पर दो वर्गों में बाँटा जा सकता
(a) Main Verb (मुख्य क्रिया) - Those action words which have both the individual meanings and identity are called main verbs.
वे क्रिया-बोधक शब्द जिनके अपने व्यक्तिगत अर्थ व अस्तित्व हों, मुख्य क्रिया कहलाते हैं।
उदाहरण के लिए-I appreciate your performance. इस वाक्य में appreciate का अर्थ “सराहना करना" होता है और इसे वाक्य से बाहर लिखने पर भी उसका अर्थ नहीं बदलता है।
(b) Helping Verb/Auxiliary (सहायक क्रिया)-Those words which in association with the main verbs provide a definite meaning and identification to the sentence are called helping verbs.
वे शब्द जो मुख्य क्रियाओं के साथ मिलकर वाक्य को एक निश्चित अर्थ व पहचान प्रदान करते हैं सहायक क्रिया कहलाते हैं।
उदाहरण के लिए - Monika is dreaming of her new companion.
इस वाक्य में is सहायक क्रिया है क्योंकि इसके कारण ही वाक्य के अन्त में "रही है" जुड़ रहा है तथा यह बोध होता है कि यह वाक्य Present Continuous Tense का है।

(2) Basis of Object (कर्म का आधार)-कर्म के आधार पर मुख्य क्रियाओं को दो भागों में बाँटा जा सकता है
(a) Transitive Verb (सकर्मक क्रिया) - Those main verbs which are accompanied with some direct or indirect object or which affect something directly or indirectly are called Transitive verbs.
वे मुख्य क्रियाएँ जिनके साथ कोई प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष कर्म जुड़ा हो या जिनका किसी पर कोई प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष प्रभाव पड़ता हो, सकर्मक क्रियाएँ कहलाती हैं।
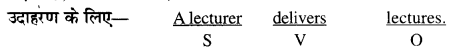
उपरोक्त वाक्य में “delivers" verb है जोकि transitive है क्योंकि उसके साथ कर्म "lectures” जुड़ा हुआ है। यदि हिन्दी के किसी वाक्य से "क्या", "किसे" या "किसको" का प्रश्न करने पर उत्तर में कुछ प्राप्त हो तो वह उस वाक्य की क्रिया का कर्म होता है। दूसरे शब्दों में हम कह सकते हैं कि उस वाक्य की क्रिया सकर्मक (transitive) है। यही प्रश्न अंग्रेजी में "what'" या "whom” की सहायता से किया जा सकता है। What (क्या) के जवाब में Direct (प्रत्यक्ष) कर्म प्राप्त होता है। Whom (किसे, किसको) के जबाव में Indirect (अप्रत्यक्ष) कर्म प्राप्त होता है।
(b) Intransitive Verb (अकर्मक क्रिया) - Those verbs which are not accompanied with any object, whether direct or indirect, or the verbs which do not affect anything directly or indirectly, or the verbs whose effect is confined with the subject only are called Intransitive Verbs.

वे क्रियाएँ, जिनके साथ कोई प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष कर्म न जुड़ा हो; या जिनका किसी पर कोई प्रत्यक्ष पर अप्रत्यक्ष प्रभाव न पड़ता हो; या जिनका प्रभाव सिर्फ कर्ता तक ही सीमित हो, अकर्मक कहलाती हैं। उदाहरण के लिए

उपरोक्त वाक्य में “laughs' Intransitive क्रिया है क्योंकि उसके साथ कोई कर्म नहीं जुड़ा हुआ है। इस वाक्य से । “What'' या “Whom" का प्रश्न करने पर उत्तर में कुछ भी प्राप्त नहीं होता है।
(3) Basis of Strength (शक्ति-रूप का आधार) - शक्ति (रूप) के आधार पर मुख्य क्रियाएँ दो प्रकार की होती हैं -
(a) Strong Verbs (सबल क्रियाएँ)-वे क्रियाएँ, जिनके तीनों रूप वर्तनी (spellings) की दृष्टि से एक-दूसरे से एकदम भिन्न होते हैं, सबल क्रियाएँ कहलाती हैं। उदाहरण के लिएI form

(b) Weak Verbs (अबल क्रियाएँ) - अबल क्रियाओं से हमारा अभिप्राय ऐसी क्रियाओं से है जिनके दो या तीनों ही रूप वर्तनी की दृष्टि से एकदम समान हों। उदाहरण के लिएI form


Tense and Time Tense
Verb का वह रूप (Form) है जो Verb द्वारा व्यक्त कार्य अथवा अवस्था के समय का बोध कराता है। सरल शब्दों में, Tense एक निश्चित वाक्य रचना का आधार अर्थात् पृष्ठभूमि है। Time (समय) एक सार्वभौमिक एवं सार्वकालिक भौतिक राशि (Physical Quantity) है।
यह हमारे जीवन का अभिन्न अंग है जो सेकण्ड, मिनट, घण्टा, दिन, सप्ताह, महीना, वर्ष आदि रूपों में व्यक्त होता है। यह किन्हीं नियमों में बँधता नहीं है। अनन्त काल से एक-एक पल निरन्तर भागता रहने वाला समय (Time) अगम्य और अगोचर है ।प्रायः देखा जाता है कि विद्यार्थी Tense और Time को एक ही अर्थ में ग्रहण करते हैं। एक ही वाक्य में Tense और Time अलग-अलग भी हो सकते हैं । इन्हें निम्नलिखित उदाहरणों से समझा जा सकता है :

1. The Prime Minister visited our city last week. (Past Tense, Past Time)
2. The Prime Minister visits our city tomorrow.
Or
The Prime Minister is visiting our city tomorrow. (Present Tense, Future Time)
3. Abhishek have finished his work. (Present Tense, Past Time)
4. Anurag is practising tennis these days. (Present Tense, Present Time)
5. The sun rises in the east. (Universal Truth)
अतः यह आवश्यक है कि विद्यार्थी Present Tense एवं Present Time, Past Tense एवं Past Time तथा Present Tense एवं Future Time को भली-भाँति समझ लें। इससे उन्हें अंग्रेजी के वाक्यों को सही ढंग से अभिव्यक्त करने में बहुत मदद मिलेगी।
Verb के मुख्यतः तीन रूप होते हैं :
1. Present Form या Base Form - इसे First Form भी कहते हैं।
2. Past Form - इसे Second Form भी कहते हैं।
3. Past Participle- यह Third Form के नाम से भी जाना जाता है।
इसके अतिरिक्त Present Participle तथा Infinitive भी Verb के दो अन्य रूप हैं।
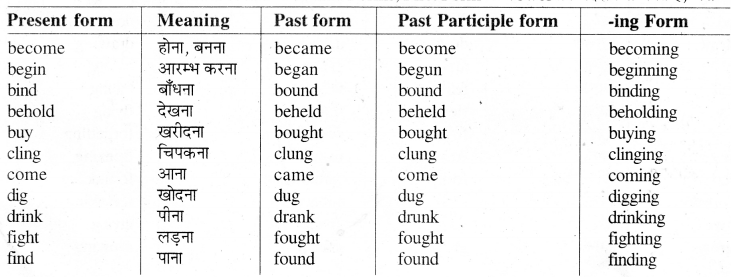
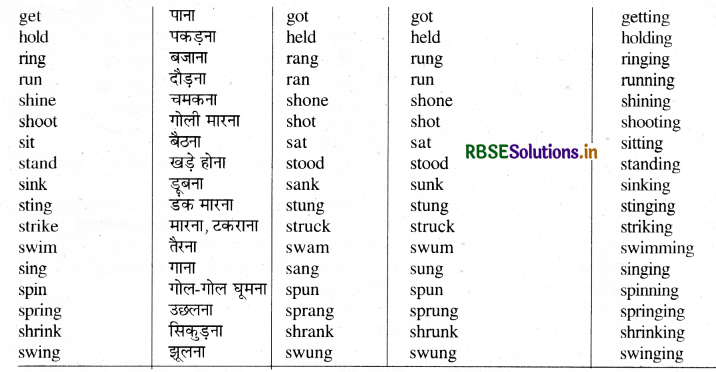
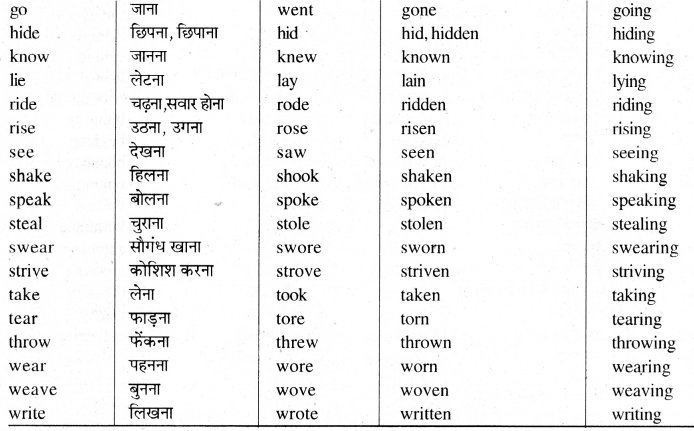
कुछ महत्वपूर्ण क्रियाओं के रूप दिये गये हैं । आप इन रूपों (Forms) को याद कर लें। म
List of Strong Verbs
Group 'A'
कुछ Strong Verbs जिनके Second और Third Forms, First Form के Vowel को बदलने से बनते हैं, जैसे

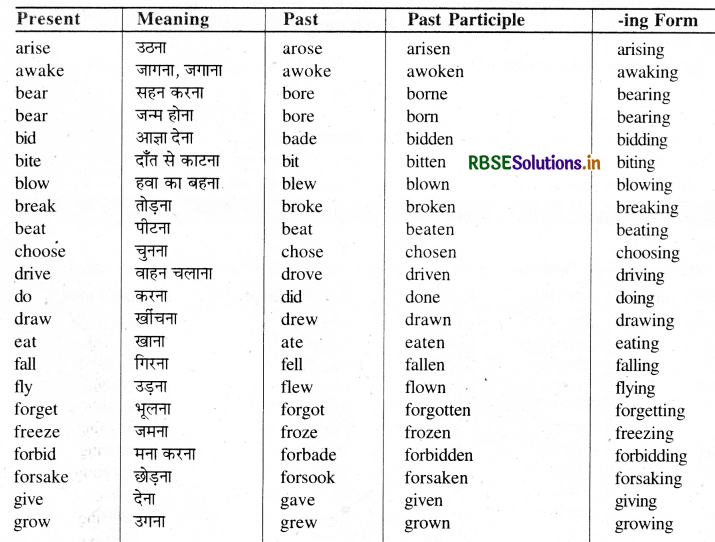
Group 'B'
कुछ Strong Verbs First Form (Present Form) Vowel a Past Form (Second Form) बनता है तथा First Form में ही en, ne या n जोड़ने से Past Participle (Third Form) बनता है, जैसे --
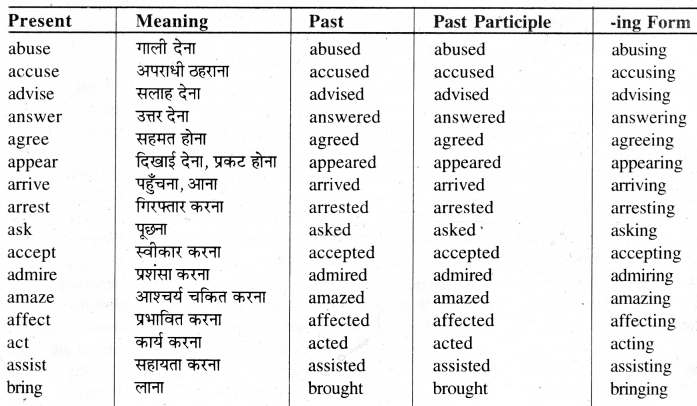
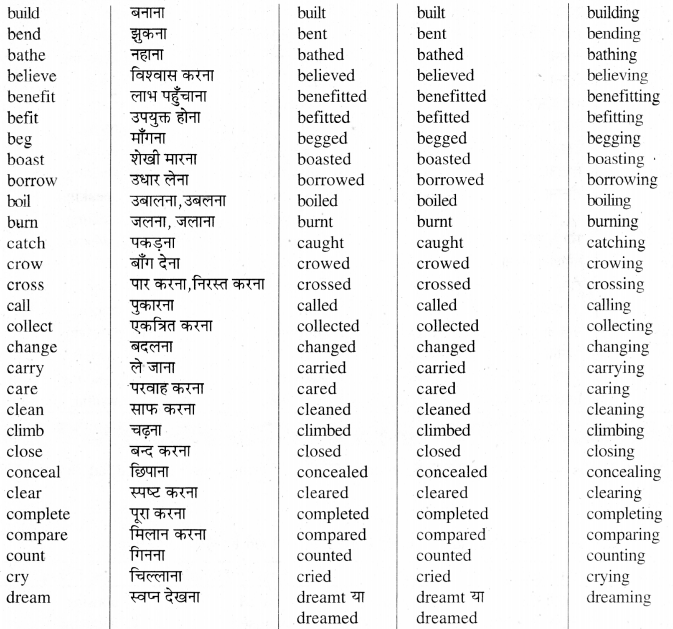
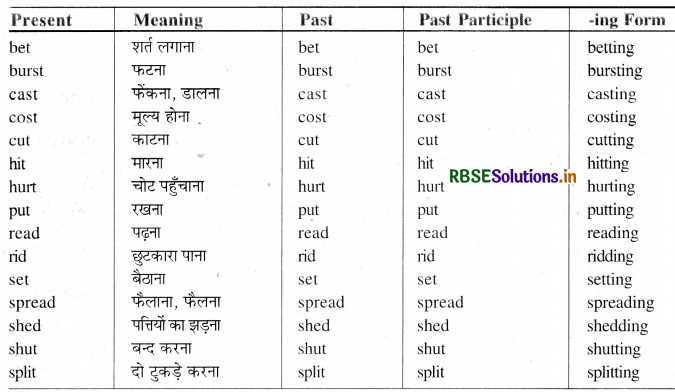
List of Weak Verbs
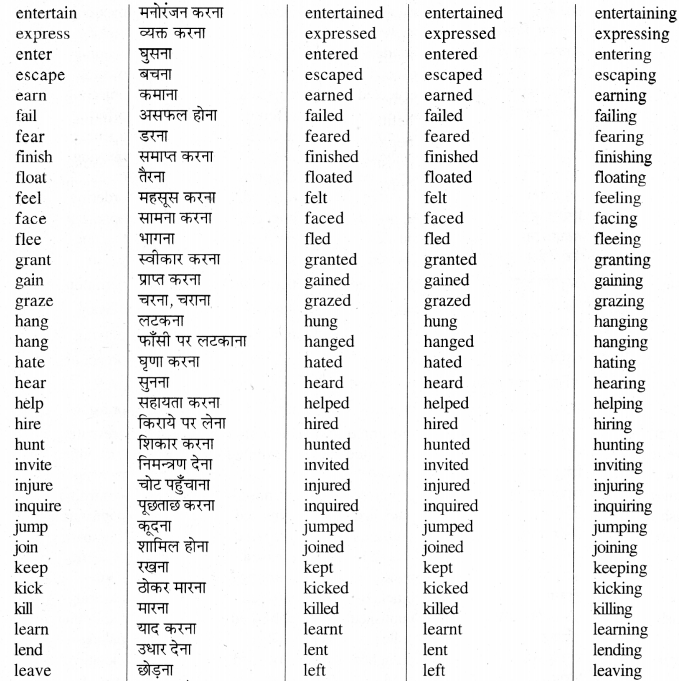
Weak Verbs -ये वे Verbs हैं जिनके Second और Third Forms, First Form में d.ed या t लगाने से बनते हैं।
Group-I
ऐसे Weak Verbs जिनके Second और Third Forms एक जैसे होते हैं। जैसे -
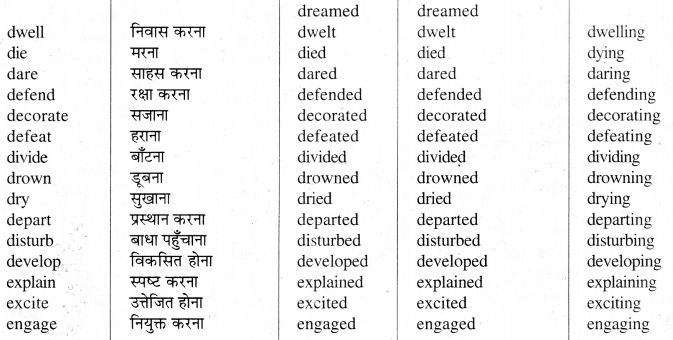

