RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Important Questions Animal Kingdom
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which of the following developed for the first time in Annelids?
(a) Cephalization
(b) Development of a true coelom
(c) Metameric segmentation
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)

Question 2.
Consider the following characters:
I. Air bladder
II. Operculum
III. Viviparity
The characters present in bony fishes include:
(a) I, II and III
(b) I and III only
(c) I and II only
(d) II and III only
Answer:
(c) I and II only
Question 3.
Homeothermy is exhibited by:
(a) All amniotes
(b) Birds and Mammals
(c) All Dueterostomes
(d) Reptiles and Mammals
Answer:
(b) Birds and Mammals
Question 4.
Consider the following characteristics of Porifers:
(a) Collared cells called as choanocytes
(b) Canal system with pores (ostia) in body wall
(c) Mineral spicules
(d) High cellular mobility and totipotency
Answer:
(d) High cellular mobility and totipotency
Question 5.
Identify the incorrect statement:
(a) Medusae of Scyphozoans are called as jelly fishes.
(b) Ctenophores are the largest animals that move with the help of cilia.
(c) Flat worms that have a digestive cavity have an incomplete gut.
(d) Nematodes are covered with thick cuticle that does not moult.
Answer:
(d) Nematodes are covered with thick cuticle that does not moult.
Question 6.
What is the most important reason for the immense success of arthropods?
(a) Chitinous exoskeleton
(b) Uricotelic nature
(c) Compound eye
(d) Multipurpose appendages
Answer:
(d) Multipurpose appendages
Question 7.
What is not true for a generalized mollusc?
(a) Body segmented into head, visceral mass and foot.
(b) A rasping tongue like organ - radula present.
(c) Mantle cavity with gills
(d) Excretory structures - nephridia
Answer:
(a) Body segmented into head, visceral mass and foot.

Question 8.
How many of the characters given below are true for echinoderms?
I. An endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles
II. The adult echinoderms are radially symmetrica] but larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
III. They are triploblastic and coelomate animals.
IV. Digestive system is complete.
V. Water vascular system
VI. Sexual reproduction, internal fertilization and direct development.
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer:
(c) 5
Question 9.
Which of the following is not seen in hemichordates?
(a) A tripartite body organization
(b) Stomochord
(c) Rudimentary notochord
(d) Proboscis gland
Answer:
(c) Rudimentary notochord
Question 10.
Consider the following features:
I. Ampulla of Lorenzini
II. Operculum or gill cover
III. Ureotelism
IV. Viviparity
V. Swim bladder
VI. Lateral line system
The features that can be attributed to cartilaginous fishes are:
(a) I, III and IV only
(b) II, V and VI only
(c) I, II, III and IV
(d) All
Answer:
(a) I, III and IV only
Question 11.
Key features that appeared for the first time in amphibians do not include:
(a) Legs
(b) Nutritional deficiencies
(c) Lungs
(d) Pulmonary veins
Answer:
(b) Nutritional deficiencies
Question 12.
Consider the following characters:
I. Wish bone furculum
II. Pneumatic bones
III. Feathers
IV. Endothermy
V. Left aortic arch
VI. Four chambered heart
Which of these are unique to birds?
(a) I, II and III only
(b) I, II, III and IV only
(c) I, II, III, IV and V only
(d) All
Answer:
(a) I, II and III only
Question 13.
Identify the incorrectly matched pair
(a) Ornithorhynchus: Oviparous mammal
(b) Macropus: Marsupial mammal
(c) Balaeonptera: Largest land animal
(d) Pteropus: Flying mammal
Answer:
(c) Balaeonptera: Largest land animal
Question 14.
Reptiles were very successful on land while amphibians were not. What evolutionary development was primarily responsible for the success of reptiles on land?
(a) Scales over skin
(b) Thoracic breathing
(c) Amniotic egg
(d) Strong jaws
Answer:
(c) Amniotic egg

Question 15.
Which of the following is not a feature of Tunicates?
(a) Only the larvae have notochord
(b) Presence of endostyle
(c) Secretion of cellulose sac
(d) Larvae are voracious eaters
Answer:
(d) Larvae are voracious eaters
Question 16.
Which of the following developed for the first time in Annelids?
(a) Cephalization
(b) True coelom
(c) Metameric segmentation
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 17.
Consider the following sets of some animals. The set that consists of all animals belonging to the same phylum is:
(a) Pinctada, Aplysia, Chaetopleura
(b) Dentallium, Pila, Echinus
(c) Asterias, Antedon, Ascidia
(d) Adamsia, Gorgonia, Pleurobrachia
Answer:
(a) Pinctada, Aplysia, Chaetopleura
Question 18.
Homeothermy is exhibited by:
(a) All amniotes
(b) Birds and Mammals
(c) All Dueterostomes
(d) Reptiles and Mammals
Answer:
(b) Birds and Mammals
Question 19.
Which of the following is not an Echinoderm character?
(a) Exclusively marine
(b) Radial symmetry in adults
(c) Protostome embryonic development
(d) Water vascular system
Answer:
(c) Protostome embryonic development
Question 20.
Birds are not characterized by:
(a) Forelimbs modified into wings
(b) Fully ossified endoskeleton
(c) Skin dry without glands except for oil gland
(d) Oviparous and external fertilization
Answer:
(d) Oviparous and external fertilization
Question 21.
Echinoderms are not characterized by:
(a) An absence of excretory system
(b) Bisexual animals
(c) Usually external fertilization
(d) Indirect development with free swimming larva.
Answer:
(b) Bisexual animals
Question 22.
Operculum and an air bladder is present in:
(a) Clarias
(b) Pristis
(c) Trygon
(d) Carcohrodon
Answer:
(a) Clarias
Question 23.
Pteropus is a/an:
(a) Limbless amphibian
(b) Extinct reptile that evolved into mammals
(c) Bony fish that migrates from sea water to fresh water for breeding
(d) Mammal with flight
Answer:
(d) Mammal with flight
Question 24.
Which of the following is not an arthropod characteristic?
(a) Jointed appendages
(b) Non - segmented bodies
(c) Periodic moulting
(d) Articulated exoskeleton
Answer:
(b) Non - segmented bodies
Question 25.
Amniotes include all except:
(a) Amphibians
(b) Reptiles
(c) Birds
(d) Mammals
Answer:
(a) Amphibians
Question 26.
Which of the following represents order of 'Horse'?
(a) Equidae
(b) Perissodactyla
(c) Caballus
(d) Ferus
Answer:
(b) Perissodactyla
Question 27.
An important characteristic that hemichordates share with chordates is:
(a) absence of notochord
(b) ventral tubular nerve cord
(c) pharynx with gill slits
(d) pharynx without gill slits
Answer:
(c) pharynx with gill slits

