RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Net sales during the year is ₹ 3,00,000, Gross profit is 25% on sales. Find out cost of goods sold.
Answer:
Gross Profit = ₹ 300,000 \(\frac{25}{100}\) = ₹ 75,000
Cost of goods sold = Net Sales-Gross Profit
= 300,000 - ₹ 75,000
= ₹ 2,25,000

Question 2.
What is the difference between net profit and operating profit?
Answer:
Net Profit: It is end result of all expenses, losses and incomes and gains whereas operating profit is the result of all operating incomes and operating expenses.
Question 3.
Give the formula to find out cost of goods sold.
Answer:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + net purchases + direct and manufacturing expenses - closing stock
Question 4.
What do you mean by marshalling of assets and liabilities?
Answer:
Marshalling of assets and liabilities refers to the order to disclose assets and liabilities.
There are two types of orders:
(a) Order of liquidity
(b) Order of permanence

Question 5.
What are the financial statements?
Answer:
Financial statements are the end results of a business organisation which are prepared at the end of a financial year to depict profitability and financial position of an enterprise.
Question 6.
What does financial statements constitute?
Answer:
Financial statements constitute Income Statement and Balance Sheet.
Question 7.
What does income statement constitute?
Answer:
Income statement constitute trading account and profit and loss account.
Question 8.
State two objectives of preparing financial statements.
Answer:
(a) To ascertain profit and loss
(b) To ascertain financial position.
Question 9.
What types of expenses and incomes are transferred in the trading account?
Answer:
Trading account includes direct expenses and direct incomes.

Question 10.
What types of expenses and incomes are transferred in the profit and loss account?
Answer:
Expenses and incomes of indirect in nature are transferred to profit and loss account.
Question 11.
What types of accounts are shown on the assets side of the balance sheet?
Answer:
Real accounts and personal accounts.
Question 12.
What types of accounts are shown on the liabilities side of balance sheet?
Answer:
Personal accounts only.
Question 13.
What price is considered for the valuation of closing stock?
Answer:
Closing stock is considered as the lowest value of market price and cost price.
Question 14.
List two items of direct expenses.
Answer:
Carriage inward and freight inward.

Question 15.
List two items of indirect expenses.
Answer:
Office expenses, administration expenses, selling expenses and distribution expenses.
Question 16.
What is the formula for finding gross loss?
Answer:
Gross loss = Cost of goods sold - Net sales
Question 17.
State the formula to calculate cost of goods sold.
Answer:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + net purchases + direct expenses - closing stock.
Question 18.
What are the abnormal losses?
Answer:
Abnormal losses are beyond the control of human beings. They refer to natural calamities.
Question 19.
What are the normal losses?
Answer:
Normal loss is the past of cost of production which is bound to incur during the production process.

Question 20.
What is operating profit?
Answer:
Operating profit refers to position of such profit which is arrived at after adding indirect incomes and deducting indirect expenses respectively to the gross profit.
Question 21.
How would you arrive at net profit?
Answer:
Net profit = Gross profit + Indirect Incomes + Non-operating Incomes - Indirect expenses - Non-operating expenses.
Question 22.
How are the assets and liabilities shown in the order of permanence?
Answer:
Long term assets and liabilities are shown first and short term assets and liabilities are shown later.
Question 23.
How are assets and liabilities shown in the order of liquidity?
Answer:
Short term assets and liabilities are shown first and long term assets and liabilities are shown later.

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the objectives of preparing financial statements.
Answer:
(a) It helps to Determine the Financial Position: Financial statement like balance sheet shows financial position of the business on a particular date. If assets are more than outside liabilities, the business is considered to be sound financial position.
(b) Help to Determine Gross Profit and Gross Loss: Trading account is prepared to know the gross profit earned or gross loss incurred by the business during accounting period.
(c) Help to Determine Net Profit and Net Loss: Profit and loss account show a profit earned or net loss incurred by the business during accounting period.
Question 2.
Differentiate between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure.
Answer:
Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
|
Basis |
Capital expenditure |
Revenue expenditure |
|
1. Meaning |
It is an expenditure which is incurred to acquire fixed assets or to increase the production capacity of the business. |
It is an expenditure which is incurred for day to day operations of a business. |
|
2. Benefits
|
Benefit of such expenditures is availed in more than one year. |
Benefit of such expenditures is availed within one year.
|
|
3. Accounting treatment |
It is debited to respective asset account. |
It is debited to respective expense account. |
|
4. Examples
|
Cost of land, purchase, extension and construction of building. |
Salaries, wages, rent paid, salaries paid etc.
|
Question 3.
State the similarities between balance sheet and trial balance.
Answer:
(a) Both contains the balances of accounts.
(b) Both are statements to summarise the balances of accounts.
(c) Both are prepared at the end of the year.