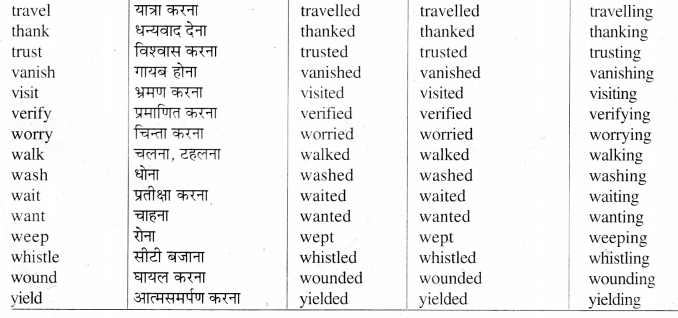

Group - II
Note : निम्नलिखित क्रियाओं के तीनों Forms एक होते हैं --
Group - III
Helping Verb

Tenses
अंग्रेजी में दो प्रकार के Tense होते हैं :
1. Present Tense (वर्तमान काल),
2. Past Tense (भूतकाल) । Future समय होता है जिसे विभिन्न प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जाता है ।
एक ही Tense (काल) में Verb की भिन्न-भिन्न अवस्थाओं को व्यक्त करने के लिए प्रत्येक Tense के चार भेद होते
1. Indefinite,
2. Continuous (Progressive),
3. Perfect,
4. Perfect Continuous
Present Tense :
1. The Present Indefinite (Simple Present) Tense इस Tense का प्रयोग वर्तमान समय में होने वाले कार्य, आदत, सामान्य अथवा शाश्वत सत्य जैसी बातों का उल्लेख करने के लिए होता है । जैसे –
(1) He plays. वह खेलता है ।
(2) They play. वे खेलते हैं ।
(3) I play. मैं खेलता हूँ ।
(4) He comes here every evening.
वह हर शाम यहाँ आता है ।
(5) The sun rises in the east.
सूर्य पूर्व में उगता है।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern - Subject + V1 / V1 + s/es .........
1. मैं अपना पाठ याद करता हूँ। I learn my lesson.
2. सीता एक मधुर गाना गाती है । Sita sings a sweet song.
3. तुम एक पत्र लिखते हो । You write a letter.
4. वे अपना पाठ याद करते हैं । They learn their lesson.
5. वह स्कूल जाता है । He goes to school.
6. हम हॉकी खेलते हैं । We play hockey.
Rule 1. Singular Number, Third Person कर्ता (He, She, It) के साथ verb में 'S' या 'es' लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 2 और 5)। किसी भी Noun Subject को Third Person समझना चाहिये ।
Rule 2.Plural Number में Subject (We, They) होने पर Verb भी Plural होगा अर्थात् verb में 's' या 'es' नहीं लगता है। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 4 और 6)
Rule 3.I और You के साथ verb में 'g' या 'es' नहीं आता है । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 और 3)
Rule 4. हिन्दी के वाक्यों में अन्त में 'ता', 'ते', 'ती' के साथ अंग्रेजी में अनुवाद करते समय 'is', 'am', 'are' का प्रयोग नहीं होता है ।
नोट - Third Person के Singular Subject के साथ प्रयुक्त होने वाले Verbs के साथ निम्नलिखित अवस्थाओं में -es जोड़ा जाता है :

(a) जिन Verbs के अन्त में 'sh', 'ch', 'o', 'ss', 'x' अथवा 'zz' होता है, उनके साथ ‘-es' लगाते हैं । जैसे:

(b) यदि Verbs के अन्त में y हो व y के पूर्व consonant (व्यंजन) हो तो y हटाकर -ies लगाते हैं : worry - worries try - tries
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern - Subject + do/does + not + V1
1. मैं अपना पाठ याद नहीं करता हूँ। I do not learn my lesson.
2. वे हॉकी नहीं खेलते हैं। They do not play hockey.
3. वह एक पत्र नहीं लिखता है । He does not write a letter.
4. सीता एक मधुर गाना नहीं गाती है । Sita does not sing a sweet song.
5. तुम स्कूल नहीं जाते हो । - You do not go to school.
6. वह स्कूल कब जाता है ? When does he go to school ?
7. वे कितनी पेंसिलें चाहते हैं ? How many pencils do they want ?
8. तुम्हारे घर प्रतिदिन कौन आता है ? Who comes to your house daily ?
9. क्या वह एक पत्र नहीं लिखती है ? Does she not write a letter ?
10. कौन दुध पसन्द नहीं करता है ? Who does not like milk ?
Rule 1. Interrogative sentences में he, she, it और एकवचन के noun कर्ता के साथ Does वाक्य में Subject (कर्ता) से पहले ले आते हैं । Verb की पहली form लगाते हैं, 'S' या 'es' नहीं लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 और 3)
Rule 2. I, we, you, they और बहुवचन noun कर्ता के साथ सबसे पहले Do, फिर कर्ता और फिर verb की पहली form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 2)
Rule 3. अगर वाक्यों के बीच में कब, क्यों, कहाँ, क्या आदि प्रश्नवाचक शब्द हों तो सबसे पहले इनकी अंग्रेजी, फिर do या does और फिर कर्ता और फिर verb की पहली form आती है । (देखिये वाक्य नं 4 और 6)
Rule 4. कितना (How much), कितने (How many), कौन-सा (Which) के साथ उनसे सम्बन्धित Nouns
भी आते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 5 और 7) ।
Rule 5. अगर वाक्य में कोई प्रश्नवाचक शब्द ही कर्ता का कार्य कर रहा हो तो पहले उसकी अंग्रेजी, फिर verb लाते हैं । Who के साथ do, does का प्रयोग सहायक क्रिया की तरह नहीं होता है । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 8)
Rule 6. Interrogative Negative वाक्य को Interrogative sentences की तरह बनाते हैं केवल कर्ता के पश्चात् not और लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 9) । इस तरह के वाक्यों में 'Who' (कौन) वाले वाक्यों में भी do या does लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 10)
Rule 7. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नसूचक चिह्न (?) अवश्य लगाते हैं ।
प्रयोग (Uses): इस Tense का प्रयोग निम्न अवस्थाओं में होता है--
1. शाश्वत सत्य (universal truth) का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए -
(i) The sun rises in the east.
(ii) Water boils at 100°C.
(iii) The earth moves round the sun.
(iv) The stars shine at night.
2. स्थायी (permanent) कार्य अथवा स्वभाव का बोध कराने के लिए -
(i). We hear with our ears.
(ii) The rose smells sweet.
3. आदत (habit) का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए -
(i) He often comes late.
(ii) Hari never goes to office late.
4. समाचार पत्रों की headlines के लिए
Two Murderers Escape.

5. आँखों देखे हाल का वर्णन करने के लिए
When the door opens, many people enter the hall.
6. इसका प्रयोग विशेष तौर पर यात्रा संबंधी planned future के साथ होता है
We leave for Jaipur at 8:00 and reach there at 9:00. We stay there for two days and then leave for Kota.
7. इतिहास-प्रसिद्ध वर्तमान (Historic Present) का बोध कराने के लिए -
(i) India defeats Pakistan in cricket.
(ii) Now Akbar calls Birbal and asks.....
Note - इतिहास-प्रसिद्ध घटनाओं का अधिक स्पष्ट रूप से वर्णन करने के लिए Simple Present Tense के प्रयोग को ही Historic Present कहते हैं ।
8. Future के समय को प्रकट करने के लिए when के साथ Simple Present का प्रयोग होता है
(i) I shall do it when he comes.
(ii) When I finish the letter, I will give it to you.
9. किसी भविष्यकालीन निश्चित कार्यक्रम के साथ जो किसी Time table के अनुसार हो । जैसे
(i) The train leaves at 4:30 p.m.
(ii) Classes begin next Monday.
10. Conditional Sentences of -
Pattern - If + Present Indefinite + Future Indefinite.
(i) If he comes to me, I shall help him.
(ii) If I see Kamal, I will tell him.
11. जिन क्रियाओं का प्रयोग Present Continuous Tense में नहीं होता है उनके साथ भी इसी tense का प्रयोग होता है।
(देखें - The Present Continuous Tense में topic - verbs normally not used in 'ing form) जैसे -
I love you. न कि I am loving you. पहचान - जव किसी वाक्य में निम्नलिखित Adverbs of Time का प्रयोग हो, तो उसे Present Indefinite या
Simple Present Tense समझना चाहिए
(a) always, often, sometimes, usually, generally, frequently, seldom, rarely,never, regularly, daily, occasionally.
(b) every day/night/month/year etc.
(c) each day/night/month/ year etc.
(d) on Sundays/Mondays.......
(e) in the mornings/evenings etc.
(f) once/twice ... a day/week/month etc.
(Present Indefinite Tense) with verb 'write'
Chart of Simple Present
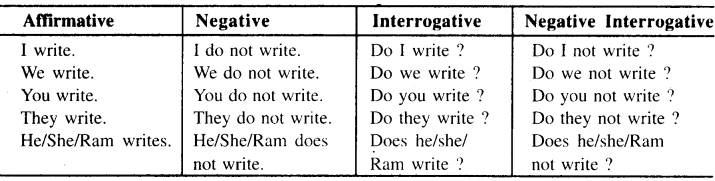
Exercise 1 (Gap Filling)
Fill in the blanks with the help of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. Ratan usually.................up at 4 o'clock in the morning. (get)
2. They often.................to the movies. (go)
3. The sun.................in the west. (set)
4. Every mother.................her children affectionately. (love)
5. Neeraj.................games regularly in the morning. (play)
6. He.................milk before going to bed. (take)
7. The Pakistan supported terrorists often.........to enter Indian territory. (try)
8. Birds usually .................nests in the trees. (make)
9. The Prime Minister.................to our town on Thursday next. (come)
10. Our brave soldiers always.................watchful eyes on the border. (keep)
11. You sometimes ........... somewhat perturb. (seem)
12. Lotus always ......... in mud. (bloom)
13. A philosopher ............. everything with a different viewpoint. (view)
14. ........... history ever .......... itself ? (repeat)
15. .......... all teachers ........... inspiration in the students? (infuse)
16. Two and two .......... four. (make)
17. Our deeds ........... our destiny. (behead) (determine)
18. Pakistani soldiers ........ two Indian soldiers on the LOC. (behead)
19. My brother seldom .......... a coat in cold days. (wear)
20. Monkeys ........... nests. (not build)
Answers:
1. gets
2. go
3. sets
4. loves
5. plays
6. takes
7. try
8. make
9. comes
10. keep
11. seem
12. blooms
13. views
14. Does, repeat
15. Do, infuse
16. make/makes
17. determine
18. behead
19. wears
20. do not build.

2. The Present Continuous (Progressive)
Tense पहचान – हिन्दी में इस Tense के Sentences में ‘रहा हूँ', 'रही है', 'रहे हैं', आदि शब्द आते हैं । वाक्यों से ज्ञात होता है कि कार्य चल रहा है और पूरा नहीं हुआ है । यह Tense - is/am/are + 'ing form' of the Verb से बनता है । जैसे -
(i) I am playing.
(ii) You are playing.
(iii) He is playing.
(iv) They are sitting.
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern - Subject + is/am/are + V1 (ing).....
1. मोहन एक पत्र लिख रहा है । - Mohan is writing a letter.
2. लड़कियाँ स्कूल जा रही हैं । The girls are going to school.
3. बढ़ई एक कुर्सी बना रहा है । The carpenter is making a chair.
4. वह मैदान में दौड़ रहा है । He is running in the field.
5. लड़के फुटबाल का एक मैच खेल रहे हैं। - The boys are playing a football match.
6. मैं एक गाना गा रहा हूँ । - I am singing a song.
Rule 1. He, She, It और एकवचन subject के साथ 'is' लगाकर verb में ing लगाते हैं। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1, 3 और 4)
Rule 2. You, We, They और बहुवचन subject के साथ 'are' लगाकर verb में ing लगाते हैं। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 2 और 5)
Rule 3. I के साथ 'am' लगाकर verb में ing लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं 6)
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern - Subject + is/am/are + not + V, (ing).....
1. मैं पुस्तक नहीं पढ़ रहा हूँ । I am not reading a book.
2. वह अपनी गुड़िया से नहीं खेल रही है । She is not playing with her doll.
3. गाय घास नहीं चर रही है । The cow is not grazing grass.
4. राम मैदान में नहीं खेल रहा है। Ram is not playing in the field.
5. वे बाजार नहीं जा रहे हैं । They are not going to the market.
Rule - not को is, are, am के ठीक बाद में रखते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern - Is/Am/Are + Subject + V1 (ing)...... ?
1. क्या लड़कियाँ कमरे में पढ़ रही हैं ? Are the girls reading in the room ?
2. क्या सूर्य आकाश में निकल रहा है ? Is the sun rising in the sky ?
3. क्या मैं एक पत्र नहीं लिख रहा हूँ ? Am I not writing a letter ?
4. क्या तुम आज स्कूल नहीं जा रहे हो ? Are you not going to school today?
5. तुम वहाँ क्यों जा रहे हो ? Why are you going there ?
6. वह अब किसकी पुस्तक पढ़ रहा है ? Whose book is he reading now?
7. तुम कमरे में क्या कर रहे हो ? What are you doing in the room ?
8. कितनी लड़कियाँ ड्रामा में भाग ले रही हैं ? How many girls are taking part in the drama ?
9. बच्चा कितना दूध पी रहा है ? How much milk is the child drinking ?
10. तुम्हारे नौकर को कौन पीट रहा है ? Who is beating your servant ?
Rule 1. अगर वाक्य के आरम्भ में 'क्या' हो तो Is, Am, Are कर्ता से पहले ले आते हैं और verb में 'ing' लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1, 2)
Rule 2. अगर हिन्दी के वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द हों तो उनकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले लाते हैं फिर is, are, am में से कर्ता के अनुसार लगाकर verb में 'ing' लगाते हैं ।
(देखिये वाक्य नं. 5, 7)
Rule 3. How many, How much, Whose के साथ इनसे सम्बन्धित nouns भी लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 6, 8, 9)
Rule 4. अगर प्रश्नवाचक शब्द 'कौन' ही कर्ता का कार्य कर रहा हो तो उसकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले लाते हैं। उसके बाद is, are, am में से एक subject के अनुसार लगाकर फिर verb की first form में ing लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 10)
Rule 5. Negative Interrogative Sentences में मुख्य क्रिया से पहले 'not' और लगा देते हैं। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3, 4)
Rule 6. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगाते हैं ।

प्रयोग (Uses)
1. इसका प्रयोग ऐसे कार्यों के लिए होता है, जो वर्तमान में जारी हों । जैसे
(i) I am writing letters.
(ii) The child is weeping.
2. ऐसे कार्यों को बताने के लिए जो वर्तमान में चल रहे हों परन्तु यह आवश्यक नहीं है कि वे बोलते समय भी चल रहे हों।जैसे -
(i) I am learning English. (परन्तु यह आवश्यक नहीं है कि वह बोलते समय भी सीख रहा हो ।)
(ii) I am reading 'Five Points Someone' by Chetan Bhagat.
3. इस Tense का प्रयोग पूर्व नियोजित कार्यक्रमों या कार्यों को व्यक्त करने में किया जाता है । भविष्य-काल का बोध कराने वाले शब्दों (tomorrow, next week आदि) का इस Tense के साथ प्रयोग होता है । जैसे - Hari is coming here next week.
पहचान – जब वाक्य में still, in the present time, at this time, at this moment, now-a-days, these days, this evening, now, today, at present आदि शब्द हों तो वह वाक्य सामान्यत: Present Continuous Tense में होता है ।
Verbs normally not used in ‘ing' form निम्नलिखित Verbs का प्रयोग सामान्यतया Continuous Tenses में नहीं होता है-
1. Verbs of perception (ज्ञानेन्द्रियों के अनुभवों को व्यक्त करने वाली क्रियाएँ)-- see, hear, taste, feel, smell, notice, prefer, please, recall.
(i) I see a picture. (Correct)
I am seeing a picture. (Incorrect)
(ii) I hear a song. (Correct)
I am hearing a song. (Incorrect)
Note
Hear के साथ ing का प्रयोग सुनने के भाव में नहीं होता अपितु सुनवाई के लिए होता है । जैसे—The judge is hearing the case. न्यायाधीश मुकदमे की सुनवाई कर रहे हैं ।
2. Verbs showing feelings or state of mind (भावनाओं अथवा मस्तिष्क की अवस्थाओं को व्यक्त करने वाली क्रियाएँ)- want, wish, desire, like, dislike, believe, care, hate, love, hope, imagine, refuse, forgive आदि। उदाहरण
उदाहरण
(i) She believes in God. (Correct)
She is believing in God. (Incorrect)
(ii) I hate you. (Correct)
I am hating you. (Incorrect)
3. Verbs showing possession (प्रभुत्व या अधिकार प्रदर्शित करने वाली क्रियाएँ)- possess, own, belong to, have. उदाहरण
(i) He possesses a vast area of land.
(iii) This horse belongs to me.
(ii) I have a dozen of horses.
4. Verbs showing mental process (मानसिक क्रिया कलाप व्यक्त करने वाली क्रियाएँ) -
think, believe, know, remember, forget, suppose, understand इत्यादि। उदाहरण
(i) I forget her name (Correct)
I am forgetting (Incorrect)