Question 28.
Which among these is the correct combination of aquatic mammals?
(a) Seals, Dolphins, Sharks
(b) Dolphins, Seals, Trygon
(c) Whales, Dolphins, Seals
(d) Trygon, Whales, Seals
Answer:
(c) Whales, Dolphins, Seals
Question 29.
In case of poriferans, the spongocoel is lined with flagellated cells called
(a) ostia
(b) oscula
(c) choanocytes
(d) mesenchymal cells
Answer:
(c) choanocytes
Question 30.
Choose the correct statements:
(a) All mammals are viviparous
(b) All cyclostomes do not possess jaws and paired fins
(c) All reptiles have a three - chambered heart
(d) All Pisces have gills covered by an operculum
Answer:
(b) All cyclostomes do not possess jaws and paired fins
Question 31.
Which of the following characteristic features always holds true for the corresponding group of animals?
(a) Viviparous; Mammalia
(b) Possess a mouth with an upper and a lower jaw; Chordata
(c) 3 - chambered heart with one incompletely divided ventricle; Reptilia
(d) Cartilaginous - endoskeleton; Chondrichthyes
Answer:
(d) Cartilaginous - endoskeleton; Chondrichthyes
Question 32.
Which one of the following characteristics is not shared by birds and mammals?
(a) Breathing using lungs
(b) Viviparity
(c) Warm blooded nature
(d) Ossified endoskeleton
Answer:
(b) Viviparity
Question 33.
Which of the following features is not present in the phylum - Arthropoda?
(a) Metameric segmentation
(b) Parapodia
(c) Jointed appendages
(d) Chitinous exoskeleton
Answer:
(b) Parapodia
Question 34.
Select the taxon mentioned that represents both marine and freshwater species:
(a) Echinoderms
(b) Ctenophora
(c) Cephalochordata
(d) Cnidaria
Answer:
(d) Cnidaria
Question 35.
Which one of the following living organisms completely lacks a cell wall?
(a) Cyanobacteria
(b) Sea - fan (Gorgonia)
(c) Saccharomyces
(d) Blue - green algae
Answer:
(b) Sea - fan (Gorgonia)
Question 36.
Planaria possess high capacity of:
(a) metamorphosis
(b) regeneration
(c) alternation of generation
(d) bioluminescence
Answer:
(b) regeneration
Question 37.
A marine cartilaginous fish that can produce electric current is:
(a) Pristis
(b) Torpedo
(c) Trygon
(d) Scoliodon
Answer:
(b) Torpedo
Question 38.
Infection of Ascaris usually occurs by:
(a) drinking water containing egg of Ascaris
(b) eating imperfectly cooked port
(c) tse - tse fly
(d) mosquito bite
Answer:
(a) drinking water containing egg of Ascaris
Question 39.
What will you look for to identify the sex of the following?
(a) Male frog - a copulatory pad on the first digit of the hind limb
(b) Female Cockroach - anal cerci
(c) Male shark - claspers bone on pelvic fins
(d) Female Ascaris - sharply curved posterior end
Answser:
(c) Male shark - claspers bone on pelvic fins
Question 40.
Which one of the following animals is correctly matched with its particular named taxonomic category?
(a) Cuttlefish - Mollusca, a class
(b) Humans - Primata, the family
(c) Housefly - Musca, an order
(d) Tiger - tigris, the species
Answer:
(d) Tiger - tigris, the species

Question 41.
Which one of the following groups of animals is correctly matched with its one characteristic feature without even a single exception?
(a) Chordata - possess a mouth provided with an upper and a lower jaw
(b) Chondrichthyes - possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
(c) Mammalia - give birth to young ones
(d) Reptilia - possess 3 - chambered heart with one incompletely divided ventricle
Answer:
(b) Chondrichthyes - possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
Question 42.
One example of animals having a single opening to the outside that serves both as mouth as well as anus is:
(a) Octopus
(b) Asterias
(c) Ascidia
(d) Fasciola
Answer:
(d) Fasciola
Question 43.
Which one of the following statements about all the four of Spongilla, leech, dolphin and penguin is correct?
(a) Penguin is homoiothermic while the remaining three are poikilothermic
(b) Leech is a fresh water form while all others are marine
(c) Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three
(d) All are bilaterally symmetrical
Answer:
(c) Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three
Question 44.
Which one of the following kinds of animals are triploblastic?
(a) Flat worms
(b) Sponges
(c) Ctenophores
(d) Corals
Answer:
(a) Flat worms
Question 45.
Which one of the following statements about certain given animals is correct?
(a) Round worms (Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates
(b) Molluscs are acoelomates
(c) Insects are pseudocoelomates
(d) Flat worms (Platyhelminthes) are coelomates
Answer:
(a) Round worms (Aschelminthes) are pseudocoelomates
Question 46.
Which one of the following groups of animals is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic?
(a) Coelenterates (cnidarians)
(b) Aschelminthes (round worms)
(c) Ctenophores
(d) Sponges
Answer:
(b) Aschelminthes (round worms)
Question 47.
Which one of the following pairs of animal comprises 'jawless fishes'?
(a) Lampreys and eels
(b) Mackerals and rohu
(c) Lampreys and hag fishes
(d) Guppies and hag fishes
Answer:
(c) Lampreys and hag fishes
Question 48.
Peripatus is a connecting link between:
(a) Ctenophora and Platyhelminthes
(b) Mollusca and Echinodermata
(c) Annelida and Arthropoda
(d) Coelenterata and Porifera
Answer:
(c) Annelida and Arthropoda
Question 49.
Which one of the following in birds, indicates their reptilian ancestry?
(a) Scales on their hind limbs
(b) Four chambered heart
(c) Two special chambers crop and gizzard in their digestive tract
(d) Eggs with a calcareous shell
Answer:
(d) Eggs with a calcareous shell
Question 50.
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of phylum - Annelida?
(a) Closed circulatory system
(b) Segmentation
(c) Pseudocoelom
(d) Ventral nerve cord
Answer:
(c) Pseudocoelom