Question 4.
Net sales during the year is ₹ 6,00,000. Gross profit is 25% on cost. Find out gross profit and cost of good sold. 25
Solution:
If sales is ₹ 600,000, Gross Profit will be 600,000 x \(\frac{25}{125}\)₹ 1,20,000
Cost of goods sold = Net Sales - Gross Profit
= ₹ 600,000 - ₹ 1,20,000 = ₹ 4,80,000
Question 5.
From the following figures calculate operating profit:
Net Profit -- ₹ 1,00,000
Rent received -- ₹ 10,000
Gain on sale of Machine -- ₹ 15,000
Interest on Loans -- ₹ 20,000
Donations -- ₹ 2,000
Solution:
Net Profit = Operating profit + Non-operating incomes - Non = operating expenses
Operating Profit = Net Profit + Non-operating expenses - Non-operating incomes
Non-operating Expenses = Interest on loans + Donations = 20,000 + 2,000 = 22,000
Non-operating Incomes = Rent received + Gain on sale of machine = 10,000 + 15,000 = 25,000
Operating Profit = 1,00,000 + 22,000 - 25,000 = 97,000.

Question 6.
Calculate Gross Profit
Total Purchase -- 680,000
Purchase Return -- 30,000
Direct Expenses -- 70,000
Carriage Outwork -- 15,000
3/4 of the goods are sold ₹ 600,000
Solution.
Cost of goods sold = Total Purchase - Purchase Return - Direct Expenses
= ₹ 6,80,000 - ₹ 30,000 + ₹ 70,000 = ₹ 7,20,000
Cost of 3/4 of the goods sold = ₹ 7,20,000 x \(\frac{3}{4}\)= ₹ 5,40,000
Gross Profit = Sales - Cost of goods sold
= ₹ 6,00,000 - ₹ 5,40,000
= ₹ 60,000
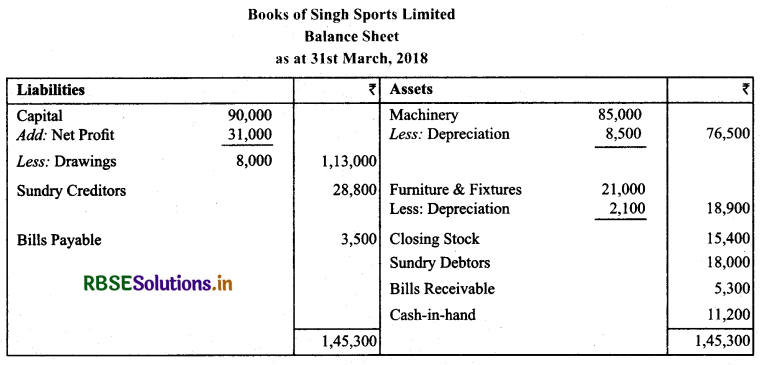
Question 7.
Prepare the Balance Sheet of Singh Sports Limited as on 31 st March, 2018 from the following information in the order of permanence.
Capital Account ₹ 90,000 & his drawings during the year ₹ 8,000. Net profit as per profit and loss account ₹ 31,000. Sundry Debtors ₹ 18,000, Sundry Creditors ₹ 28,800,
Bills Payable ₹ 3,500 & Bills Receivable ₹ 5,300,
Cash in hand ₹ 11,200,
Machine on April 1,2017 ₹ 85,000 and depreciation provided for the year ₹ 8,500
Furniture and Fixtures as on 1st April, 2017 ₹ 21,000 and Depreciation provided for the year ₹ 2,100,
Closing Stock ₹ 15,400.
Solution.

Higher Order Thinking Skills Questions
Question 1.
It is the book which is the collection of all accounts which helps prepare trial balance. Name this book.
Answer:
Ledger
Question 2.
When an account is said to have credit balance?
Answer:
An account is said to have credit balance when the credit side of an account is more than the debit side.
Question 3.
Why does sales account always have credit balance?
Answer:
Sales account always has credit balance as it represents income.
Question 4.
Ram says Trial balance is an account as debit balances are shown on the debit side and credit balances are shown on the
credit side of it whereas Shyam says it is a statement of all debit balances and credit balances. Who is correct?
Answer:
Shyam is correct as trial balance is prepare to check the arithmetical accuracy of accounts.
Question 5.
Final accounts cannot be prepared unless trial balance is prepared. Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
Answer:
Yes, in order to prepare final accounts, it is necessary to prepare trial balance to ensure the sum of debits is equal to sum of credits so that the agreement of balance sheet can be ensured.