Note - ज्ञानेन्द्रियों के अनुभव, भावनाओं या संवेगों को व्यक्त करने वाली कुछ क्रियाओं में जब -ing लगता है तो उनका अर्थ ही बदल जाता है। जैसे
1. The doctor is seeing the patient. (see = जाँच करना) डॉक्टर मरीज की जाँच कर रहा है।
2. He is seeing me today. (see = मिलना) वह आज मुझसे मिलने वाला है।
3. Sita is seeing the town. (see = भ्रमण करना) सीता कस्वे का भ्रमण कर रही है ।
4. The doctor is feeling the pulse of the patient. (feel = नब्ज़ गिनना) डॉक्टर रोगी की नब्ज गिन रहा है।
5. I think you are wrong. (मेरे विचार से तुम गलत हो)
6. I am thinking to buy a car. (मैं एक कार खरीदने की सोच रहा हूँ।)
नियम 1. जिन - Verbs' के अन्त में केवल एक ही ‘e' हो उनमें 'ing' लगाते समय 'ए' को हटा दिया जाता है । जैसे
come + ing = coming take + ing = taking write + ing = writing
नियम 2. एक बलाघात (Syllable) वाले 'Verbs' के अन्त में केवल एक ही Consonant (व्यंजन) हो और उससे पहले केवल एक ही Vowel (a, e.i, o, u) हो तो अन्तिम Consonant double हो जाता है। जैसे -
stop + ing = stopping cut + ing = cutting
set + ing = setting
नोट-किन्तु h, q, u, w, y तथा x पर समाप्त होने वाले verbs के साथ 'ing' जोड़ने पर ये double नहीं होते हैं । जैसे -
grow + ing = growing
fix + ing = fixing
draw + ing = drawing
नियम 3. जिन verbs के अन्त में । या ।। हो, उनमें 'ing' लगाते समय । या ।। नहीं हटता है । जैसेfly + ing = flying tell + ing = telling play + ing = playing
नियम 4. ऐसे Verbs जिनके अन्त में ie आते हैं, उनमें ing जोड़ने पर ie के स्थान पर y कर देते हैं । जैसे
lie + ing = lying
die + ing = dying
tie + ing = tying
नियम 5. यदि verb के अन्त में single vowel + 1 (केवल एक) हो, तो ing लगाते समय 'I' को double कर देते हैं। जैसे - travel = travelling quarrel = quarrelling
Exercise 2. (Gap Filling)
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. My father wears dhoti and kurta daily but he........a white suit today. (wear)
2. She..........in her bed now. (sleep)
3. The sun..........behind the clouds now. (hide)
4. Suresh..........a lot these days. (earn)
5. The Education Minister..........this place next week. (visit)
6. She.........clothes at this time. (wash)
7. My younger brothers..........a factory these days. (run)
8. Look there ! They..........towards us.
Answers:
1. is wearing
2. is sleeping
3. is hiding
4. is earning
5. is visiting
6. is washing
7. are running
8. are coming
9. is cooking
10. is going,
11. are hovering
12. is honking
13. is not gaining
14. Are, healing
15. Is, breaking
16. is, carrying out
17. are, doing
18. are, going
19. is, making
20. are, worsening.

Exercise 3.
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. The schools never...............on Sundays but they...............today. (open)
2. My uncle seldom...............a hat but he..............one now. (wear)
3. My mother ............ newspaper now, she always ............ it at this time of the day. (read)
4. Ganpat usually ......... at the front of the class, but today he ........... in the last row. (sit)
5. Why ..........you ........ a coat this morning ? I never ......... one till October. (wear)
6. My mother usually ........... on the oiled stove but today she ........... on the gas stove. (cook)
7. What ........... you ........... at this moment ? If you ........... not ........... anything, please help me. (do)
8. Ravi ........ only newspapers, but this week he ........ magazines as well. (sell)
9. I usually ........... coffee but today I ........... milk. (drink)
10. I generally ........... by bus but tomorrow L........... in Kamal's car. (go)
11. I .................... football right now. (play)
12. I........................... football on Saturdays. (play)
13. .......... football every Tuesday. (play)
14. I. ... English at school 2 hours a week. (learn)
15. Margie .......................... in the kitchen now. (cook)
Answer:
1. open, are opening
2. wears, is wearing
3. is reading, reads
4. sits, is sitting
5. are, wearing, wear
6. cooks, is cooking
7. are, doing, are, doing
8. sells, is selling
9. drink, am drinking
10. go, am going
11. am playing
12. play
13. play
14. learn
15. is cooking.
3. Present Perfect Tense
इस Tense के वाक्यों में काम का वर्तमान काल में पूरा हो जाना पाया जाता है और वाक्यों के अन्त में 'चुका है', 'चुकी है', या 'आ है, ई है, ये हैं' आदि शब्द आते हैं ।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences Pattern - Subject + has/have + V3 .......
1. राम स्कूल जा चुका है । Ram has gone to school. (राम स्कूल गया है ।)
2. मैंने उसको एक पत्र भेजा है। I have sent a letter to him.
3. तुमने उसकी प्लेट तोड़ दी है । You have broken his plate.
4. उसने एक साँप मार दिया है। He has killed a snake.
5. उन्होंने सब पाठ याद कर लिये हैं। They have learnt all the lessons.
Rule-He, She, It और एकवचन कर्ता के साथ has और I, You, We, They तथा plural subject के साथ have लगाकर verb की third form लगाते हैं ।
(B) Negative Sentences Pattern -
Subject + has/have + not + V3 .......
1. उसने गाना नहीं गाया है । She (या He) has not sung the song.
2. बढ़ई ने कुर्सी नहीं बनाई है । The carpenter has not made the chair.
3. मैंने तुम्हारा पत्र नहीं पढ़ा है । I have not read your letter.
4. उन्होंने घोड़ा नहीं बेचा है । They have not sold the horse.
5. हमने ऐसा जानवर नहीं देखा है। We have not seen such an animal.

Rule -Negative sentences में has या have के बाद not लगाते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern - Has/Have + Subject +V3 ....... ?
1. क्या उसने अपनी गाय बेच दी है ? Has he sold his cow ?
2. क्या तुमने अपना पाठ याद कर लिया है ? Have you learnt your lesson ?
3. क्या मैंने एक चोर नहीं पकड़ा है ? Have I not caught a thief ?
4. तुमने यह पुस्तक क्यों नहीं पढ़ी है ? Why have you not read this book ?
5. कितने लड़के आज आये हैं ? How many boys have come today?
6. कौन अपनी पुस्तक नहीं लाया है ? Who has not brought his book ?
7. लड़का कहाँ भाग गया है ? Where has the boy run away ?
8. उन्होंने यह कैसे किया है ? . How have they done this ?
Rule 1. यदि वाक्य प्रश्नसूचक शब्द 'क्या' से आरम्भ हुआ हो तो सबसे पहले Has या Have लगाते हैं और उसके बाद subject, फिर क्रिया की third form और अन्त में कर्म आदि आते हैं । (देखें उदाहरण 1, 2)
Rule 2. अगर वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नसूचक शब्द दिये हों तो उनकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले लगाते हैं, फिर has या have, फिर कर्ता, फिर verb की third form लागते हैं । (देखें उदाहरण 7, 8)
Rule 3. Negative Interrogative Sentences में subject के पश्चात् not लगा देते हैं । (उदाहरण 3, 4)
Rule 4. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नसूचक चिह्न (?) लगाते हैं ।
प्रयोग (Uses)
1. हिन्दी के वाक्यों के अन्त में ‘चुका है', 'चुके हैं', 'दिया है', 'लिया है' आदि शब्द आते हैं । इस Tense का प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए होता है, जो अभी हाल में ही समाप्त हुआ है । ऐसे में हम बहुधा just, recently, already का प्रयोग करते हैं । जैसे -
(i) He has just gone out. वह अभी-अभी बाहर गया है ।
(ii) He has already explained his problem to me. वह पहले ही मुझे अपनी समस्या बता चुका है। नोट - Just का प्रयोग Helping Verb व Main Verb के बीच किया जाता है ।
2. इसका प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए भी होता है, जो भूतकाल में आरम्भ हुआ हो और अब भी जारी हो। इसके साथ प्रायः for और since का प्रयोग होता है ।
जैसे -
(i) He has been here for two weeks. वह दो सप्ताह से यहाँ है । (और अब भी यहीं है ।)
(iii) Mr Sharma has lived in Jaipur since 2005. शर्मा 2005 से जयपुर में रहते हैं। (और अब भी वहीं हैं।)
3. इस Tense का प्रयोग उन कार्यों के लिए भी होता है, जो भूतकाल में पूरे हो गये हैं पर उनका प्रभाव वर्तमान समय में भी दिखाई देता है । जैसे -
(i) He has cut his finger. उसने अपनी उँगली काट ली है । (अभी भी खून बह रहा है ।) ।
(ii) The Chetak Express has arrived. चेतक एक्सप्रेस आ चुकी है ।
(और अभी भी प्लेटफॉर्म पर है ।)
4. ऐसे कार्यों को बताने के लिए जो बोलते समय ही समाप्त हुए हों।
(i) I haven't seen you for ages. (लेकिन अब तुम्हें देख लिया है ।)
(ii) She hasn't taken food for two days. (अब वह खा रही है ।)
5. इसका प्रयोग ऐसे भूतकालीन कार्यों के साथ किया जाता है जिनका समय निश्चित नहीं है।
(i) I have read the book. (No time)
(ii) Have you taken food ? (No time)
6. इसका प्रयोग अपूर्ण समय जैसे- this morning/afternoon/evening/week/month/year etc. के साथ किया जाता है । जैसे -
(i) I have drunk four cups of tea today.
अभी कार्य समाप्त नहीं हुआ है । (सम्भव है कि और भी चाय हो जाए ।)
(ii) I haven't seen Ram this morning. (at 11:00 a.m.)
मैंने राम को सुबह से नहीं देखा है । (11 बजे)

पहचान - जब किसी Sentence में this week/monthly etc., just, till now, already, recently, lately, not yet, so far by now, always, never आदि का प्रयोग किया गया हो, तो वह Sentence Present Perfect Tense में होता है ।
Exercise 4.
Fill in the blanks with suitable Present Tense of the Verbs given in the brackets :
1. A : Have a chocolate ?
B : No, thank you, I ............. (not like) it.
2. A : Let's have a lunch in the garden.
B : No, it ................ (rain).
3. I can't find my watch. .................. you ................... (see) it recently ?
4. A: Is it raining outside ?
B : It ...................... just .................. (stop).
5. The car isn't here at this time because Sheelu..............(use) it. She generally..................... (go) by bus, but today it is bus strike.
6. We usually................. (stay) at home on Sundays, but we came out tonight because we...................(celebrate) our son's birthday.
7. I....................... (stay) with my uncle now-a-days though I ..................(have) my own plot.
8. I usually...............(work) at night but today I .............(work) in the morning.
9. Sorry you can't talk to him because he ....................(take) bath now.
10. I .............. (read) the instruction, but I can't understand them.
Answer:
1. don't like
2. is raining
3. Have, seen
4. has, stopped
5. is using, goes
6. stay, are celebrating
7. am staying, have
8. work, am working
9. is taking
10. have read.
Exercise 5.
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the Verbs given in the brackets (Only Present):
1. Those boys .............. their time for nothing. (waste)
2. The cricket match .............. on in the field. (go)
3. ............. the cows .............. grass ? (eat)
4. You ............. my book yet. (not return)
5. My uncle .............. just .............. from his office. (arrive)
6. It .............. heavily. (rain)
7. They .............. their house lately. (sell)
8. The Indian farmers .............. commercial crops. (not grow)
9. She .............. the class today. (not attend)
10. I ............. over your proposal at this time. (think)
11. Please shut the door. The hot breeze .............. (blow)
12. My son .............. the examination in first division. (pass)
13. They ............... a noise. (make)
14. Every day my father .............. exercise in the garden. (take)
15. They ............. a lie now. (tell)
Answer:
1. are wasting
2. is going
3. Do, eat
4. have not returned
5. has, arrived
6. is raining
7. have sold
8. do not grow
9. is not attending
10. am thinking
11. is blowing
12. has passed
13. are making
14. takes
15. are telling.

4. The Present Perfect Continuous Tense
यह Tense - has been या have been + Verb के ‘ing' form से बनता है । जैसे
(i) I have been reading for two hours.
(ii) He has been working since 3 o'clock.
अंग्रेजी में अनुवाद करने के नियम :
(1) He, She, It तथा Singular Subject (एकवचन कर्ता) के साथ has been तथा I, We, You, They तथा Plural Subject (बहुवचन कर्ता) के साथ have been का प्रयोग होता है । main verb की ing form का in a होता है |
Pattern - Subject + has/have + been + V1 (ing) ......... since/for + time
(2) Negative Sentences में not का प्रयोग has/have और been के मध्य होता है । जैसे
He has not been living in this house for four years.
(3) Interrogative Sentences में has तथा have का प्रयोग Subject के पहले होता है तथा वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिन्ह (?) का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे Have you been learning your lesson for two hours ?
प्रयोग (Uses)
1. इस Tense का प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए होता है, जो भूतकाल में किसी समय पर आरम्भ हुआ हो और
अब भी जारी हो । इस Tense में since/for/all के साथ समय अवश्य ही दिया होता है । यदि समय नहीं दिया होता है, तो sentence Present Continuous Tense में माना जाता है । उदाहरणार्थ -
(i) It is raining. वर्षा हो रही है । (Present Continuous Tense)
(ii) It has been raining for two hours. दो घंटे से वर्षा हो रही है। (Present Perfect Continuous Tense)
2. Present Continuous यह दर्शाता है कि कोई काम लगातार चल रहा है जबकि Perfect Continuous यह दर्शाता है कि काम किसी भूतकालीन समय से अभी तक चल रहा है।

3. Present Perfect Tense कार्य की पूर्णता पर जोर देता है जबकि Present Perfect Continuous यह दर्शाता है कि कोई कार्य कितने समय से चल रहा है ।
|
Present Perfect |
Present Perfect Continuous |
|
(i) The bicycle is O.K. now. |
(i) My hands are dirty. |
Exercise 6. (Gap Filling)
Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. The cattle..........in the field since morning. (graze)
2. Ramesh..........very hard for the last two days. (work)
3. He.......... medical treatment in a hospital since last Sunday. (take)
4. Some kind-hearted people..........the orphans for the last two years. (feed)
5. Mr Sharma......... a novel for two months. (write)
6. She is tired because she.......... for the entire morning. (work)
7. I.......... this book recently. (read)
8. The train .......... just. .......... (leave)
9. The Mumbai Mail .......... already.......... (arrive)
10. She .......... a new car recently. (buy)
11. My friends ...... to folk songs on radio for a week. (listen)
12. Ants ...... already ........ anthill in the corner of the courtyard. (build)
13. .......... she ....... sweater for her son since last Sunday ? (knit)
14. So far no one ......... up for our help. (turn)
15. Somebody ......... just ......... at the door. (knock)
Answers:
1. have been grazing
2. has been working
3. has been taking
4. have been feeding
5. has been writing
6. has been working
7. have read
8. has, left
9. has, arrived
10. has bought.
11. have been listining
12. have, built
13. Has, been knitting
14. has turned
15. has, knocked.