Question 51.
Which one of the the following phyla is correctly matched with its two general characteristics?
(a) Arthropoda - Body divided into head, thorax and abdomen and respiration by tracheae
(b) Chordata - Notochord at some stage and separate anal and urinary openings to the outside
(c) Echinodermata - Pentamerous radial symmetry and mostly internal fertilization
(d) Mollusca - Normally oviparous and development through a trochophore or veliger larva
Answer:
(a) Arthropoda - Body divided into head, thorax and abdomen and respiration by tracheae
Question 52.
Ascaris is characterised by:
(a) absence of true coelom but presence of metamerism
(b) presence of neither true coelom not metamerism
(c) presence of true coelom but absence of metamerism
(d) presence of true coelom and metamerism (metamerisation)
Answer:
(b) presence of neither true coelom not metamerism
Question 53.
Which one of the following groups of three animals each is correctly matched with their one characteristic morphological feature?
(a) Liver fluke, sea anemone, sea cucumber - Bilateral
(b) Earthworm, prawn, scorpion - Jointed appendages
(c) Scorpion, spider, cockroach - Ventral solid central nervous system
(d) Cockroach, locust, Taenia - Metameric segmentation
Answer:
(c) Scorpion, spider, cockroach - Ventral solid central nervous system
Question 54.
Which one of the following pairs is mismatched?
(a) Pila globosa - pearl
(b) Apis indica - honey
(c) Kenia lacca - lac
(d) Bombyx mori - silk
Answer:
(a) Pila globosa - pearl
Question 55.
What is common between parrot, platypus and kangaroo?
(a) Homeothermy
(b) Toothless jaws
(c) Functional post - anal tail
(d) Oviparity
Answer:
(a) Homeothermy
Question 56.
Which one of the following is a matching pair of a body feature and the animal possessing it?
(a) Post - anal tail - Octopus
(b) Ventral Central nervous system - Leech
(c) Pharyngeal gills slits absent in embryo - Chamaeleon
(d) Ventral heart - Scorpion
Answer:
(b) Ventral Central nervous system - Leech
Question 57.
Which of the following pairs are correctly matched?
A. Crocodile - 4 - chambered heart
B. Sea urchin - Parapodia
C. Obelia - Metagenesis
D. Lemur - Thecodont
(a) A, C and D
(b) B, C and D
(c) Only A and D
(d) Only A and B
Answer:
(a) A, C and D
Question 58.
What is true about Nereis, Scorpion, Cockroach and Silver fish?
(a) They all have jointed paired appendages
(b) They all possess dorsal heart
(c) None of them is aquatic
(d) They all belong to the same phylum
Answer:
(b) They all possess dorsal heart
Question 59.
What is common to whale, seal and shark?
(a) Seasonal migration
(b) Thick subcutaneous fat
(c) Convergent evolution
(d) Homeothermy
Answer:
(c) Convergent evolution
Question 60.
Which one of the following is not a living fossil?
(a) King crab
(b) Sphenodon
(c) Archaeopteryx
(d) Peripatus
Answer:
(c) Archaeopteryx
Question 61.
Which one of the following is a matching set of a phylum and its three examples?
(a) Cnidaria - Bonellia, Physalia, Aurelia
(b) Platyhelminthes - Planaria, Schistosoma, Enterobius
(c) Mollusca - Loligo, Teredo, Octopus
(d) Porifera - Spongilla, Euplectella, Pennatula
Answer:
(c) Mollusca - Loligo, Teredo, Octopus

Question 62.
Metameric segmentation is the characteristic of:
(a) Platyhelminthes and Arthropoda
(b) Echinodermata and Annelida
(c) Annelida and Arthropoda
(d) Mollusca and Chordata
Answer:
(c) Annelida and Arthropoda
Question 63.
Biradial symmetry and lack of cnidoblasts are the characteristics of:
(a) Starfish and sea anemone
(b) Ctenoplana and Beroe
(c) Aurelia and Paramoecium
(d) Hydra and starfish
Answer:
(b) Ctenoplana and Beroe
Question 64.
In which one of the following sets of animals do all the four give birth to young ones?
(a) Lion, bat, whale, ostrich
(b) Platypus, penguin, bat, hippopotamus
(c) Shrew, bat, cat, kiwi
(d) Kangaroo, hedgehog, dolphin, Loris
Answer:
(d) Kangaroo, hedgehog, dolphin, Loris
Question 65.
Two common characters found in centipede, cockroach and crab are:
(a) compound eyes and anal cerci
(b) jointed legs and chitinous exoskeleton
(c) green gland and tracheae
(d) book lungs and antennae
Answer:
(b) jointed legs and chitinous exoskeleton
Question 66.
A jawless fish, which lays eggs in fresh water and whose ammocoetes larvae after metamorphosis return to the ocean is
(a) Eptatretus
(b) Myxine
(c) Neomyxine
(d) Petromyzon
Answer:
(d) Petromyzon
Question 67.
Metagenesis refers to:
(a) the presence of different morphic forms
(b) alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
(c) occurance of a drastic change in form during post embryonic development
(d) the presence of a segmented body and parthenogenetic mode of reproduction
Answer:
(b) alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
Question 68.
Body having meshwork of cells, internal cavities lined with,food filtering flagellated cells and indirect development are the characteristics of phylum:
(a) Coelenterata
(b) Porifera
(c) Mollusca
(d) Protozoa
Answer:
(a) Coelenterata
Question 69.
Pick the odd pair out.
(a) Porifera: choanoflagellates
(b) Cnidaria: nematocysts
(c) Nematoda: pseudocoelom
(d) Mollusca: torsion
Answer:
(a) Porifera: choanoflagellates
Quesiton 70.
Chitin is a polysaccharide found in the exoskeleton of
(a) prawn
(b) insects
(c) crabs
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these