Past Tense
1. Past Indefinite Tense (Simple Past)
(1) इस Tense के वाक्यों में काम का करमा पा होमा भूराकाल में पाप जाता है ।
(2) ऐसे वाक्यों के अन्त में 'आ', 'या', 'ई', 'यो', 'या', 'ता था', 'ते थे', 'ती थी' आदि आते हैं ।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences Pattern- Subject + V1 .......
1. उसने कल मुझे एक कलम दिया । He gave me a pen yesterday.
2. मैं इस घर में रहता था । I lived in this house.
3. मोहन कल अपने पिता को देखने दिल्ली Mohan went to Delhi to see his father गया । yesterday.
4. हमने अपना पाठ याद किया ।। We learnt our lesson.
5. उसने अपने पिता को एक पत्र लिखा । He wrotea letter to his father.
6. बढ़ई ने एक कुर्सी बनाई । The carpenter made a chair.
Rule 1. एकवचन तथा बहुवचन दोनों में ही Subject के साथ verb की second form आती है। (देखें उदाहरण 1 से 6)
Rule 2. Subject के भिन्न-भिन्न Number या Person के साथ verb में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है।
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern - Subject + did not+V1.......
1. वह कल हॉकी नहीं खेला ।। He did not play hockey yesterday.
2. लड़कों ने अपना पाठ याद नहीं किया ।। The boys did not learn their lesson.
3. मैं कभी देर से नहीं आया । I never came late.
4. चपरासी ने घण्टी नहीं बजाई । The peon did not ring the bell.
5. उसने अपने पिता को एक पत्र नहीं लिखा । She did not write a letter to her father.
Rule 1. Negative sentences में प्रत्येक कर्ता के बाद में did not लगाकर verb की first form लगाते हैं।
Rule 2. यदि sentence में 'कभी नहीं आया हो तो 'never' का प्रयोग करते हैं; never के साथ did not नहीं लगाते, केवल verb की second form लगाते हैं । जैसे वाक्य नं. 3 में किया गया है ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern - Did + Subject +V1 .......?
1. क्या तुम स्कूल गये थे ? Did you go to school ?
2. क्या तुम्हारी बहिन ने कल गाना गाया ? Did your sister sing a song yesterday?
3. क्या मोहन ने अपना कोट नहीं पहना ? Did Mohan not put on his coat?
4. क्या उसने तुम्हारा पत्र नहीं पढ़ा ? Did he not read your letter?
5. तुम मेरे साथ क्यों नहीं दौड़े ? Why did you not run with me?
6. तुमने कक्षा में किसकी किताब पढ़ी ? Whose book did you read in the class ?
7. तुम्हारा भाई कल कहाँ गया ? . Where did your brother go yesterday?
8. राम कब लौटकर आया ? When did Ram return?
9. कितने लड़के कक्षा में नहीं आये ? How many boys did not come to the class?
10. उस बच्चे ने कितना दूध पिया ? How much milk did that baby drink?
11. तुम्हारे घर कल कौन आया ? Who came to your house yesterday?
Rule 1.अगर वाक्य के आरम्भ में 'क्या' लगा हो तो Did कर्ता से पहले ले आते हैं और verb की first form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1, 2 और 3)
Rule 2 अगर वाक्य के बीच में कब, क्यों, कहाँ, क्या आदि प्रश्नवाचक शब्द हों तो सबसे पहले इन शब्दों की अंग्रेजी, फिर did, फिर कर्ता और फिर verb की first form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 7 और 8)
Rule 3.How much, How many, Whose प्रश्नवाचक शब्दों के साथ ही उनसे सम्बन्धित noun भी आते हैं। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 6, 9 और 10)
Rule 4.अगर वाक्य में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द Who ही कर्ता का कार्य करता है तो उसके पश्चात् verb की second form आती है । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 11)
Rule 5. Interrogative Negative sentences का अनुवाद Interrogative Affirmative sentences के अनुसार ही होता है, केवल कर्ता के बाद not लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3, 4 और 5)
Rule 6. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगा देते हैं ।

Chart of Simple Past (Past Indefinite Tense) with verb 'eat'
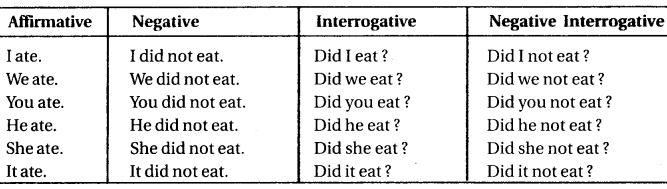
प्रयोग (Uses)
1. इस Tense का प्रयोग भूतकाल में होने वाले कार्यों या घटनाओं को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता
है। जब इस Tense का प्रयोग होता है तो वाक्य में किसी शब्द (Word) या वाक्यांश (Phrase) के द्वारा भूतकाल के समय को व्यक्त किया जाता है । जैसे
(i) He wrotea novel last year.
(ii) India became free in 1947.
2. used to का प्रयोग भूतकाल की आदत बताने के लिए होता है, परन्तु यह ऐसी आदत प्रकट करता है जो भूतकाल में होती रही हो लेकिन वर्तमान में नहीं । जैसे
When he was young, he used to play cricket.
जब वह युवक था, वह क्रिकेट खेला करता था। (लेकिन अब नहीं खेलता है ।)
3. किसी व्यक्ति या वस्तु के बारे में किसी प्रकार की सूचना देने अथवा उसकी स्थिति पूछने या बताने के लिए
Verb be' के Past Form-was/were का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे -
(i) She wasan expert pilot.
(ii) Wasshe an expert pilot?
(iii) No, she wasn'tan expert pilot.
4. Conditional Sentence type-II के साथ
If + past Indefinite + ...... would/should + Verb की I form
If I had money, I would buy a car.
पहचान - इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में निम्नलिखित Adverbials का प्रयोग किया जाता है --
last night, last year, last month, last week, long ago, some time back, yesterday, once, in 2009, इत्यादि।
Exercise 7.
Put the verbs in bracket into the correct tense :
1. I .............. (see) a lion in the forest.
2. We .............. (go) to meet my friend last night.
3. He .............. (lose) his mobile on the train yesterday.
4. Ratan .............. (buy) a new mobile phone last week.
5. She .............. (win) the match on Sunday.
6. Tom .............. (steal) a book from the library.
7. I .............. (write) a new story last year.
8. Hari .............. (get) late in the prayer.
9. I .............. (come) here in the morning.
10. Why .............. you .............. (call) me last night?
11. I was watching TV when my father .............. (call) me.
12. Where .............. you .............. (see) him last ?
13. Where .............. the child .............. (drop) the ten-rupees note?
14. For what reason .............. the boys .............. (not play) well?
15. She cooked food and .............. (serve) it to her children.
Answer:
1. saw
2. went
3. lost
4. bought
5. won
6. stole
7. wrote
8. got
9. came
10. did, call
11. called
12. did, see
13. did, drop
14. did, not play
15. served.

The Simple Past and the Present Perfect
(1) जब कोई कार्य भूतकाल में पूरा हो जाये व इसका समय नहीं दिया हो तो Present Perfect का प्रयोग होता है परन्तु यदि उसके साथ कार्य का समय दिया हो तो Past Indefinite का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे
|
Present Perfect |
Past Indefinite |
|
कोई समय नहीं दिया है । |
समय दिया है । |
|
1. I have bought a new TV. |
1. I bought a new TV last week. |
(2) यदि कोई कार्य भूतकाल में घटित हो जाये व उसके भविष्य में पुनः होने की सम्भावना हो तो Present Perfect का और जब पुनः होने की सम्भावना न हो तो Past Indefinite का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे -
|
Present Perfect |
Past Indefinite |
|
प्रभाव वर्तमान में मौजूद है |
प्रभाव वर्तमान में मौजूद नहीं है| |
|
1. Sita has had an accident. 2. I have lost my pen. |
Sita had an accident.
|
(3) यदि कोई कार्य भूतकाल में घटित हो जाये व उसके भविष्य में पुनः होने की सम्भावना हो तो Present Perfect का और जब पुनः होने की सम्भावना न हो तो Past Indefinite का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे -
|
Present Perfect |
Past Indefinite |
|
भविष्य में पुनः होने की सम्भावना है। |
भविष्य में पुनः होने की सम्भावना है। |
|
1. Chetan has written a number of dramas. |
Kalidas wrote a number of dramas. |

(4) जब किसी कार्य का वर्णन समयावधि के पूरे होने से पहले किया जाये तो Present Perfect का और समयावधि के पूरे होने के पश्चात् किया जाये तो Past Indefinite का प्रयोग होगा जैसे -
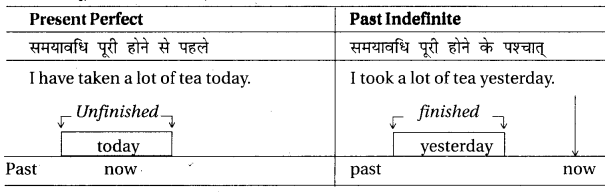
(4) जब किसी कार्य का वर्णन समयावधि के पूरे होने से पहले किया जाये तो Present Perfect का और समयावधि के पूरे होने के पश्चात् किया जाये तो Past Indefinite का प्रयोग होगा जैसे -
|
अन्य उदाहरण |
|
| 1. She has phoned me six times this morning. (at 11:00 am) 2. Have you seen him this week? 3. I have never played cricket in my life. Unfinished time सामान्यतया this morning/ afternoon /week! month/year, today, since etc. द्वारा व्यक्त किया जाता है |
She phoned me six times this morning. (at 2:00 pm) |
Exercise 8.
Fill in the blanks with Present Perfect or Past Indefinite:
1. I ........... in Jaipur for five years. (live)
2. Some one .......................... my bike ! Now I'll have to walk home. (steal)
3. When Bharat was young he .......................... in Mathura. (live)
4. I would like to visit South India sometime. Unfortunately, I ............... there. (never be)
5. Tina ..................... to Jodhpur last year. (go)
6. I'm afraid I'm not hungry any more. I .................... (already eat)
7. They don't live here anymore. They .......................... two years ago. (leave)
8. ........... Ann ................. reading the newspaper yet? (not finish)
9. We. .................... football yesterday afternoon. (play)
10. The weather ....................... Very good last week. (be)
11. Where are the girls ? They .......................... yet. (not arrive)
12. Her friend is an actor. He. ....... in many movies. (act)
13. We ........................ Our vacation in Kullu last summer. (spend)
14. His grandfather ........................ in April last year. (die)
15. I'm ready to go shopping. I....... my homework. (just finish)
Answers:
1. have lived
2. has stolen
3. lived
4. have never been
5. went
6. have already eaten
7. left
8. Has, not finished
9. played
10. was
11. have not arrived
12. has acted
13. spent
14. died
15. have just finished.

2. Past Continuous Tense
ऐसे वाक्यों में काम का जारी रहना भूतकाल में पाया जाता है । वाक्य के अन्त में 'रहा था', 'रही थी', 'रहे थे' पाया जाता है।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern-Subject + was/were+V1 (ing).......
1. मैं अपनी किताब पढ़ रहा था । I was reading my book.
2. वे फुटबाल खेल रहे थे । They were playing football.
3. हम अपना पाठ याद कर रहे थे । We were learning our lesson.
4. तुम मेरे नौकर को बुला रहे थे । You were calling my servant.
5. वह एक मधुर गाना गा रही थी । She was singing a sweet song.
Rule 1. He, She, It, I और एकवचन noun subject के साथ was लगाकर verb में 'ing' लगाते हैं ।
(देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 तथा 5)
Rule 2. You, We, They और बहुवचन noun subject के साथ were का प्रयोग कर verb में 'ing' लगाते हैं ।
(देखिये वाक्य नं. 2, 3, 4)
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern - Subject + was/were + not +V1 (ing) .......
1. वे घर नहीं जा रहे थे । They were not going home.
2. राम दीवार से नहीं कूद रहा था । Ram was not jumping over the wall.
3. हम मेज पर नहीं सो रहे थे । We were not sleeping on the table.
4. मैं स्कूल नहीं जा रहा था । I was not going to school.
5. वह एक गाय नहीं खरीद रहा था । He was not buying a cow.
Rule-Negative sentences में was या were के पश्चात् not लगा देते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences Pattern - Was/Were + Subject +V1 (ing) ......?
1. क्या हम बाजार जा रहे थे ? Were we going to the market ?
2. क्या मोहन अपने नौकर को गाली दे रहा था ? Was Mohanabusing his servant?
3. क्या वे लड़के शोर नहीं मचा रहे थे ? Were those boys not making a noise ?
4. क्या मैं तुम्हारे साथ नहीं जा रहा था ? Was I not going with you?
5. कितने लड़के मैदान में खेल रहे थे ? How many boys were playing in the field ?
6. किसान अपना खेत क्यों नहीं जोत रहा था ? Why was the farmer not ploughing his field ?
7. वह कमरे में क्या कर रहा था ? What was he doing in the room ?
8. कक्षा में कौन रो रहा था ? Who was weeping in the class ?

Rule 1. Interrogative sentences में Was या Were कर्ता से पहले लगाते हैं और verb में 'ing' लगा देते हैं । वाक्य में सबसे पहले 'क्या' हो तो 'क्या' के लिये what मत लगाओ । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1, 2 और 4)
Rule 2. यदि वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नसूचक शब्द 'क्यों', 'क्या', 'कब', 'कहाँ', 'कैसे' आदि में से कोई दिया हो तो सबसे पहले उसकी अंग्रेजी लगाकर फिर was या were को लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 6 तथा 7)
Rule 3. How much, How many आदि के साथ उनसे सम्बन्धित nouns भी लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 5)
Rule 4. अगर वाक्य में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द अर्थात् 'कौन' ही कर्ता का कार्य कर रहा हो, तो सबसे पहले उसकी अंग्रेजी, उसके बाद was या were लाते हैं, तत्पश्चात् verb में 'ing' लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 8)
Rule 5. Negative Interrogative sentences में मुख्य क्रिया से पहले not लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3 तथा 4)
Rule 6. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नसूचक चिह्न (?) लगाते हैं ।
प्रयोग (Uses)
1. इसका प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए किया जाता है जो भूतकाल में किसी समय जारी रहा हो । जैसे
He was lying in the sun. वह धूप में लेटा हुआ था ।
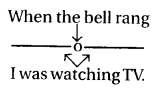
2. इसका प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए भी होता है जो भूतकाल में कुछ समय तक जारी रहा हो और उसी बीच कोई दूसरा कार्य भी हुआ हो। इस दूसरे कार्य के लिए जो तुरन्त समाप्त हो जाता है, Simple Past Tense का प्रयोग करते हैं तथा जिस Clause में कार्य जारी रहा हो उसमें Past Continuous का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे
3. इसका प्रयोग ऐसे दो या दो से अधिक वाक्यों के लिए भी होता है जो भूतकाल में साथ-साथ जारी रहे हों। ये प्राय: while से जुड़े होते हैं। जैसे
(i) I was reading a story while Hari was writing letters.
(ii) She was singing a song while her brother was playing the flute.
4. यदि इस tense के वाक्य के साथ time दिया हो तो वह यह दर्शाता है कि कोई कार्य उस समय पर लगातार चल रहा था । जैसे - At 3:00 p.m. they were playing tennis.
5. कहीं घटित हो रही घटना का वर्णन करने के लिए । जैसे- When, he came, my father was reading newspaper. My mother was preparing breakfast. when I was studying.
6. As के साथ भी Past Continuous Tense का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे- As he was Bold crossing the road, he saw a banana skin on the road. पहचान : इस प्रकार के वाक्यों की कोई विशिष्ट पहचान नहीं होती, परन्तु इन वाक्यों में at that time, at that moment, those days, then जैसे Adverbials आते हैं। इसी प्रकार while से जुड़े दो वाक्यों में से यदि एक वाक्य Past Continuous में हो तो दूसरा भी इसी Tense में मानना चाहिए।

Exercise 9.
Fill in the blanks with Past Indefinite or Past Continuous :
1. When I............. to school, I ............... Jaya. (walk, see)
2. When I ....... ..... in the kitchen, Maya ......................... (help, come)
3. While she .......................... the food, the children ........................... (cook, play)
4. While they ........................ cards, the baby. ...................... (play, sleep)
5. When I ......................... in the garden, my uncle ......................... me. (work, call)
6. Arvind ........................ TV, while Varsha and Rani ...................... football. (watch, play)
7. When she ...................... her hair, the baby ..................... to cry. (wash, begin)
8. A strong wind. ......................, when the plane .................. .(blow, land)
9. When she ....................... tennis, it ........................ to rain. (play, begin)
10. When I ........................ TV, the lights ..................... out. (watch, go)
11. While he ...................... the piano, she .................... to him. (play, listen)
12. While she ....................... up her room, he. .................... his car. (tidy, wash)
13. The boys ...................... in the garden, while she ....................... the flowers. (help, water)
14. He ...................... Mary, when he .......................... through the park. (meet, walk)
15. We. ..................... computer games, while she............ a book. (play, read)
Answers:
1. was walking, saw
2. was helping, came
3. was cooking, were playing
4. were playing, was sleeping
5. was working, called
6. was watching, were playing
7. was washing, began
8. blew, was landing
9. was playing, began
10. was watching, went
11. was playing, listened
12. was tidying, was washing
13. were helping, was watering
14. met, was walking
15. were playing, was reading.

Exercise 10.
Fill in the blanks with Past Indefinite or Past Continuous :
1. They. ...................... (play) cards, when the postman ......................... (come).
2. I.. ................... (sweep) the floor, when I........................... (hear) a noise.
3. She ........................ (watch) TV, when the doorbell ....................... (ring).
4. We ................... (hear) a cry and........ (run) into the kitchen.
5. First Shamim ......................... (buy) the newspaper and then he ........................ (take) the plane to Kathmandu.
6. Suresh and Shashi. ................. ... (play) tennis when it ....................... (begin) to rain.
7. I think she ........... (wear) her new hat, when I .............. (see) her at the zoo.
8. A lot of children .......................... (wait) at the station, when the heroine .................(arrive).
9. They.......................... (have) their supper, when they.......................... (hear) about the accident.
10. When the phone .................. (ring) mom ............... (work) in the garden.
11. Veena.......................... (take) a photo, when........................... (dance).
12. They.......................... (read) a book, when the lights .......................... (go) out.
13. While Gautam....................... (repair) his bike, Ramesh...................... (play) computer games.
14. We.............. (talk)about the movie while we .......................... (walk) home.
15. They .......................... (forget) their lunch at home last Friday.
Answers:
1. were playing, came
2. was sweeping, heard
3. was watching, rang
4. heard, ran
5. bought, took
6. were playing, began
7. was wearing, saw
8. were waiting, arrived
9. were having, heard
10. rang, was working
11. took, was dancing
12. were reading, went
13. was repairing, was playing
14. talked, were walking
15. forgot.
3. Past Perfect Tense
1. इस Tense के वाक्यों में भतकाल में किसी कार्य का निश्चित अवधि से पहले समाप्त हो जाना पाया जाता है अथवा दो कार्य भूतकाल में समाप्त होते हैं एक पहले तथा दूसरा बाद में ।
2. इन वाक्यों के अन्त में साधारणतया ‘चुका था', 'चुकी थी', 'चुके थे', 'या था', 'ये थे' आदि शब्द आते हैं।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences Pattern- Subject + had + V1 .......
1. वर्षा होने से पहले हम घर पहुंच चुके थे ।
We had reached home before it rained.
2. मेरे स्टेशन पहुंचने से पहले गाड़ी छूट चुकी थी ।
The train had started before I reached the station.
3. सोने से पहले वह अपनी किताब पढ़ चुकी थी ।
She had read her book before she slept.
4. अपना पाठ याद करने के पश्चात् राम स्कूल चला गया ।
Ram went to school after he had learnt his lesson.
Rule 1. एकवचन तथा बहुवचन कर्ता दोनों के साथ 'had' लगाकर verb की third form लगाते हैं ।
Rule 2. जिन वाक्यों में दो कार्य भूतकाल में पाये जायें उनमें से जो काम पहले समाप्त हो चुका हो उसको Past Perfect Tense में अर्थात् कर्ता, फिर had, इसके बाद क्रिया की third form लगाते हैं और जो कार्य बाद में हुआ हो उसको Past Indefinite में बनाते हैं अर्थात् सबसे पहले कर्ता और फिर verb की second form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1. 2. 3)

Rule 3. वाक्यों में 'पश्चात्' या 'बाद' शब्द प्रयोग होने पर बाद में होने वाला कार्य प्रधान उपवाक्य (Principal clause) होगा तथा पहले होने वाला कार्य आश्रित उपवाक्य (Subordinate clause) होगा । ऐसी स्थिति में Principal clause में प्रत्येक कर्ता के साथ की क्रिया की second form का प्रयोग होगा तथा Subordinate clause में had के साथ क्रिया की third form का प्रयोग होगा । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 4)
(B) Negative Sentences Pattern -
Subject + had + not + V3 .......
1. मैंने यह घर पहले नहीं देखा था ।
I had not seen this house before.
2. डॉक्टर के आने से पहले मरीज मरा नहीं था ।
The patient had not died before the doctor came.
3. पुलिस के आने से पूर्व चोर भाग न चुका था ।
The thief had not run away before the police came.
4. अध्यापक परीक्षा आरम्भ होने से पहले कोर्स समाप्त नहीं कर चुके थे ।
The teacher had not finished the course before the examination began.
Rule- Negative sentences में had के आगे not का प्रयोग करते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern-Had + Subject + V3 .......?
1. क्या मेरे स्कूल पहुँचने से पहले घण्टा बज चुका था ?
Had the bell rung before I reached the school ?
2. क्या सूरज निकलने से पहले वे चाय पी चुके थे ?
Had they taken tea before the sun rose ?
3. क्या बस छूटने से पहले हम बस स्टेण्ड नहीं पहुँच गये थे ?
Had we not reached the bus-stand before the bus started ?
4. सूरज छिपने से पहले कितने बच्चे सो चुके थे ?
How many children had slept before the sun set?
5. हमारे आने से पहले वह लड़की कौन-सा गाना गा चुकी थी ?
Which song had that girl sung before we came?
6. मेरे सोने से पहले तुम पत्र क्यों लिख चुके थे ?
Why had you written a letter before I slept?
7. डॉक्टर साहब के जाने के बाद रोगी ने क्या खाया था ?
What did the patient eat after the doctor had gone?
Rule 1. प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में यदि 'क्या' सबसे पहले आये तो Had को subject से पहले ले आते हैं । ऐसे वाक्यों में what का प्रयोग मत करो । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1, 2 और 3)
Rule 2. अगर वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द हों तो अनुवाद करते समय उनकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले आती है, फिर had आता है, फिर कर्ता और फिर verb की third form आती है । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 6)
Rule 3. कितने, कितना, कौन-सा, किसको आदि प्रश्नवाचक शब्दों के साथ उनसे सम्बन्ध रखने वाले nouns भी लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 4 और 5)
Rule 4. Negative Interrogative sentences में subject के बाद not लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3)
Rule 5. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नसूचक चिह्न (?) लगाते हैं ।
संकेत - 'बाद' वाले वाक्यों के पहले भाग में did लगाओ । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 7)

प्रयोग (Uses)
1. इस Tense का प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए होता है जो भूतकाल में किसी दूसरे कार्य से पहले समाप्त हो
गया हो अर्थात् जो कार्य पहले हो जाता है, उसमें Past Perfect Tense का प्रयोग होता है तथा जो कार्य बाद में होता है, उसमें Simple Past Tense का प्रयोग होता है। ऐसे दो वाक्यों को जोड़ने के लिए before, when, after, till, until आदि Conjunctions का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे
(i) They had practised before they did it. | Before they did it they had practised.
(यहाँ पर 'they had practised' कार्य पहले हुआ है तथा 'they did it'' बाद में हुआ है ।)
(ii) He had seen the ball before he hit it.
(iii) He had worked very hard before he finally won.
(iv) He went out after the rain had stopped. ('The rain had stopped' यह कार्य पहले हुआ है । "He went out" यह कार्य बाद में हुआ है ।)
या
After the rain had stopped he went out.
नोट - (a) after के पश्चात् सामान्यतया Past Perfect का प्रयोग होता है ।
अर्थात्
After + Past Perfect + Past Indefinite या Past Indefinite + after + Past Perfect
(b) सामान्यतया before के पश्चात् वाला Clause Past Indefinite में होता है ।
अर्थात्
Past Perfect + before + Past Indefinite 11 Before + Past Indefinite + Past Perfect
(i) He had liked it before this happened.
(ii) The report had been ready before you spilled the coffee.
(c) till/until के साथ
till/until + past perfect + past Indefinite का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
He had been healthy until he started overeating.
Note : (a) जब दो कार्य साथ-साथ हो रहे हों तो दोनों में Simple Past Tense का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे
As soon as he saw the police, he ran away.
(b) भूतकाल की अकेली घटना के लिए इस Tense का प्रयोग नहीं हो सकता है । जैसे
Thad finished my work yesterday. (Incorrect)
I finished my work yesterday. (Correct)
2. Direct Speech on Simple Past Tense at Present Perfect Tense, Indirect Speech Past Perfect Tense में बदल दिये जाते हैं। जैसे
(i) Direct : He said, "I left the school a few months ago."
Indirect : He said that he had left the school a few months before.
(ii) Direct : Sita said, I have already read this book."
Indirect : Sita said that she had already read that book.
3. इस Tense का प्रयोग ऐसे Conditional Clause में होता है जिसमें शर्त भूतकाल में पूरी न हुई हो ।
Conditional Sentences Type - III के साथ ।

Pattern: If + Past perfect +.......would have/should have + V3.
If you had reached the station in time, you would have met your friend. यदि तुम समय से स्टेशन पहुँच गये होते तो तुम्हें तुम्हारा मित्र मिल गया होता। (लेकिन नहीं मिला।)
(ii) Direct : Sita said, “I have already read this book.”
Indirect : Sita said that she had already read that book.
4. भूतकाल (Past Time) की किसी अपूर्ण इच्छा को व्यक्त करने के लिए इस Tense का प्रयोग wish, would sooner/rather, if only, as if, as thought.
(i) I wish I hadn't telephoned her ( = I am sorry I telephoned her).
(ii) If only I had seen the thief ( = but couldn't see).
Exercise 11.
Fill in the blanks with Past Indefinite and Past Perfect Tense:
1. After they ....................... (see) the Tower, they .......................... (go) to Delhi.
2. He. ...................... (ask) me which animals I....................... (hunt) in Africa.
3. After Columbus ...................... (discover) America he .............. (return) to Spain.
4. Before they .... (move) to Udaipur, they ....... (sell) everything.
5. After he ........................ (work) very hard, he ..................... (fall) ill.
6. She ......................... (open) the box after she .......................... (find) the key.
7. They .......................... (go) to a restaurant after they.......................... (sail).
8. Before they .....................(start) the party, they ........................ (invite) some friends.
9. After she ......................... (wash) the curtains, she ......................... (clean) the windows.
10. They .................... (go) for a sightseeing tour after the bus ..................... (arrive).
11. Before he ....................... (move) away from the lawn , he ....................... (pick) some roses.
12. After he .......................... (finish) school work he ........................ (work) for a magazine.
13. They .......................... (drink) a cup of tea after they ......................... (finish) lunch.
14. He ................ (ask) me for her telephone number before he ................ (phone) her.
15. My sister....................... (eat) all the chocolate before my parents ....................... (come) home.
Answers:
1. had seen, went
2. asked, had hunted
3. had discovered, returned
4. moved, had sold
5. had worked, fell
6. opened, had found
7. went, had sailed
8. started, had invited
9. had washed, cleaned
10. went, had arrived
11. moved, had picked
12. had finished, worked
13. drank, had finished
14. had asked, phoned
15. had eaten, came

Present Perfect व Past Perfect star में अंतर
|
Present Perfect का प्रयोग ऐसे कार्यों को व्यक्त |
Past Perfect का प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य को व्यक्त करने |
|
(i) Who is that boy? |
(i) I didn't know who he was. I had never seen I have never seen him. (= उस समय से पहले) |
Exercise 12.
Fill in the blanks with the Present Perfect or Past Perfect:
1. They .................... (go) on a trip to Jaipur before moving to Kota.
2. She........ (cut) her hair but she didn't like it.
3. Where .......................... you.......................... (be)?
4. He .......................... (work) here since last spring when he had an accident.
5. My car .......................... (steal).
6. They .......................... (not come) to his party because they were sick.
7. When I went to the car park, I found that my car .............. (steal).
8. They wouldn't let him in because he ................ (forget) his membership card.
9. They said : "You can't come in because you.......................... (forget) your membership card."
10. .......................... you .......................... (see) the new film by Rajkumar Santoshi?
11. They .......................... (drink) a lot of wine by the time the party ended.
12. They told that I.......................... (lose) my chance.
Answer:
1. had gone
2. had cut
3. have, been
4. had worked
5. has been stolen
6. had not come
7. had been stolen
8. had forgotten
9. have forgotten
10. Have, seen
11. had drunk
12. had lost

4. The Past Perfect Continuous Tense
इस Tense के वाक्यों से प्रकट होता है कि कार्य भूतकाल में किसी समय चालू होकर उसके बाद तक चलता रहा। भूतकाल में कार्य जारी रहने का समय दिया होता है। अंग्रेजी में अनुवाद करने के नियम
1. सभी प्रकार के Subjects के साथ had been लगाकर क्रिया के First Form के अन्त में ing लगाते हैं।
Pattern : Subject + had been + V1 (ing) + object + for/since + time. जैसे
(i) He had been studying for two hours last night.
(ii) I had been walking in the park since yesterday morning.
2. Negative Sentences में had के ठीक बाद not लगाते हैं। जैसे - It had not been raining today since morning.
3. प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में had को कर्ता से पहले रखते हैं। जैसे -
Had your brother been buying toys for two hours yesterday ?
प्रयोग (Uses)
इसका प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए होता है जो भूतकाल में किसी समय से चालू होकर भूतकाल में ही किसी समय तक जारी रहा हो। इस tense के वाक्य में since/for/all के साथ समय के साथ ही साथ एक और भूतकाल का समय या clause अवश्य ही दिया हआ होता है । जैसे -
(i) When he came, I had been watching TV for two hours.
(ii) When he came, I was very tired. I had been working all day.
Exercise 13.
Fill in the blanks with the Past Perfect or the Past Perfect Continuous form of the verbs given in the brackets.
1. We .............. (cook) all day for the party that evening and by 9 o'clock we still weren't ready.
2. Radha ............ (prepare) a beautiful meal for her guests and everybody enjoyed it.
3. When I reached there, he................(sing) for two hours.
4. I knew she .............. (do) the washing because when I reached there she was ready to go out.
5. By 11 o'clock the children ........ (complete) their homework and were ready to go to bed.
6. The children .............. (do) their homework and by 11 o'clock they still hadn't finished.
7. When I entered the office, I found that a clerk was sleeping. He .............. (sleep) in the office all afternoon.
8. When it started raining, we ............ (play) cricket for an hour.
9. I looked at her wondering where I . .... (see) her before.
10. It was 6 p.m. and I was tired because I .............. (work) hard all day.
Answers:
1. had been cooking
2. had prepared
3. had been singing
4. had done
5. had completed
6. had been doing
7. had been sleeping
8. had been playing
9. had seen
10. had been working

The Present Perfect Continuous and the Past Perfect Continuous
Exercise 14.
Fill in the blanks with the Present Perfect Continuous or the Past Perfect Continuous Tense.
1. I was tired. I .............. (work) all day.
2. We ............... (wait) for your phone call all evening.
3. How long .............. you .............. (wait) here?
4. I ............... (stand) here since 9 o'clock.
5. She .............. (learn) English for two months before she visited London.
6. It started raining yesterday and it .............. (rain) ever since.
7. They .............. (send) me message about it everyday for the last week.
8. A - I knew you .............. (paint).
B - How did you know ?
9. Since when................she............(live) in this house ?
10. Before he came to film, he........(act) on stage for five years.
Answers:
1. had been working
2. have been waiting
3. have, been waiting
4. have been standing
5. had been learning
6. has been raining
7. had been sending
8. had been painting
9. has, been living,
10. had been acting

Exercise 15. (Gap Filling)
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the bracket :
1. Hari........ the game when I went to his house. (play)
2. When we reached his home, he....... plants. (water)
3. Sita....... her work before I went to her. (complete)
4. As soon as he saw the teacher, he...... away. (run)
5. When I went to Sita, she........ a letter. (write)
6. When we reached the hospital, the patient......... (die)
7. If he........ me, I would have helped him. (ask)
8. If we....... early, we would have caught the train. (leave)
9. He said that he ............his work. (complete)
10. He........ in Mumbai for ten years before 2009. (live)
Answers:
1. was playing
2. was watering
3. had completed
4. ran
5. was writing
6. had died
7. had asked
8. had left
9. had completed
10. had been living.
Future Action
आधुनिक अंग्रेजी में केवल दो ही tenses होते हैं- Present तथा Past. Future समय होता है जिसे निम्नलिखित प्रकार से व्यक्त किया जा सकता है
1. The Simple Present Present Indefinite
2. Will + infinitive - इरादा व्यक्त करने के लिए ।
3. The Present Continuous Tense
4. The "be + going to" form
5. The Future Simple
6. The Future Continuous
7. The Future Perfect
8. The Future Perfect Continuous

1. The Simple Present for Future Action
इस tense का प्रयोग निम्नलिखित स्थितियों में Future Action को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जा सकता है|
(A) जब कोई Future Action निश्चित Time-Table के अनुसार हो
(i) Our school opens at 10.30 a.m.
(ii) I go to cinema tonight. (मैं आज सिनेमा जा रहा हूँ परन्तु यह plan सम्भवतया मेरे द्वारा नहीं बनाया गया है । यह plan का एक हिस्सा है।)
अर्थात इसके द्वारा व्यक्त किया गया कार्य impersonal होता है । इसमें कर्ता का कोई involvement नहीं होता है। जबकि Present Continuous व्यक्तिगत होता है । जैसे
I am going cinema tonight. (यह मेरा अपना व्यक्तिगत plan है ।)
(B) इसका प्रयोग औपचारिक घोषणाओं के साथ किया जाता है जो कि future plan से संबंधित हों
जैसे - Wall Mart opens a new store at Kota next week.
जबकि Present Continuous अनौपचारिक होता है । जैसे
I am opening a new store at Kota next week.
(C) Series of Future Actions (जब भविष्य की योजना एक श्रृंखला के रूप में हो) विशेष तौर पर यात्रा संबंधी Future plan के लिए भी इसी का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे We leave at 7:00, arrive in Jaipur at 11:00 and take the train for Kota at 11:30 .....
(D) Time Clause के साथ
(i) She will phone when she reaches home.
(जब वह घर पहुँच जाएगी तो वह फोन करेगी।)
(ii) Wait here, until I return.
(जब तक मैं नहीं लौटूं यहीं इंतजार करो।)
(iii) The teacher will be pleased when he hears this.
(अध्यापक जी प्रसन्न होंगे जब वे इसके बारे में सुनेंगे ।)
2. Will + Infinitive (will + I form of Verb)
इस form का प्रयोग ऐसे Future Action को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है जिनको करने का निश्चय बोलते समय ही किया गया हो । ये कार्य पूर्वनियोजित नहीं होते हैं । जैसे
(i) Mother : The milk is boiling.
Son : I will put out the stove.
(ii) Waiter : What would you like to have ?
Customer : I will have a potato paratha.
परन्तु यदि किसी कार्य को करने का निर्णय कर लेने के पश्चात् यदि वक्ता उस कार्य का वर्णन दुबारा करे तो be going to या Present Continuous का ही प्रयोग किया जायेगा will + infinitive का नहीं । जैसे उपरोक्त उदाहरण
(i) में mother कहेगी Tom is putting out/going to put out the stove.
उदाहरण (ii) में Customer से यदि दुबारा कोई पूछता है तो वह कहेगा
I am having/am going to have a potato paratha.
उदाहरण (iv) में Anupam अपने मित्रों से कहेगाI am going there today.