Question 71.
Which of these is not a coelenterate?
(a) Sea pen
(b) Sea fur
(c) Sea anemone
(d) Sea lily
Answer:
(d) Sea lily
Question 72.
Protonephridia are the excretory structures present in
(a) Planaria
(b) roundworm
(c) tapeworm
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Question 73.
Carapace is present can be observed in:
(a) Hemidactylus
(b) Testudo
(c) Naja
(d) Bufo
Answer:
(b) Testudo
Question 74.
Closed circulatory system is not found in
(a) octopus
(b) tunicates
(c) echinoderms
(d) squids
Answer:
(c) echinoderms
Question 75.
Polyp phase is absent in the life cycle of:
(a) Hydra
(b) Hormiphora
(c) Pennatula
(d) Physalia
Answer:
(b) Hormiphora
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why classification of animal is important?
Answer:
For identification and characterization.

Question 2.
What is the use of classification of animals?
Answer:
It helps in assigning a systematic position of newly found species.
Question 3.
What is body symmetry?
Answer:
It refers to the division of body into equal parts by lines or planes.
Question 4.
What is coelom?
Answer:
Cavity present between body wall and alimentary canal.
Question 5.
What is tissue level of organization?
Answer:
Number of cells arranged in complex performing same functions.
Question 6.
What organ level of organization?
Answer:
Group of tissue joined together to form an organ performing a particular function.
Question 7.
What is incomplete digestive system?
Answer:
Digestive system with single opening to the outside the body.
Question 8.
What is complete digestive system?
Answer:
Digestive system having two openings one mouth and another anus.
Question 9.
What is mesoglea?
Answer:
Undifferentiated layer present between ectoderm and endoderm.
Question 10.
What are coelomates?
Answer:
Animals possessing body cavity.
Question 11.
What are acoeloniates?
Answer:
Animals in which body cavity is absent.

Question 12.
What are germ layers?
Answer:
Embryonic layers from which tissues and organs are derived.
Question 13.
What are chordates?
Answer:
Animals having notochord.
Question 14.
Which group of animal is called sponges?
Answer:
Members of phylum porifera.
Question 15.
What is the function of canal system?
Answer:
Helps in gathering food, exchanges of gases and removes waste.
Question 16.
What is indirect development?
Answer:
Development involving larval stage.
Question 17.
What are nematocytes?
Answer:
Cells with long thread like tentacles.
Question 18.
Which animal phylum is called sea walnut or comb jellies?
Answer:
Ctenophora
Question 19.
Why members of platyhelminthes is commonly called flatworms.
Answer:
Body is dorso ventrally flattened.
Question 20.
In which platyhelminthes forms, hooks & suckers are present?
Answer:
In parasitic form.

Question 21.
What is the function of hooks and suckers?
Answer:
They help in absorption of nutrients form host and also attach to the surface.
Question 22.
What are flame cells?
Answer:
Specialized cells involved in osmoregulation and excretion.
Quesiton 23.
Why aschelminthes are named as round worms?
Answer:
Body is circular in cross section.
Question 24.
Which level of body organization is seen in aschelminthes?
Answer:
Organ system level of organization.
Question 25.
How excretory products are removed from the body of round worms?
Answer:
Through excretory pores of the excretory tube.
Question 26.
Metameric segmentation can be found for the first time in which animal phylum?
Answer:
Annelida.
Question 27.
What type of circulation is found in annelids?
Answer:
Closed circulation.

Question 28.
Write the scientific name of blood sucking leech.
Answer:
Hirudinaria.
Question 29.
Which is the largest phylum in the animal kingdom?
Answer:
Arthropoda.
Question 30.
What is the nature of exoskeleton that covers the body of an arthropod?
Answer:
Chitinous exoskeleton.
Question 31.
What is the meaning of the term arthropoda?
Answer:
Joined appendage.
Question 32.
Name the excretory structure of arthropods.
Answer:
Malpighian tubules.
Question 33.
What is the nature of body cover of molluscan?
Answer:
Calcareous shell.
Question 34
What is mantle?
Answer:
Soft and spongy layer of skin.
Question 35.
Where are the gills located in molluscan body?
Answer:
Gills are located in the mantle cavity.
Question 36.
Which is the most distinctive features of echinoderms?
Answer:
Presence of water vascular system.
Question 37.
What type of fertilization is seen in echinoderms?
Answer:
External fertilization.
Question 38.
What is the nature of development in echinodermates?
Answer:
Indirect development.

Question 39.
What is the function of mantle cavity?
Answer:
Mantle cavity help in respiration & excretion.
Question 40.
What is radula?
Answer:
An anatomical structure present in the mouth of molluscs for feeding.
Question 41.
What are oviparous animals?
Answer:
Animals which lay eggs.
Question 42.
What is the general body form of hemichordate?
Answer:
Worm like marine form.
Question 43.
Name the excretory structure of hemichordate.
Answer:
Proboscis gland.
Question 44.
What type of circulation is found in hemichordate?
Answer:
Open type of circulation.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
Write down the significance of symmetry in animals.
Answer:
Animals show various patterns in their morphology. Relationships between animals or groups of animals are best explained by their cooperative morphology and embryology. The gross external morphology of animals falls under a limited number of patterns (criteria).
- These include form of animals (symmetry),
- arrangement of body parts in segments (metamerism),
- formation of a head (cephalization), and progressive sequence of specialization of structure (levels or grades of organization).
Similary, the criteria of internal morphology are differences in formation of body cavity (coelom) and reproduction (embryology), etc.
Symmetry and its significance: Symmetry means an arrangement of body parts into geometrical designs. It refers to the division of body into equal parts by lines or planes.
- An animal is called symmetrical when a plane passing through its centre will divide into similar halves. When an animal cannot be divided into like parts by a plane, it is called asymmetrical e.g. sponge, some Protozoa (Amoeba:) and few others.
- Certain terms are often used when explaining symmetry.
- An axis is an imaginary line passing through the center of body, such as longitudinal axis and oral - aboral axis. Either end of an axis is termed a pole. Thus, each axis has two poles.
- A plane of symmetry is a straight line that divides into corresponding halves.
- Metazoa commonly display two types of symmetry, radial and bilateral. Two other types of symmetry are also recognized, spherical and biradial.
- Protozoa are not only asymmetrical but display all four types of symmetry in their diverse body forms.