3. The Present Continuous for Future Acton,
(a) इसका प्रयोग निकट भविष्य में definite arrangement को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है । जैसेI am buying a new car next week...
इस वाक्य से तात्पर्य है कि मैंने कार खरीदने की पक्की योजना बना ली । मैंने model भी बुक करा दिया है।
I am seeing my dentist tonight, से तात्पर्य है कि मैंने dentist से मिलने का समय व इजाजत ले ली है ।
(b) निम्नलिखित प्रकार की क्रियाओं के साथ Present Continuous का प्रयोग किया जाता है । ये बगैर किसी definite arrangement के एक decision या plan को व्यक्त करती हैं ।
ये क्रियाएँ हैं
(i) एक स्थान से दूसरे स्थान को गति (movement) बताने वाली verbs - go, come, arrive, reach,drive, sail, fly, start, travel इत्यादि ।
(ii) Position बतानी वाली क्रियाएँ- stay, remain इत्यादि ।
(iii) खाना तथा पीना बताने के लिए do तथा have जैसे
(i) I am going home.
(ii) We are flying to New York.
(iii) She is staying at home.
(iv) He is not doing anything.
(c) जिन Verbs का प्रयोग Continuous Tense में किया जा सकता है उनका प्रयोग Future Simple में ही करते हैं । जैसे
(i) You will understand it tomorrow.
(ii) The principal will think over it.
Some More Examples of will + infinitive Present Continuous
(a) A : Why are you holding a piece of paper?
B : Iam writing a letter to my friend, Anil but I don't know his address.
A : Don't worry. I will tell you.
(b) A: I am about to fall asleep. I need to wake up!
B : I will get you a cup of coffee. That will wake you up.
(c) Kavita : Oh!I have forgotten my fee at home.
Sita : Don't worry, I will lend you.
4. The 'be going to' form used for intention
Form- 'be going to' + V की I form
इस form का प्रयोग कर्ता के किसी Future Action को करने के इरादे (Intention) को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है । यह इरादा हमेशा ही पूर्व नियोजित होता है और यह भी पता चलता है कि इसके लिए कुछ तैयारी भी कर ली गई है । अर्थात् be going to द्वारा व्यक्त किये गये Future Action के घटित होने की पूरी सम्भावना होती है। इस संदर्भ में निम्नलिखित बिन्दुओं को ध्यान में रखा जाना चाहिये
(A) समय के साथ निकट भविष्य में होने वाले कार्य को व्यक्त करने के लिए Present Continuous के स्थान पर इसका प्रयोग किया जा सकता है । जैसे
(i) I am receiving my mother at the station at 9.00.
(ii) I am going to receive my mother at the station at 9.00
परन्तु दोनों ही वाक्यों के कार्य में arrangement का अन्तर है ।
वाक्य (i) बताता है कि यहाँ पर arrangement है । मैं अपनी माताजी को receive कर रहा हूँ जिसके बारे में उन्हें पता है ।
वाक्य (ii) में arrangement नहीं है । हो सकता है कि मेरी माताजी मुझे देखकर चौंके ।
(B) The "be going to" form का प्रयोग हमेशा ही पूर्वनियोजित इरादों तथा intention + plan को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है जबकि will + infinitive form का प्रयोग ऐसे इरादों को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है जो कि पूर्व-नियोजित नहीं होते हैं । इसलिए यदि किसी कार्य को करने की तैयारी कर ली गई है तो be going to का ही प्रयोग किया जायेगा । जैसे
(i) A : Why are you buying a soap ?
B : I am going to wash my clothes.
(ii) A : Iam cooking rice but I don't know to cook them?
B : Don't worry, I will be teaching you everything.

(C) सामान्यतया will + infinitive का प्रयोग I person के साथ intention व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है। II तथा III person के साथ intention को व्यक्त करने के लिए सामान्यतया "be going to" का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे
(i) They are going to join American Institute.
(ii) He is going to join American Institute.
लेकिन won't का प्रयोग सभी persons के साथ negative intention व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है जिसका तात्पर्य refuse होता है ।
He won't come. (वह आने से इंकार करता है ।)
Exercise 16.
Fill in the blanks with Present Continuous or 'be going to form of the verbs given in the brackets:
1. I............ (play) tennis with Radha and Ravi.
2. My father ............ (have) bye-pass surgery next week.
3. It's very hot. I ............ (turn) on the AC.
4. I............ (have) some friends for dinner tomorrow.
5. Ram: ............ you............ (go) to school tomorrow ?
Hari : Yes, I ............ (go).
6. I ............ (get) my hair cut tomorrow.
7. Our school ............ (start) French next term.
8. I ............ (spend) a few days in Jaipur next month.
9. Panchayat ........... (build) a new school building here.
10. He ............ (leave) tomorrow.
11. I ........... (giving) her a gift on her birthday.
12. She ........... (see) a dentist next week.
13. He ........... (wash) his car.
14. What ............ you ............ (do) with that money?
15. The principal ........... (read) my answer to his letter of clarification.
Answers:
1. am playing
2. is having
3. am going to turn
4. am having
5. Are, going, am going
6. am getting
7. is starting
8. am spending
9. is going to build
10. is leaving
11. am giving
12. is seeing
13. is going to wash
14. are, going to do
15. is going to read.
Exercise 17.
Fill in the blanks with "be going to" or will + infinitive form:
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति "be going to" या will + infinitive रूप से करो
1. A : I can't hear that television !
B : I.......... (turn) it up so you can hear it.
2. We are so excited about our trip to Uttar Pradesh. We ............ (visit) Mathura, Agra and Vrindavan. After I pass 12th, I ........... (attend) medical school and become a doctor. I have wanted to
become a doctor all my life.
4. A : The light has gone!
B : So, it has. I ............ (go) and start the generator.
5. A : Have you bought a ticket for me?
B : Oh no. I forgot. I ............ (buy) one now.
6. I have bought a computer and I ............ (learn) how to operate it.
7. A : I can't open this message.
B : ................... (call) my son. He ............ (open) it for you.
8. You have bought a lot of vegetables........... some guests .......... (attend) the fuction?
9. A : What are you going to do with that micro-wave oven?
B : ............ (cook) some food for you.
10. You look tired. Sit down and I .......... (get) you a cup of tea.
11. I haven't bought any wine because I ............ (give) up drinking.
12. Child : I have lost my pencil.
Mother: I ............ (buy) new one.
13. A : ............. you .......... (have) some more coffee?
B : No, thanks.
14. ............ you ........... (drive), please? I can't drive at night.
Answers:
1. will turn
2. are going to visit
3. am going to attend.
4. will go
5. will buy
6. am going to learn
7. will call, will open
8. Are, going to attend
9. am going to cook
10. will get
11. am going to give
12. will buy
13. Will, have.
14. will, drive.

Exercise 18.
Fill in the blanks with Present Indefinite or Present Continuous for Future Action:
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति Future Action के लिए Present Indefinite या Present Continuous से करो--
1. ........ (take) my wife out for dinner tonight.
2. The 10:30 train ............ (return) by 14:20.
3. The girls and I ........... (go) out tonight.
4. At 7:00 a.m., we ............. (leave) for Kota.
5. The return train .............. (depart) one hour late.
6. We .............. (see) each other sometime in the future.
7. The office .............. (throw) a fare-well party for me.
8. They .............. (have) a very small wedding on the beach.
9. Eating sandwiches everyday is boring, so I.............. (eat) out today.
10............... you.............. (go) to the cinema tonight?
11. I ambored with this T.V. programme. I wonder when.............. it .............. (finish) ?
12. A : .............. you.............. (do) anything tomorrow?
B : No, I am free. 13. The new photographic exhibition ...... (open) on 12 October and ....... (finish) on 18 October.
14. A : What time ..............you.............. (finish) your work on Fridays?
B : At 4:00, but this FridayI.............. (finish) early.
Answers:
1. am taking
2. returns
3. are going
4. leave
5. departs
6. are seeing
7. is throwing
8. are having
9. am eating
10. Are, going
11. does, finish
12. Are, doing
13. opens, finishes
14. do, finish, am finishing

'Will or be going to" to Express Prediction (पूर्वानुमान)
पूर्वानुमान वे अनुमान होते हैं जो कि यह बताते हैं कि भविष्य में क्या होगा । इन पर Subject का कोई control नहीं होता है । Prediction व्यक्त करने के लिए दोनों में से किसी का भी प्रयोग किया जा सकता है । जैसे
(i) J. K. Singh will be the next chairperson.
(ii) J. K. Singh is going to be the next chairperson.
(iii) Year 2018 will be a very interesting year.
(iv) Year 2018 is going to be a very interesting year.
परन्तु इन दोनों के अर्थों में अन्तर इस प्रकार से है --
(a) be going to बताता है कि कुछ घटित होने के संकेत हैं जबकि will दर्शाता है कि ऐसा वक्ता का विश्वास है या वक्ता ऐसा सोचता है ।
Look at those clouds! It is going to rain.
I think it will rain tonight.
(b) सामान्यतया begoing to का प्रयोग निकट भविष्य के लिए किया जाता है जबकि will + infinitive का प्रयोग भविष्य के किसी समय या दूरस्थ भविष्य (remote future) को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है । जैसे
This motor-cycle is going to breakdown. इससे तात्पर्य है कि मोटर साईकिल में कुछ गड़बड़ी है जिसे देखकर हमें ऐसा लगता है । This motor-cycle will break down. से तात्पर्य है कि यह मोटर-साईकिल कभी-ना-कभी तो खराब होनी ही
1. The Future Simple
वैसे तो आधुनिक व्याकरण में कोई Future Tense नहीं होता है लेकिन सुविधा के लिए will/shall + bare infinitive (verb की I form) को Future Simple के रूप में व्यक्त किया जाता है ।
(1) इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में काम का होना या करना भविष्यत्काल में पाया जाता है ।
(2) वाक्य के अन्त में गा, गी, गे पाये जाते हैं ।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern - Subject + will/shall +V1
1. मैं एक पत्र लिखूगा । -- I shall write a letter.
2 हम कल स्कूल जायेंगे । -- We shall go to school tomorrow.
3. तुम एक किताब पढ़ोगे । -- You will read a book.
4. उसके पिता कल देहली से आयेंगे । -- His father will come from Delhi tomorrow.
5. ये लड़के सोमवार को फुटबाल का -- These boys will play football match on Monday. मैच खेलेंगे ।
Rule- अंग्रेजी में अनुवाद करते समय I और We के साथ shall और अन्य subjects के साथ will लगाकर verb की first form लगाते हैं ।
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern - Subject + will/shall + not +V1 (ing) .......?
1. मैं कल अलीगढ़ नहीं जाऊँगा । I shall not go to Aligarh tomorrow.
2. लड़के दिन में नहीं सोयेंगे । The boys will not sleep in the day.
3. तुम पुस्तक नहीं पढ़ोगे । -- You will not read the book.
4. हम कल हॉकी का मैच नहीं खेलेंगे । -- We shall not playahockey match tomorrow.
Rule-Negative sentences में will या shall के पश्चात् not लगा देते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern-Will/Shall + Subject +V1 (ing) .......?
1. क्या वह तुमको कुछ कलमें देगा ? -- Will he give you some pens?
2. क्या हम आम खायेंगे ? -- Shall we eat mangoes ?
3. क्या तुम्हारे भाई कल नहीं आयेंगे ? -- Will your brother not come tomorrow?
4. सीता कौन-सा गाना गायेगी ? -- Which song will Sita sing ?
5. वह कितनी पुस्तकें खरीदेगा ? -- How many books will he buy?
6. हम कल कहाँ जायेंगे ? -- Where shall we go tomorrow?
7. तुम्हारे पुत्र को कौन पीटेगा ? -- Who will beat your son ?
Rule 1. जिन वाक्यों में क्या' सबसे पहले आये, अंग्रेजी में अनुवाद करते समय Shall या Will वाक्यों में subject से पहले ले आते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 और 2)
Rule 2. यदि वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द हो तो उसकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले लगाते हैं, उसके पश्चात् shall या will, फिर verb की first form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 6)
Rule 3. How much, How many, Whose, Which के साथ उनसे सम्बन्धित noun भी लगाते हैं ।
(देखिये वाक्य नं. 4 व 5)
Rule 4. अगर कोई प्रश्नवाचक शब्द subject का कार्य कर रहा है तो उसकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले लगाते हैं, फिर will या shall फिर verb की first form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 7)
Rule 5.Negative Interrogative sentences का अनुवाद Interrogative Affirmative sentences की तरह ही होगा केवल Subject के बाद not लग जाता है । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3)
Rule 6. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नसूचक चिह्न (?) लगा देते हैं ।

प्रयोग (Uses) -
इसका प्रयोग निम्नलिखित कार्यों के लिए होता है
(a) वक्ता की भविष्य के बारे में राय, विचार, तुलना इत्यादि व्यक्त करने के लिए इसका प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे
(i) She will get first division. (मुझे पक्का विश्वास है ।)
(ii) We will find the teacher at home. (सम्भवतया)
(iii) My brother will sell his car. (मेरा मानना है।) इस tense का प्रयोग time-expression के साथ तथा इसके बगैर भी किया जा सकता है ।।
(b) इसका प्रयोग Future के उन habitual action के साथ किया जा सकता है जो हमारे विचार से भविष्य में हो सकते हैं । जैसे
(i) Summer will come again.
(ii) Monkeys will not build nests.
(iii) People will plough their fields.
(iv) We will take exam.
(c) Conditional Sentences type-I के साथ|
If + present + Future
If you come to me, I'll help you
(d) Time Clause के साथ Future बताने के लिए
Future + Time Clause in Present
We'll go home when he comes.
Exercise 19.
Fill in the blanks with Present Continuous or Future Simple:
1. I.................... (not reply) you unless you write to me.
2. I....................(wait) here until she comes back.
3. If you don't work hard you.................... (not pass) this year.
4. Our class .................... (play) a friendly football match next Sunday.
5. My mother.................... (come) on Monday.
6. She.................... (go) again next Monday.
7. He.................... (know) about it tonight.
8. You....................(believe) it when you see it.
9. I.................... (have) my fan repaired next week.
10. The plumber.................... (come) at 10:00 tomorrow.
11. I.................... (catch) 11:30 train.
12. I have turned out the light. ...................it.................... (matter)?
13. I.................... (remember) you.
14. She.................... (be) back by 10.30.
15. You................... (understand) when you are older.
Answers:
1. will not reply
2. shall wait
3. will not pass
4. is playing
5. is coming
6. is going
7. will know
8. will believe
9. am having
10. is coming
11. am catching
12. Will, matter
13. shall remember
14. will be
15. will understand.
2. The Future Continuous इन वाक्यों के अन्त में 'रहा होगा', 'रही होगी', 'रहा हूँगा', 'रहे होंगे' आदि पाया जाता है ।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern - Subject + will/shall + be + V1 (ing) .......
1. मैं अपना पाठ याद कर रहा हूँगा । I shall be learning my lesson.
2. वह एक पत्र लिख रही होगी । She will be writing a letter.
3. लड़के फुटबाल खेल रहे होंगे । The boys will be playing football.
4. किसान अपने खेत जोत रहे होंगे । The farmers will be ploughing their fields.
5. हम तुम्हारे घर आ रहे होंगे । We shall be coming to your house.
Rule 1.1 और We के साथ shall be लगाते हैं और verb की I form में 'ing' लगाते हैं ।
Rule 2. शेष सब कर्ताओं के साथ will be लाकर verb की I form में 'ing' लगाते हैं ।
(B) Negative Sentences:
Pattern- Subject + will/shall + not + be + V, (ing) .......?
1. मैं कक्षा में नहीं पढ़ रहा हूँगा । I shall not be reading in the class.
2. हम एक गेंद नहीं फेंक रहे होंगे । we shall not be throwinga ball.
3. वह एक प्याला चाय नहीं ला रही होगी। She will not be bringinga cup of tea.
4. वे लड़कों को नहीं पढ़ा रहे होंगे । They will not be teaching the boys.
5. तुम कल इस समय स्कूल नहीं जा रहे You will not be going to school at this होंगे। time tomorrow.
Rule- Negative sentences में will या shall के बाद not लगाते हैं ।

(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern-Will/Shall + Subject + be + V1 (ing).......?
1. क्या वह अपना पाठ याद कर रहा होगा? Will he be learning his lesson?
2. क्या मैं अपने गाँव पैदल जा रहा हूँगा ? Shall I be going to my village on foot?
3. क्या वह बच्चा अपने खिलौनों से नहीं खेल रहा होगा ? Will the child not be playing with his toys?
4. तुम्हारे पिताजी कल कहाँ जा रहे होंगे ? Where will your father be going tomorrow?
5. वह अपनी पुस्तक क्यों नहीं पढ़ रहा होगा ? Why will he not be reading his book?
6. कमरे में कितने लड़के सो रहे होंगे ? How many boys will be sleeping in the room?
7. मैदान में कौन खेल रहा होगा ? Who will be playing in the field?
8. अब स्कूल कौन आ रहा होगा ? Who will be coming to school now?
Rule 1. जिन वाक्यों में सबसे पहले 'क्या' लगा हो उनका अनुवाद करते समय Will या Shall वाक्य में सबसे पहले लगाते हैं । उसके बाद कर्ता, फिर be और इसके पश्चात् verb की I form में 'ing' लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 तथा 2)
Rule 2. अगर वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द हो तो उसकी अंग्रेजी सर्वप्रथम लाकर will या shall लगाते हैं। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 4)
Rule 3. How much, How many, Which के साथ उनसे सम्बन्धित nouns भी लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं.6)
Rule 4. यदि प्रश्नवाचक शब्द अर्थात् Who कर्ता का कार्य कर रहा हो तो सबसे पहले उसे लाकर will be या shall be लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 7, 8)
Rule 5. Negative Interrogative sentences में be से पहिले not और लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3, 5)
Rule 6. वाक्य के अन्त में प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) लगाते हैं ।
प्रयोग (Uses) -
इसका प्रयोग निम्नलिखित स्थिति में किया जाता है -
(a) एक सामान्य Continuous Tense की तरह
अन्य Continuous Tenses की ही तरह से सामान्यतया इसका प्रयोग समय बिन्दु के साथ किया जा सकता है । कोई action जो कि भविष्य में उस समय के पूर्व शुरू होकर उसके कुछ समय पश्चात् भी चलता रहेगा।

|
Today at 11.00a.m. Friday |
The students are sitting in the class. They are studying their lessons. |
|
Tomorrow at 11.00 a.m. Saturday |
The students will be studying. The teacher will be teaching them. |
|
The day after tomorrow at 11.00 a.m. Sunday |
The students will not be doing anything. |
(b) To express future without intention -
जब कोई कार्य Future में बगैर किसी intention के घटित होता है तो भी इसका प्रयोग किया जाता है। इसमें कर्ता का कोई involvement नहीं होता है । ये कार्य स्वतः ही होते हुए पाये जाते हैं । जैसे
(i) I will be seeing Ms Rita tomorrow. We work in the same office.
(ii) We will be travelling next Sunday at this time.
Future Continuous तथा Present Continuous में अंतर
Present Continuous में arrangement होता है जबकि Future Continuous में intention तथा arrangement नहीं होता है । जैसे
I am seeing Ms Rita tomorrow.
से तात्पर्य है कि मैंने रीता से कल मिलने का समय लिया है । जबकि
I will be seeing Ms Rita tomorrow.
से तात्पर्य है कि हो सकता है कि दोनों एक ही office में कार्य करते हैं और यह उनके Routine का कार्य है। यहाँ पर न तो intention है और न ही arrangement है ।
Will + infinitive तथा Future Continuous में अन्तर
(i) Will + infinitive में intention होता है । इसमें कार्य करने का निश्चय बोलते समय ही किया जाता है। जैसे
Customer : There is something in the milk.
Waiter: Don't worry. I'll get you another.
जबकि Future Continuous में intention नहीं होता है । यह एक स्वाभाविक रूप से भविष्य में होने वाले कार्य को बताता है।
Ratna : Are you coming to the cinema?
Ratan : I'd love to, but I will be doing my home work then.
(ii) Will + infinitive invitation, request या command व्यक्त कर सकता है लेकिन Future Continuous नहीं व्यक्त कर सकता है ।
Will you have a drink, please ? (प्रार्थना)
Will you be helping me? (एक सामान्य प्रश्न)

Exercise 20.
Fill in the blanks with will + infinitive or Future Continuous of the verbs given in the brackets.
1. Anil: What are you doing next Sunday?
Sunil : Oh, I............... (work) as usual. Sunday is a working day for me.
2. Kamal : We have missed the train.
Naman : Never mind, we............... (walk)
3. Teacher : Your hands are dirty.
Student: All right, I............... (wash) them.
4. I............... (work) for Mittal Publishing House next week as their manager will be on leave.
5. Mother : You have left the tap running.
Son: So, I have. ............... (turn) it off.
6. Come on the gate, the train............... (pass) through atunnel.
7. Everything is ready. Our chief guest............... (arrive) any minute.
8. She............... (come) if you ask her.
9. That oak tree............... (still stand) here hundred years from now.
10. I............... (send) message in code if you insist.
Answers:
1. will be working
2. will walk
3. will wash
4. will be working
5. will turn
6. will be passing
7. will be arriving
8. will come
9. will still be standing
10. will send.
3. The Future Perfect
ऐसे वाक्यों के अन्त में 'चुकेगा', 'चुकूँगा', 'चुकोगे' आदि शब्द आते हैं ।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern-Subject + will/shall + have +V3 .......
1. तुम्हारे आने से पहले वह अपना पाठ याद कर चुकेगा ।
He will have learnt his lesson before you come.
2. सात बजने से पहले हम अपना खाना खा चुके होंगे ।
We shall have taken our food before it is seven.
3. सूरज छिपने से पहले वे मैच खेल चुके होंगे ।
They will have played the match before the sun sets.
4. आपके आने से पहले मैं अपनी पुस्तक पढ़ चुकूँगा ।
I shall have read my book before you come.
Rule 1. यदि एक ही वाक्य में भविष्य में दो कामों का होना पाया जाये तो पहले होने वाले काम के लिये will have या shall have तथा मुख्य verb की third form का प्रयोग करते हैं । दूसरे काम के लिये subject के अनुसार Present Indefinite Tense की verb का प्रयोग करते हैं ।
Rules 2. I और We के साथ shall have लगाते हैं और बाकी सबके साथ will have लगाते हैं ।
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern- Subject + will/shall + not + have +V3 ....... 1. हरी के आने से पहले वह पत्र नहीं लिख चुकी होगी ।
She will not have written the letter before Hari comes. 2. उसके सोने से पहले बच्चे ने दूध नहीं पिया होगा ।
The child will not have drunk milk before he sleeps. 3. अध्यापक के आने से पहले मैंने अपना काम समाप्त नहीं किया होगा ।
I shall not have done my work before the teacher comes.
Rule ---Negative वाक्यों में will या shall के बाद not लगाते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern-Will/Shall + Subject + have +V3.......?
1. क्या सात बजने से पहले लड़के मैच खेल चुकेंगे ?
Will the boys have played the match before it is seven?
2. क्या गाड़ी आने से पहले हम टिकट नहीं ले चुके होंगे ?
Shall we not have taken the tickets before the train arrives?
3. सूरज छिपने से पहले कितने लड़के यहाँ आ चुके होंगे ?
How many boys will have come here before the sun sets ?
4. अध्यापक के आने से पहले कौन तुम्हारे पुत्र को सजा दे चुकेगा ?
Who will have punished your son before the teacher comes ?
5. वर्षा होने से पहले वह कहाँ जा चुका होगा ?
Where will he have gone before it rains ?
Rule 1. Interrogative sentences में Will या Shall सबसे आरम्भ में लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 तथा 2)
Rule 2. अगर वाक्य के बीच में प्रश्नवाचक शब्द दिये हों तो सबसे पहले उनकी अंग्रेजी, फिर will या shall, फिर कर्ता और फिर have के साथ verb की third form लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 5) Rule 3. How much, How many, Whose और Which के साथ उनसे सम्बन्ध रखने वाले nouns भी लगाते हैं। (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3)
Rule 4. अगर वाक्य Negative Interrogative हो तो subject के पश्चात् not लगा देते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 2)
(Uses) 1. इस Tense का प्रयोग ऐसे कार्य के लिए होता है जो भविष्य में किसी निर्धारित समय तक समाप्त हो
चुकेगा। जैसे- He will have returned home by next month.

2. इस Tense का प्रयोग समयसूचक Clauses के साथ भी होता है। जो Clause समय बताता है, उसमें Simple Present Tense का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे --
When you come back, I shall have bought the book.
जब तुम वापस आओगे तो मैं पुस्तक खरीद चुका होऊँगा।
पहचान :प्रायः इन वाक्यों के प्रारम्भ या अन्त में by + time या by the end of (time) दिया हुआ होता है। जैसे
(i) They will have finished their work by evening.
(ii) We shall have made this building by the end of March.
4. The Future Perfect Continuous इस Tense के वाक्यों में कार्य का भविष्य काल में जारी रहना पाया जाता है तथा साथ ही साथ समय दिया होता है । वाक्य के अन्त में रहेंगे, रहेगी, रहूँगा, रहोगे, रहेंगी या रहा होगा, रही होगी, रहे होंगे, रही होंगी, रहा हूँगा' आते हैं । कार्य शुरू होने का समय दिया होता है ।।
(A) Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Pattern - Subject + will/shall + have been +V1 (ing) + since / for + time.
1. वे दो घण्टे तक खेलते रहेंगे । -- They will have been playing for two hours.
2. लड़के चार बजे से तालाब में तैरते रहे होंगे । -- The boys will have been swimming in the tank since 4 o'clock.
3. हम तीन साल से इस कॉलेज में पढ़ रहे होंगे । -- We shall have been studying in this college for three years.
Rule 1.1 और We के साथ shall have been और अन्य के साथ will have been लगाकर verb की first form में 'ing' लगाते हैं ।
Rule 2. समय दिखाने के लिये since या for का प्रयोग करते हैं ।
(B) Negative Sentences
Pattern- Subject + will/shall + not + have been +V1 (ing) + since / for + time.
1. वह दो वर्ष से कठिन परिश्रम नहीं कर रही होगी ।। -- She will not have been working hard for two years.
2. तुम्हें दो दिन से बुखार नहीं आ रहा होगा । -- You will not have been suffering from fever for two days.
Rule --Negative sentences में will या shall के पश्चात् not लगाते हैं ।
(C) Interrogative Sentences
Pattern - Will/Shall + subject + have been +V1 (ing) + since / for + time.?
1. क्या हम उसका इन्तजार सुबह से करते रहेंगे ? -- Shall we have been waiting for him since morning?
2. क्या वह आलसी लड़का दो घण्टे से सो रहा होगा ? -- Will that lazy boy have been sleeping for two hours ?
3. क्या तुम दो दिन से नहीं पढ़ रहे होंगे ? -- Will you not have been reading for two days ?
4. वे पाँच बजे से अपना समय क्यों नष्ट करते रहेंगे ? -- Why will they have been wasting their time since 5 o'clock?
5. कितने लड़के दोपहर से शोर मचाते रहे होंगे ? -- How many boys will have been making a noise since noon?
6. लड़के दो बजे से कहाँ खेलते रहे होंगे ? -- Where will the boys have been playing since 2 o'clock?
Rule 1. वाक्यों के प्रारम्भ में क्या' लगा रहने पर Will या Shall कर्ता से पहले ले आते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 1 तथा 2)
Rule 2. अगर वाक्य के बीच में 'प्रश्नवाचक शब्द' हो तो उसकी अंग्रेजी सबसे पहले लगाकर will या shall का प्रयोग करते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 4 तथा 6)
Rule 3. How many, How much, Whose, Which के साथ इनसे सम्बन्धित nouns भी लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 5)
Rule 4. Negative Interrogative Sentences में subject के बाद में not लगाते हैं । (देखिये वाक्य नं. 3)
(Uses) इस Tense का प्रयोग भविष्य में किसी समय विशेष तक जारी रहने वाले कार्य के लिए होता है ।
यदि since/for/all के साथ समय के साथ ही साथ या तो by + time दिया हो या time clause in present हो तो इसका ही प्रयोग होगा ।

By+time+ Future Perfect Continuous + since/for+time T Time clause in Present + Future Perfect Continuous + since/for + time
(1) When he arrives here, they will have been playing since 3 o'clock.
(2) By the end of this month we shall have been working here for two months.
Exercise 21.
Write the correct forms of the verbs given in the brackets in the spaces provide:
1. I ........................ to Mathura tomorrow. (go)
2. He ........................ on me next Sunday. (call)
3. If he works hard, he... (pass)
4. When he meets you, he ...................... you. (love)
5. The library .................... closed till the librarian comes. (remain)
6. She ....................... food at this time tomorrow. (cook)
7. We ........................ in our new house at this time next Sunday. (sit)
8. At this time the day after tomorrow, I ........... my friends. (entertain)
9. Who ...................... a bell round the cat's neck? (tie)
10. I ........................ my courses by tomorrow. (finish)
11. She ...................... her courses by next month. (revise)
12. I ...................... a bath before the day dawns. (take)
13. He ...................... ready before the train arrives.
14. My mother ..................... breakfast for us before the guest arrive. (prepare)
15. When you are in bed I ..................... at home. (be)
16. By tomorrow she ........ her sums for ten days. (do)
17. By the end of this week, he ....................... a book for fifteen days. (write)
18. By the end of this month, I ........................ music for six months. (learn)
19. By the next Monday I ....................... at my uncle's house for two weeks. (stay)
20. More and more people ........................ by air in the days to come. (travel)
21. I hope you ....................... your promise by tomorrow. (not forget)
22. I ........................ this examination before 2015. (pass)
23. By the end of this month she ........................ English for four months. (learn)
24. I .................... off the radio before I go to bed. (switch)
25. If she comes to us, we ...... ........ to the cinema. (go)
Answers:
1. shall go
2. will call
3. will pass
4. will love
5. will remain
6. will be cooking
7. shall be sitting
8. shall be entertaining
9. will tie
10. shall have finished
11. will have revised
12. shall take
13. will get
14. will have prepared
15. will/shall be
16. will have been doing
17. will have been writing
18. shall have been learning
19. shall have been staying
20. will travel
21. will not forget
22. shall have passed
23. will have been learning
24. will switch
25. shall go.