Question 2.
Mention the phylum - Porifera affinities with Metazoa.
Answer:
(a) Resemblance with Metazoa
- Both are sedentary in habit.
- Both are diploblastic and acoelomates.
- Both reproduce asexually and form colonies.
- Both sponges and coelenterates show the presence of same nucleic acids and amino acids.
- Parenchymula larva of sponges resembles planula larva of coelenterates.
- Spongocoel in sponges opening out through osculum can be compared with gastrovascular cavity of coelenterates opening out through mouth.
(b) Differences with Metazoa
- In sponges, cells are less specialised and less independent than those of metazoa.
- Sponges do not have anterior end though osculum serves physiologically as controlling region.
- Primary openings are not present as osculum in sponges.
- Body surface is perforated by inhalent pores or ostia extend by water channels, a unique feature of sponges only.
- Tissue formation is restricted to the formation of epithelial lining on the surface. There are no organs as found in higher animals.
- Sponges lack true mouth. Osculum does not correspond with the mouth of coelenterates.
- Stinging cells are found in coelenterates are lacking in sponges.
- Nervous system is lacking in sponges.
Question 3.
Write about general characteristics of Arthropods.
Answer:
General characters of Arthropods:
- Arthropoda is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and metamerically segmented animals.
- Body can be divided into head, thorax and abdomen; head and thorax are often fused to form cephalothorax.
- Body is covered with a thick chitinous cuticle forming an exoskeleton.
- Body segments usually bear paired and jointed appendages.
- Coelom largely a blood - filled haemocoel.
- Muscles are mostly, striated, usually capable of rapid contraction.
- Digestive tract is complete. The mouth and anus lie at opposite ends of the body.
- Circulatory system is open with dorsal heart and arteries and blood sinuses.
- Respiration through by general body surface, by gills in aquatic forms, by tracheae and by book lungs.
- Nervous system has dorsal nerve ring.
- Excretory organs are Malpighian tubules (in insects) and green glands (in Crabs and prawn).
- Cilia are absent from all parts of the body.
- Sexes are generally separate.
- Fertilization is internal, oviparous and ovoviviparous.
- Parental care is well marked in many arthropods.
Question 4.
How the Urochordates resembles with Chordates.
Answer:
Urochordates resemble the chordates owing to the following features:
- Presence of dorsal tubular nerve cord.
- Presence of notochord.
- Well developed pharynx with gill - slits.
- Presence of endostyle on the ventral side of the pharynx.
- Presence of atrium around the pharynx.
- Presence of post - anal tail with tail fin.
Examples: Urochordata - Ascidia, Salpa, Doliolum.
Question 5.
Describe the general characters of Fishes.
Answer:
General characters of Fishes:
- Their body is divisible into head, trunk and tail. Neck is absent.
- It has a spindle shaped body. It is helpful in swimming.
- The body is covered by scales. They are placoid scales, cycloid scales ctenoid scales, ganoid scales etc.
- Respiration is by gills. Gills are the extensions of the pharynx. In the elasmobranch fishes, the gills will open separate. In bony fishes the gill slits are covered by operculum.
- On the head a pair of nostrils is present. Internal nostrils are visually absent. But Dipnoi i.e internal nostrils are present.
- On the head a pair of eyes is present.
- On the lateral sides of the body 'Lateral Line Sense' organs are present. They detect the pressure changes of water.
- The body shows paired and unpaired fins. Pelvic and pectoral fins are paired. Dorsal and ventral fins are unpaired. They maintain balance in water. They are useful for locomotion.
- The digestive system is well developed. In the intestine of shark scroll valve is present.
- The nervous system contains brain and spinal cord. Brain is small and it will' not occupy the entire cranial cavity.
- Ten pairs of cranial nerves are present.
- Kidneys are mesonephric.
- Urinary bladder is absent.

Question 6.
Write down difference between phylum - Annelida and Arthropoda.
Answer:
Difference between phylum - Annelida and Arthropoda:
|
Characteristics |
Phylum - Annelida |
Phylum - Arthropoda |
|
1. Appendages |
1. They are unjointed |
1. They are jointed |
|
2. Blood Circulation |
2. Blood flows inside |
2. Blood flows through |
|
3. Coelom |
3. True coelom is well developed |
3. True coelom is small. Instead blood filled cavity called haemocoel is present |
|
4. Chitinous exoskeleton |
4. It is absent |
4. It is present |
|
5. Excretory organs |
5. They are nephridia |
5. They are green glands and malphigian tubules. |
|
6. Sensory organs |
6. It is less developed |
6. It is well developed. |
|
7. Locomotary organs |
7. They have parapodia and setae |
7. They, have legs and wings |
Question 7.
What are Viviparous and Oviparous Animals?
Answer:
We have learnt that some animals give birth to young ones while some animals lay eggs which later develop into young ones. The animals which give birth to young ones are called viviparous animals. Those animals which lay eggs are called oviparous animals.
In some animals, the young ones may look very different from the adults. Recall the life cycle of the silkworm (egg → larva or caterpillar → pupa → adult) (egg → tadpole (larva) → adult). The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis.
Question 8.
Write down the characteristic features of Vertebrates.
Answer:
Characteristic features of Vertebrates are:
- These animals have a true vertebral column and internal skeleton, allowing a completely different distribution of muscle attachment points to be used for movement.
- The members of subphylum Vertebrata possess notochord during the embryonic period.
- The notochord is replaced by a cartilaginous or bony vertebral column in the adult.
- Thus all vertebrates are chordates but all chordates are not vertebrates.
- Besides the basic chordate characters, vertebrates have a ventral muscular heart with two, three or four chambers, kidneys for excretion and osmoregulation and paired appendages which may be fins or limbs.
- Vertebrates are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomic and segmented, with complex differentiation of body tissues and organs.
Short Answer Type Questions - II
Question 1.
What is symmetry in animals? Describe the types of symmetry.
Answer:
Symmetry: Symmetry means an arrangement of body parts into geometrical designs. It refers to the division of body into equal parts by lines or planes. An animal is called symmetrical when a plane passing through its center will divide into similar halves. When an animal cannot be divided into like parts by a plane, it is called asymmetrical e.g. sponge, some Protozoa (Amoeba) and few others.
1. Radial Symmetry: When any plane passing through the central axis of the body divides the organism into two identical halves, it is called radial symmetry. Coelenterates, ctenophores and echinoderms have this kind of body plan.
2. Bilateral Symmetry: In higher animals, the longitudinal axis of body runs from the anterior end (head) to the posterior end (tail). There is a single plane, the median longitudinal or sagittal plane, through which the body can be divided into two similar rights and left halves. This is called bilateral symmetry. Animals like annelids, arthropods, etc., where the body can be divided into identical left and right halves in only one plane, exhibit bilateral symmetry.
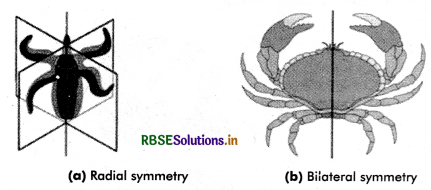
Question 2.
Write down the morphological features of molluscs after which the phylum has been named.
Answer:
Morphological features of Molluscs:
- Molluscs are essentially aquatic, mostly marine, few freshwater and some terrestrial animals.
- Body is soft, bilaterally symmetrical, unsegmented and without jointed appendages.
- Body can be divided into head, mantle, visceral mass and foot.
- Body is commonly protected by an exoskeletal calcareous shell of one or more pieces, secreted by the mantle.
- The head carries mouth, eyes and tentacles.
- The mantle is a thick, muscular fold of body wall extended over the viscera and thus enclosing a space, the mantle cavity.
- Visceral mass contains the visceral organs of the body in a compact form.
- The foot is ventral in position and is usually thick and muscular being variously modified for creeping, ploughing and seizing but is absent in oysters.
- Body cavity is haemocoel. The true coelom is generally limited to the pericardial cavity and the lumen of the gonads and nephridia.
- Digestive system is complete. Digestive glands are liver or hepatopancreas. Radula is mostly present.
- Circulatory system is closed type. Heart has one or two auricles and one ventricle.
- Respiration direct or by gills or lungs or both. The respiratory pigment is haemocyanin.
- Excretion is performed by nephridia or kidneys.
- Nervous system consists of paired cerebral, pleural, pedal and visceral ganglia joined by longitudinal and transverse connectives and nerves.
- Sexes are separating (dioecious) but some are hermaphrodite. Fertilization occurs externally as well as internally.
- Development is either direct or with metamorphosis through the trochophore stage called veliger larva.

Question 3.
How Urochordates ressembles with Cephalochordates?
Answer:
Urochordates resemble the Cephalochordates owing to the following features:
- Presence of notochord.
- Presence of dorsal tubular nerve cord.
- Presence of large pharynx with gill slits.
- Presence of atrium and atriopore.
- Presence of muscle band.
Thus, the urochordates show close relation with Cephalochordates.
Question 4.
How Urochordates differs from Chordates?
Answer:
Urochordates differ from other Chordates owing to the following characters:
- Presence of retrogressive metamorphosis.
- Absence of segmentation.
- Because of these characters zoologists included these animals in a separate sub - phylum Urochordata.
- During recent years many zoologists regarded the tunicates as primitive and ancestral forms of chordates as a whole.
Question 5.
Write down difference between class - Amphibia and Reptilia.
Answer:
Difference between class - Amphibia and Reptilia:
|
Characteristics |
class - Amphibia |
class - Reptilia |
|
1. Habitat |
1. Animals live on both land and fresh water |
1. They are mostly terrestrial. A few live in water but come on land to lay eggs. |
|
2. Skin |
2. Skin is smooth |
2. Skin bears scales. |
|
3. Respiratory organs |
3. They have lungs and gills in some. Skin is also used as respiratory organ |
3. Respiration is exclusively through lungs. |
|
4. Chambers of heart |
4. Three |
4. Heart is incompletely 4 chambered |
|
5. Reproduction |
5. Fertilization is external. Eggs have soft covering. |
5. Fertilization is internal. Eggs are hard shelled. |
Question 6.
What is hibernation?
Answer:
Hibernation is a state of inactivity and metabolic depression in few endotherms (warm blooded animals - bear, rodents) and ectotherms (many reptiles like snakes, turtles an amphibians like frogs. Snakes, lizards, toads, frogs, salamanders and most turtles will mostly hibernate during harsh winters. Hibernating animals usually retreat to a den, a burrow, or a hollow log for protection and shelter. During "true hibernation," the animal's body temperature drops, and its rate of breathing slows down. These hibernating animals are very difficult to awaken. Some warm - blooded animals such as bears, rodents etc. hibernate during extreme weather seasons and unfavorable conditions. During hibernation these animals live off of stored body fat and can drop their body temperatures significantly.