More About Verbs
Imperatives (Verb I Form)
Imperatives (आज्ञार्थक वाक्यों) में Verb की I form का प्रयोग किया जाता है । Imperatives की पहचान निम्नलिखित है :
1. वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में Subject (कर्ता) नहीं दिया गया होता है । Verb की I form से ही वाक्य आरम्भ होता है।
2. कई बार वाक्य Please या Kindly से प्रारम्भ होता है ।
3. Negative Imperative हमेशा Do not + Verb I form से प्रारम्भ होता है । (get)
4. कभी-कभी Imperative वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में ही किसी व्यक्ति को Sir या Mr आदि कहकर सम्बोधित कर दिया जाता है। इन सब परिस्थितियों में वाक्य में Verb की I form का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है।
उदाहरण :
1................. the window, please. (open)
2. ................ a noise. (not make)
3. Mr Mohan, ................. to the market and bring some fruits. (go)
4. Sir, ....................... .me please. (help)
5. Kindly .................... me leave for three days. (grant)
Answer:
1. Open
2. Do not make
3. go
4. help
5. grant
Passive
कई बार Correct form of the Verbs के प्रश्नों में Passive Voice के वाक्य दे दिये जाते हैं । इन वाक्यों की पहचान निम्न प्रकार करनी चाहिए :
1. Verb की प्रकृति को पहचानना चाहिए । यथा :
(i) The lion .......................in a net. (catch)
Answer: was caught.
(ii) The hunter................the lion in a net. (catch)
Answer: caught.
Catch का अर्थ है - पकड़ना । इस Verb का कर्त्ता hunter है न कि lion. अतः यदि वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में कर्ता दिया गया है तो उत्तर Active Voice में 'caught' होगा जैसा कि वाक्य नम्बर (ii) में दिया है । यदि वाक्य के आरम्भ में Object (कर्म) दिया गया है तो उत्तर Passive Voice में ‘was caught' होगा ।
2. यह भी देखना चाहिये कि वाक्य में by + कर्ता' दिया गया है या नहीं। यदि वाक्य में 'by + कर्ता' है तो वाक्य निश्चित तौर पर Passive Voice का ही है।
3. Passive Voice की पहचान के साथ 'समय व काल' (Time and Tense) सम्बन्धी पहचान भी करनी चाहिए जो पूर्व में बताए गए Tenses के अनुसार ही होती है, तत्पश्चात् ही रिक्त स्थान में Verb form का निर्धारण करना चाहिए । Verb की सही form के लिए Passive Voice Chart देखिए ।

उदाहरण :
1. The thief yesterday. (arrest)
2. When they reached the place the chairs ....... (remove)
3. A letter .................... by her yesterday. (write)
4. The water tank .............. before it was filled. (clean)
5. Gandhiji ................... dead by Godse. (shoot)
6. The freedom fighters..........several times by the British Government. (arrest)
Answer:
1. was arrested. (arrest क्रिया का कर्ता the police होना चाहिए था। arrest का अर्थ है 'गिरफ्तार करना' ।)
2. were being removed. (remove का कर्त्ता ‘the men' आना चाहिए था । remove का अर्थ है 'हटाना' ।)
3. was written. (by her' आया है ।)
4. had been cleaned (clean का कर्त्ता some one या man आदि आना चाहिए था । clean का अर्थ है – 'साफ करना' ।)
5. was shot (by Godse' आया है।)
6. were arrested. ('by the British Government' आया है ।)
कुछ महत्वपूर्ण तथ्य
क्रिया के सही-सही रूप का प्रयोग करने के लिए तथा शुद्ध वाक्य-रचना के लिए Tenses के अतिरिक्त निम्नलिखित बातों को ध्यान में रखना आवश्यक है :
1. had better, would rather तथा let के साथ क्रिया के First Form का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे -
(i) You had better wash your face
(ii) Let me go.
2. क्रिया का वह रूप जो कर्ता एवं काल की सीमा में न रहे अर्थात् कर्ता एवं काल के परिवर्तन से न बदले, Infinitive कहलाता है । ऐसे Verb के First Form के पूर्व to का प्रयोग करते हैं । जैसे -
(i) He goes there to read newspapers.
(ii) He will go there to read newspapers.
(iii) He went there to read newspapers.
Note : इन वाक्यों में to read अपरिवर्तनशील है । किन्तु कुछ क्रियाओं के बाद Infinitive का प्रयोग बिना to के भी होता है । उन क्रियाओं में से कुछ क्रियाएँ, dare, need, hear, feel, know, make, help, let, bid, see हैं । जैसे -
(i) Please help me lift this box.
(iii) She heard me sing.
(ii) You need not worry.
(iv) Let me read.
3. जब Simple Present का Future के अर्थ में प्रयोग हो तो in case, unless, if, when, as soon as के साथ Verb का First Form आता है । अगर Subject एकवचन हो तो क्रिया के साथ s या es जोड़ दिया जाता है। जैसे -
(i) In case I forget, please remind me to clear your bill.
(ii) He will teach you provided you pay him the money he asks for.
4. have, get, make, cause चार Causatives हैं । जब कर्ता स्वयं कार्य न करके दूसरे से कराता है तो इन Causatives का प्रयोग होता है । इनमें क्रिया की स्थिति इस प्रकार होती है
(a) Sub. + get/cause + doer + Infinitive + Object. (Active Form)
(i) He got a workman to whitewash his house.
(ii) He caused a washerman to wash his clothes.
(b) Sub. + have/make + doer + Verb का First Form + Object. (Active Form)
(i) I have my sister stitch my shirt.
(ii) He made us laugh in the class.
(c) Sub. + get/have + Object + Third Form of the Verb + by (doer). (Passive Form)
(i) She had her chair repaired by a carpenter.
(ii) I got my shoes polished by a cobbler.
5. without, on, for, of, need, help, mind, by, in, after, before, instead of a के साथ Verb की
First Form मे - ing लगते है| जैसे -

(i) He ran without stopping.
(ii) He kept on singing.
(iii) Her hair needs cutting.
(iv) I do not mind your smoking.
6. Lest के वाक्यांश में सभी कर्ताओं के बाद should + Verb का First Form आता है। जैसे Work hard lest you should fail.
Exercise 22.
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. I have my clothes ......... by my mother. (wash)
2. He ate all the fruits without... (stop)
3. She kept on..........clothes in her room. (stitch)
4. We heard her......... a song. (sing)
5. I requested him to let me.......... my home. (go)
6. Rahul and Pramod.........real brothers. (be)
7. The thief entered the room and..........away all the ornaments. (take)
8. He went on...........the fence the whole day. (whitewash)
9. He could not help ....................... that side. (look)
10. Instead of ..... his books, he gave them to Ram free of cost. (sell)
11. The train.............. before I came. (stop)
12. He.............. out just now. (go)
13. The farmer.............. in the field. (work)
14. He.............. an hour ago. (come)
15. He.............. asleep while reading. (fall)
16. I shall see him when he (return)
17. A barking dog seldom .............. (bite)
18. The Ganga .............. in the Himalayas. (rise)
19. He.............. newspapers in childhood. (sell)
20. I.............. my homework before it was dark. (do)
Answers:
1. washed
2. stopping
3. stitching
4. sing
5. go
6. are
7. took
8. whitewashing
9. looking
10. selling
11. had stopped
12. has gone
13. works
14. came
15. fell
16. returns
17. bites
18. rises
19. sold
20. had done.

Exercise 23.
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. We .... freedom in 1947 as a result of what I call the first vision for the nation. (get)
2. After Independence, India .................... forward to development through Five Year Plans. (look)
3. What we .............. are some young men who will renounce everything. (want)
4. If we ................... these areas of our core competency, we can create Indian MNCs and aim at a target of $150 billion by 2010. (exploit)
5. India ......... the 10th Five Year Plan with a focus on all round development. (enter)
6. I .................. you will be surprised to hear me say this. (know)
7. If you ................... any special tastes here in England, you will find plenty to satisfy them in India (acquire)
8. If you .......... for geology, there is work for you from the Himalayas to Ceylon. (care)
9. The debt which the world .............. to our Motherland is immense. (owe)
10. Now you ............. clearly where the soul of this ogress is. (understand)
11. If it ever .............. to trace back its course, it will simply dry up by being dissipated in ever directions.
12. .............. man .............. laws, or do laws make man? (do, make)
13. India ............. not with the power of the flesh, but with the power of the spirit. (raise)
14. We Indians .............. from a great defect. (suffer)
15. It is opposition which ............. success. (fortell)
Answers:
(1) got
(2) looked
(3) want
(4) exploit
(5) has entered
(6) know
(7) have acquired
(8) care
(9) own
(10) understand
(11) tries
(12) Does make
(13) will be raised
(14) suffer
(15) foretells.
Exercise 24.
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. For the last three-quarters of a century, India .............. over with reform societies and reformers. (bubble)
2. They had not .............. the great lesson to be learned. (learn)
3. If you are really my children, you will .............. nothing, stop at nothing (fear)
4. The time has ............. for us to consider seriously the question of a Bharat brand of English. (come)
5. The rhinoceros ............ a swampy grass jungle to exist. (require)
6. Freedom is fragile and evanescent. Man has .............. so little of it in his entire history. (know)
7. Human rights violations ............. more deaths and more human misery than have all the weapons of mass destruction. (create)
8. As a concept, eco-tourism has .............. momentum recently in India. (gain)
9. I will not .............. your motive because it has given me a chance to do a beautiful and good thing. (question)
10. God .............. a great green wonderland when he spread out the span of the United States. (make)
11. I trust that I am .............. everybody very deeply. (offend)
12. An artist has the privileges of the court fool, you . (know)
13. The Internet .............. the hope of a more democratic society. (offer)
14. Let us .............. an example. (consider)
15. Machinery ............. society. (reform)
Answers:(1) has been bubbling
(2) learned
(3) fear
(4) come
(5) requires
(6) known
(7) have created
(8) has gained
(9) will not question
(10) made
(11)am offending
(12) know
(13) offers
(14)consider
(15) does not reform

Exercise 25. (From Textbook)
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. The train ................ beyond the long tunnel. (stop)
2. It ................. a small station called Sarhad. (be)
3. They were ................. only to make the local centres self sufficient. (accept)
4. So you have ................. to wait until tomorrow to know your fate. (get)
5. But you ................. then as well as I do. (know)
6. I can't ................. what the joke was. (remember)
7. And sometimes I think he ................. it and that seems to shrivel him up. (see)
8. He .... most particularly I was to came. (say)
9. He ............ towards the door up right. (cross)
10. You can ................. a job for him. (do)
Answers:
(1) stopped
(2) was
(3) accepted
(4) got
(5) know
(6) remember
(7) sees
(8) said
(9) crosses
(10) do.
Exercise 26 (From Textbook)
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. Please let me ................. your majesty the way. (show)
2. Such stories ............... an important part in China's classical education. (play)
3. They are deeply ................. of the spirit in which art was considered. (reveal)
4. But only the artist ................. the way within. (know)
5. The Chinese painter does not ................ you to borrow his eyes. (Want)
6. We have ................ to take a holistic view of the very basis of our existence. (begin)
7. The population of India is ................. be 920 million today. (estimate)
8. We have ................. it from our children. (borrow)
9. She ................. about the house in spotless white with one hand resting on her waist. (hobble)
10. When I ................ back she would ask me what the teacher had taught me. (come)
Answers:
(1) show
(2) played
(3) revealing
(4) knows
(5) want
(6) begun
(7) estimated
(8) borrowed
(9) hobbled
(10) came.

Exercise 27.
Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs given in the brackets :
1. The modern world .............. by its metaphysics. (shape)
2. All this ............ our suspicion that modern technology is developing. (confirm)
3. I have ............... it intermediate technolory to signify. (name)
4. The Internet can be a powerful tool for education if it ............. into a coherent pedagogy. (integrate)
5. For the first time in my life 1 heard such words or the first time 1 water into his cupped hands. (pour)
6. My heart has .........ever since. (dance)
7. He had everything in your beauty. (forget)
8. My soul and body danced and danced together. as the painted flames in the fire. (dance)
9. Who, says the girl Prakriti the wonder ? (do)
10. I bathed in the river Gambhira below the water. (plunge)
11. Orr discovered that they actually much of their expertise informally while drinking beer together. (acquire)
Answers:
(1) has been shaped
(2) confirms
(3) named
(4) is integrated
(5) poured
(6) been dancing
(7) forgotten
(8) dance
(9) has done
(10) plunging
(11) acquired.
Exercise 28.
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate forms of the verbs given in the brackets:
(i) At that moment Manisha and Rekha .....1...... (work) in front of my house yesterday. They .....2...... (mend) a water pipe. The man on the left .....3...... (have) a bidi in his hand. The water .....4...... (come) out of the hole: the water .....5...... (run) down the road.
(ii) There are some huts here. Every day some of the people living in the huts .....1...... (eat) their food outside the hut and .....2...... (throw) all the garbage on the road. They do not .....3...... (keep) the place clean.
(iii) Mohan .....1...... (leave) india in 2008 and .....2...... (go) to the United States. He .....3...... (be) in the States for nearly six years now, and he .....4...... (be) very happy there. But his old mother in India is not happy. .
(iv) Mohan’s father .....1...... (die) two years ago, and Mohan’s mother .....2...... (be) lonely since then. She .....3...... (not see) her son since 2012. and he .....5...... (not write) to her for over six months. She .....5...... (make) up her mind to go to the States, but she .....6...... (not get) enough money yet for the fare. She .....7...... (save) only 20,000/- but the journey will cost more.
Answers:
(i) (1) were working, (2) were mending. (3) had, (4) was coming, (5) was running.
(ii) (1) eat, (2) throw. (3) keep.
(iii) (1) left, (2) went, (3) has been, (4) is.
(iv) (1) died, (2) has been. (3) has not seen, (4) has not written, (5) is making, (6) has not got, (7) has saved.
Reordering Sentences
Exercise 29.
Arrange the given words and phrases Into meaningful sentences:
1. capture/wait/to/the/we/image.
2. voice/with/my/trembIed/danxiety.
3. development/the/meaning/need/we/to/redefine/of.
4. experience/how/with/was/monkeys/yourt!
5. founded/his/in 1998/was/coIIege.
6. atlhouse/last/my/meeting/rememberly/do/herlycar?
7. car/lacking/forgot/completely/my.
8. ago/an/about/hour/left/they.
9. what/know/happened/has/ScciflalWafltslt
10. as/after/were/him/he/ran/the/devil
11. down/the wall/camela/with/crash.
12. gave away/the queen/her/money/all/died/before/she.
13. Vibha/write down/did/words/those/difflcult/?
14. Vandana/the film/self/all/stay/not/did
15. bad/children/avoid/should/company.
Answers:
1. We wait to capture the image.
2. My voice trembled with anxiety.
3. We need to redefine the meaning of development.
4. How was your experience with monkeys?
5. This college was founded in 1998.
6. Do you remember meeting her at my house last year?
7. I completely forgot locking my car.
8. They left about an hour ago.
9. Seema wants to know what has happened.
10. He ran as if the devil were after him.
11. The wall came down with a crash.
12. The queen gave away all her money before she died.
13. Did Vihha write down those difficult words?
14. Vandana did not stay to see all the film.
15. Children should avoid had company.
Dialogue Completion
Exercise 30.
Complete the sentences using the correct form of the verbs :
Atul ...... (1) you ever ....... (2) (hear) anything about Ruskin Bond ?
Vipul : He ....... (3) (be) a legendary author.
Atul : Where ........... (4) he ....... (5) (live) ?
Vipul : He ....... (6) (live) at Mussoorie.
Atul : How old ....... (7) (be) he ?
Vipul : He ....... (8) (turn) 76 in may 2010.
Atul : .....(9) (come) to know last week that he ..... (10) (offer) a role in a film.
Vipul : Oh yes, he was offered the role of an old monk in it. But he .......(11) (not accept) this offer.
Atul : Perhaps he always ....... (12) (want) to be a writer.
Vipul : And that happened. He ....... (13) (remain) so engrossed in his writings that he ....... (14) (not have) enough time to get married.
Answers:
1. Have.
2. heard
3. is.
4. does.
5. live
6. lives
7. is.
8. turned.
9. came.
10. was offered.
11. did not accept.
12. wanted.
13. remained
14. did not have.

Exercise 31.
Complete the sentences using the correct form of verbs :
Naman : Caste is a much ....... (1) (talk) about issue these days.
Aman : It ....... (2) (have) ever ....... (3) (be) an issue in India. Caste identities ..... (4) (forge) our minds.
Naman : More often than not caste ....... (5) (determine) our social status.
Aman : Of course, at times it ....... (6) (use) to exalt a person and at another time to degrade him.
Naman : Rightly ....... (7) (say), they ....... (8) (not admit) it but their conversation ...... (9) (pepper) with caste references.
Aman : Matrimonial ads ....... (10) (classify) castewise.
Naman : Even the new age media (11) ....... (fail) to break down caste barriers. A host of matrimonial websites cater exclusively to one caste or the other.
Aman : We have caste-based organizations too such as Agarwal Mahasabha, Kshatriya Sabha etc.
Naman : (12) ....... (do) that mean we Indians cannot do without caste-tag ?
Answers:
1. talked.
2. has.
3. been.
4. forge
5. determines
6. is used.
7. said
8. won’t admit.
9. is peppered.
10. are classified.
11. fails
12. Does.

Sentence Transformation
Exercise 32.
Transform the following sentences as directed using suitable form of verbs :
1. Tell me your residence. (Use : live)
2. He is too weak to run. (Use : cannot run)
3. No sooner did the teacher enter the class than all the students stood up. (Use : 'entered')
4. Hari is not as great as you. (Use : are)
5. She helped you. (Change into interrogative)
6. Nobody will deny it. (Use : admit)
7. Inspite of hard work, she failed. (Use : worked)
8. Besides making a promise, he kept it. (Use : made)
9. Tell me his birth place. (Use : was born)
10. You must obey your officers or you will be punished. (Use : to escape)
11. If you work hard, you will succeed. (Use : unless)
12. No one can put up with such an insult. (Chang into interrogative)
13. How can he do this ? (Change into assertive)
14. Hari left no plan untried. (Change into affirmative)
15. No sooner did he see the tiger than he fled. (Use : as soon as)
16. He is stronger than I. (Change into negative)
17. We expect good news. (Change into passive)
18. They made him king. (Change into passive)
19. I was too tired to go out. (Use : cannot)
20. I saw the Taj Mahal. (Change into negative)
Answer:
1. Tell me where you live.
2. He is so weak that he cannot run.
3. As soon as the teacher entered the class all the students stood up.
4. You are greater than Han.
5. Did she not help you?
6. Everybody will admit it.
7. Though she worked hard yet she failed.
8. He not only made a promise but kept it also.
9. Tell me where he was born.
10. You must obey your officers to escape punishment.
11. Unless you work hard, you will not succeed.
12. Who can put up with such an insult?
13. He cannot do this anyhow.
14. Han tried every plan.
15. As soon as he saw the tiger, he fled.
16. I am not so strong as he.
17. Good news is expected by us.
18. He was made king.
19. I was so tired that I cannot go out.
20. I did not fail to see the Taj Mahal.