Question 7.
Write down the characteristic features of class - Reptilia.
Answer:
Characteristic features of class - Reptilia are:
- The class name refers to their creeping or crawling mode of locomotion (Latin, repere or reptum, to creep or crawl).
- They are mostly terrestrial animals and their body is covered by dry and cornified skin, epidermal scales or scutes. Snakes and lizards shed their scales as skin cast.
- They do not have external ear openings. Tympanum represents ear. Limbs, when present, are two pairs.
- Heart is usually three - chambered, but four - chambered in crocodiles.
- Reptiles are poikilotherms [cold - blooded animals].
- They lay eggs with tough coverings and do not need to lay their eggs in water, unlike amphibians.
- Sexes are separate.
- Fertilisation is internal.
- They are oviparous and development is direct.
- Examples: (Turtle), Tortoise, Chameleon (Tree lizard), Garden lizard, Crocodile, Alligator, Wall lizard, Poisonous snakes - Naja (Cobra), Bangarus (Krait), Vipera (Viper).
Question 8.
Compare between warm blooded and cold blooded animals.
Answer:
Comparision between warm blooded and cold blooded animals:
|
Warm blooded animals |
Cold blooded animals |
|
1. Warm Blooded animals are called endotherms or homoiothermous animals |
1. Cold Blooded animals are called ectotherms or poikilothermous animals. |
|
2. All mammals and birds with few exceptions are warm blooded. (Bats, Echidnas, Mole Rats etc. cannot regulate their body temperature.) |
2. All reptiles, insects, arachnids, amphibians and fish are cold blooded. |
|
3. They maintain a constant internal body temperature irrespective of external environment. (Can regulate their body temperature by generating their own heat when they are in a cooler environment, and by cooling themselves when they are in a hotter environment.) |
3. Their body temperature changes according to the external environment. (If a cold blooded animal is taken to the equator its body temperature increases and if taken to the poles its body temperature decreases.) |
|
4. They can survive in a wide of environments as they are able to regulate their body temperature. |
4. They cannot survive in a wide of environments. Tropical animals cannot survive in the polar region and vice versa. |
|
5. They require a lot of food for their survival. Most of the food consumed is utilized to maintain a constant body temperature. |
5. Most of the food consumed is converted into body mass. So they need less food compared to warm blooded animals. |
|
6. They are active in both warm and cold environments. |
6. They are active in warm environments and are very sluggish in cold environment. |
|
7. To stay cool, warm - blooded animals usually sweat. Animals like elephants use their ears to cool their body (large, thin ears which loose heat quickly). * Some warm - blooded animals, especially birds, migrate from colder to warmer regions in the winter. * Mammals have hair, fur and birds have feathers to help keep them warm. * Warm - blooded animals can also shiver to generate more heat when they get too cold. |
7. Cold - blooded animals often like to bask in the sun to warm up and increase their metabolism. * Some cold - blooded animals, such as bees or dragonflies, shiver to stay warm when in a cold environment. |
|
8. Constant body temperature provide a nice warm environment for viruses, bacteria and parasites to live in. |
8. Constantly changing body temperatures make life more difficult for the parasites. |
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What is classification? Describe the basics of classification in detail.
Answer:
Classification is the process of identifying and and grouping objects or ideas into predetermined categories. In data management, classification enables the separation and sorting of data according to set requirements for various business or personal objectives.
Inspite of differences in structure and form of different animals, there are fundamental features common to various individuals in relation to the arrangement of cells, body symmetry, nature of coelom, patterns of digestive, circulatory or reproductive systems. These features are used as the basis of animal classification and some of them are discussed here.

Question 2.
Describe the characteristic features of phylum - Arthropoda. Give examples.
Answer:
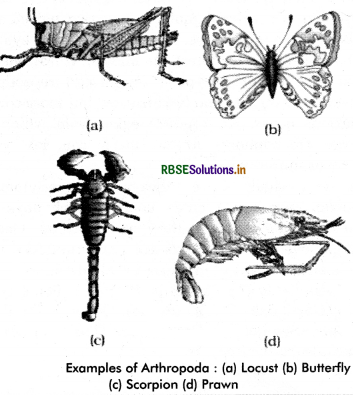
Phylum arthropoda (Gr., arthros = joint + podos = foot) is the largest phylum and most varied in the animal kingdom which includes insects. Over two - thirds of all named species on earth are arthropods (Figure 4.12). Von Siebold gave the name arthropoda. It includes well over one million described species and many million remain unstudied. Some of the more well - known arthropods include insects, crustaceans, spiders, scorpion and centipede as well as the fossil trilobites. Arthropods are mainly terrestrial but marine and freshwater species are also well known.
Arthropoda varies tremendously in their habitats, life histories, and dietary preferences. Arthropod bodies are divided into segments. However, a number of segments are sometimes fused to form integrated body parts known as tagmata. This process of fusion is called tagmosis. The head, thorax, and abdomen are examples of tagmata. Exoskeleton serves as protection and provides places for muscle attachment. Arthropods must molt because their exoskeletons don't grow with them.
However, in most species some appendages have been modified to form other structures, such as mouthparts, antennae, or reproductive organs. Arthropod appendages may be either biramous (branched) or uniramous (unbranched). In insects, the anterior portion of the heart is extended into a tube that is called an aorta which directs the blood forward as it goes out into the body cavity. Arthropods have a well-developed, mesodermal, solid nerve cord, ventral and well - developed sense organs. They range in size from microscopic plankton to life-forms that are a few meter long. Arthropods primary internal cavity is known as haemocoel, which accommodates their internal organs, and through which their haemolymph - analogue of blood - circulates; they have open circulatory systems.
Respiration occurs in various ways for e.g. some species have gills, while others employ tracheae, or book lungs. The tracheal respiratory system consists of external openings called spiracles that are linked to a system of branched tubules which allow respiratory gases to reach internal tissues.
Arthropods are characterized by a brain as well as a nerve ring around the area of the pharynx, in the oral cavity. A double nerve cord extends backwards along the ventral surface of the body, and each body segment is associated with its own ganglion, or mass of nerve cells.
Generally, the sexes are separate in phylum arthropoda. Fertilization usually occurs internally, and most species are egg laying. Development may be direct or indirect.While some species exhibit direct development, in which eggs hatch as miniature versions of adults, other species pass through an immature larval stage and undergo a dramatic metamorphosis before reaching adult form. Arthropods contribute directly (as food) as well as indirectly (crop pollination) to human food supply chain. Some specific species are known to spread severe disease to humans, livestock, and crops. Examples : Economically important insects - Apis (Honey bee), Bombyx (Silkworm), Laccifer (Lac insect) Vectors : Anopheles, Culex and Aedes (Mosquitoes) Gregarious pest: Locusta (Locust)
Living fossil: Limulus (King crab).
Question 3.
Describe the characteristic features of phylum - Mollusca. Give examples.
Answer:
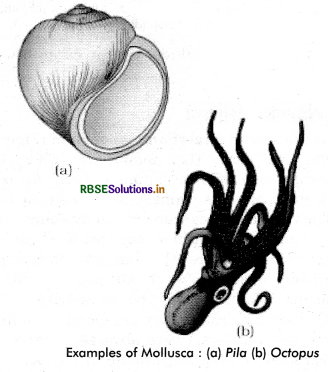
This is the second largest animal phylum (Figure 4.13). Phylum mollusca (L., molluscus, soft) includes soft-bodied invertebrate animals such as octopods, snails, slugs, mussels, clams, oysters, tusk-shells, squids etc. The term mollusca were coined by Johnston. It is a diverse and widespread group, with about 112,000 species. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Molluscs may be terrestrial or aquatic (freshwater or marine). They are found in all habitats - deserts, forests, lakes, rivers, abysses of sea, coral reefs, underground or even as parasite in the body of other animals.
They may be found clinging to the rocks, crawling, and swimming, burrowing or even digging. They have diversified feeding habit and can be herbivores, carnivores or omnivores. They vary in size from giant squids (nearly 2m long) to little snails, a millimeter long. The largest of the molluscan -classes is Gastropoda, which is represented by about 35,000 living and some 15,000 fossil species.
The three most universal features defining molluscs are - a mantle with a significant cavity used for breathing and excretion, the presence of a radula, and the structure of the nervous system. The "generalized" mollusc's feeding system consists of a rasping "tongue", the radula, and a complex digestive system. Although molluscs are coelomates, the coelom tends to be small, and the main body cavity is a haemocoel through which blood circulates; their circulatory systems are mainly open., The generalized mollusc has two paired nerve cords, or three in bivalves.
Most molluscs have eyes, and all have sensors to detect chemicals, vibrations, and touch. The simplest type of molluscan reproductive system relies on external fertilization, but more complex variations occur. All produce eggs, from which may emerge trochophore larvae, more complex veliger larvae, or miniature adults.
Molluscan shells have always been economically important, having served as money in early days. They have been used in jewellery and buttons. Octopus, scallops, oysters and squids are important food items. The scientific study of molluscs is called malacology. Examples : Pila (Apple snail), Pinctada (Pearl oyster), Sepia (Cuttlefish), Loligo (Squid), Octopus (Devil fish), Aplysia (Sea-hare), Dentalium (Tusk shell) and Chaetopleura (Chiton).
Question 4.
Describe the characteristic features of phylum - Echinodermata. Why they are considered important both biologically and geologically. Give examples.
Answer:
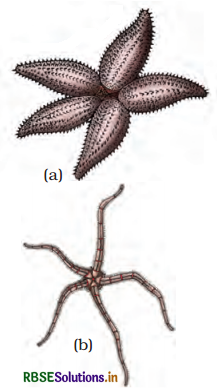
Phylum Echinodermata (Gr., echinos = spiny + derma = skin, ata = characterised by) includes exclusively marine invertebrates displaying pentamerous radial symmetry and an endoskeleton of calcareous plates and spines (Fig., 4.14). Jacob Klein gave the name echinodermata. This phylum is a collection of about 7,000 living species and constitute some of the most beautiful members of sea fauna, such as starfishes or sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumber, sea Tillies and sand dollars etc. The name 'starfish' is, however, misleading as these animals are not true fishes. A more suitable name suggested for them is ‘sea star’,
The echinoderms are important both biologically and geologically. Biologically, there are few other groupings so abundant in the biotic desert of the deep sea, as well as shallower oceans. Echinoderms generally have remarkable powers of regeneration of tissue, organs, limbs, and of asexual reproduction, and in some cases, complete regeneration from a single limb. Geologically, the value of echinoderms is in their ossified skeletons, which are major contributors to many limestone formations, and can provide valuable clues as to the geological environment.
Echinoderms possess a simple digestive system which varies according to diet. In many species, the large cardiac stomach can be everted and digest food outside the body. Gonads are present in each arm. In echinoderms such as sea stars, every arm bears two rows of tube feet on the oral side which help in attachment to the substratum. Echinoderms are efficient scavengers of decaying matter on the seafloor. They prey upon a variety of small organisms, thereby helping to regulate their numbers. In addition, echinoderms produce vast numbers of larvae that provide food for other planktonic organisms.
Examples: Asterias (Star fish). Echinus (Sea urchin), Antedon (Sea lily), Cucumaria (Sea cucumber) and Ophiura (Brittle star).

Question 5.
Describe salient distinguishing features of all phyla under animal kingdom.
Answer:
R.H. Whittaker organized organisms into five kingdoms. He classified organisms based on cell structure, mode and source of nutrition and body design. The five kingdoms proposed by Whittaker are Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae and Animalia. Let us learn about the animal kingdom, i.e., Kingdom Animalia.
Kingdom Animalia:
Kingdom Animalia constitutes all animals. Amongst the five kingdoms, the largest kingdom is the animal kingdom. Animals are multicellular eukaryotes. However, like plants, they do not possess chlorophyll or a cell wall. Therefore, members of the animal kingdom exhibit a heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Kingdom Animalia has been classified into ten different subphyla based on their body design or differentiation.
The different phylum of the animal kingdom are as follows:
- Porifera
- Coelenterata (Cnidaria)
- Platyhelminthes
- Nematoda
- Annelida
- Arthropoda
- Mollusca
- Echinodermata
- Hemichordata
- Chordata