Question 6.
Why sometimes closing stock is seen inside the trial balance and sometimes, it is seen outside the trial balance?
Answer:
When it is valued before the preparation of trial balance, it comes on the debit side of trial balance after closing of purchases account and when it is valued after the preparation of trial balance, it is shown outside the trial balance.
Question 7.
How would you calculate adjusted purchases?
Answer:
Adjusted purchases = Opening stock + Net Purchases - Closing Stock
Question 8.
How can grouping of assets and liabilities be done?
Answer:
Grouping of assets and liabilities can be done in two ways:
(a) Order of liquidity
(b) Order of permanence
Question 9.
What is grouping of assets and liabilities?
Answer:
Grouping of assets and liabilities refers to allocation of assets and liabilities of similar nature under a common heading

Question 10.
What is marshalling of assets and liabilities?
Answer:
Marshaling of assets and liabilities means arranging of assets and liabilities in specific order.
Question 11.
Why the words ‘To’ and ‘By’ are not written in the balance sheet?
Answer:
Such words are not written in balance sheet as balance sheet is a statement but not an account.
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
The objective of preparing financial statements is to find out the purpose of preparing final accounts is to ascertain:
(a) Profit or loss
(b) Profit and Loss & Financial Position
(c) To compare current results with the previous years results
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 2.
The profit and loss accounts represents ..............
(a) Net profit or loss
(b) Gross profit or loss
(c) Financial position
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Net profit or loss
Question 3.
Balance sheet represents ..............
(a) Financial position
(b) Profitability position
(c) Capital position
(d) Balances of all accounts
Answer:
(a) Financial position
Question 4.
Financial statements are prepared at the end ..............
(a) Of every month
(b) Of every quarter
(c) Every each half
(d) Every year
Answer:
(d) Every year

Question 5.
Income statement consist of ..............
(a) Trading account
(b) Profit and loss account
(c) Both (a) & (b)
(d) All incomes
Answer:
(c) Both (a) & (b)
Question 6.
Any transaction which enhances the revenue generation capacity is called ..............
(a) capital transaction
(b) revenue transaction
(c) deferred revenue transaction
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) deferred revenue transaction
Question 7.
Salaries and wages in the trial balance is shown ..............
(a) On the debit side of trading account
(b) On the debit side of profit and loss account
(c) On the assets side of balance sheet
(d) On the liabilities side of balance sheet
Answer:
(b) On the debit side of profit and loss account
Question 8.
Shikher introduced 5 lakhs into the business, it will be known as ..............
(a) capital receipt
(b) revenue receipt
(c) cash receipt
(d) loan receipt
Answer:
(a) capital receipt
Question 9.
The balance sheet is prepared with the help of ..............
1. All nominal accounts
2. All personal accounts
3. All real accounts
4. All representative personal accounts
Find the correct option:
(a) 1 & 2 only
(b) 2 & 3 only
(c) 2, 3 & 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 & 4
Answer:
(c) 2, 3 & 4 only

Question 10.
Good willis .............
1. An intangible asset
2. Fixed asset
3. Fictitious asset
4. Tangible asset
The correct option would be
(a) 1 & 2 only
(b) 1, 2 & 3 only
(c) 2, 3, & 4 only
(d) 1,2, 3 & 4
Answer:
(a) 1 & 2 only
Question 11.
The purpose to acquire fixed assets is .............
(a) To produce goods for resale
(b) Resale at higher price in the future
(c) To mortgage to obtain loan
(d) Converted into cash with in a period of I accounting year
Answer:
(a) To produce goods for resale

Question 12.
Rent received is a ..............
(a) Revenue receipt
(b) Capital receipt
(c) Cash receipt
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Revenue receipt
Question 13.
If closing stock appears inside the trial balance, it will be shown .............
(a) On the credit side of trading account
(b) On the credit side of trading account and on the assets side
(c) On the assets side
(d) Nowhere in the balance sheet
Answer:
(c) On the assets side
Question 14.
What would be the gross profit if gross profit is calculated @25 % on sales and cost of the goods sold is ₹ 1,20,000?
(a) 30,000
(b) 60,000
(c) 40,000
(d) 1,50,000
Answer:
(b) 60,000

Question 15.
Income tax paid by the proprietor is shown .............
(a) On the debit side of trading account
(b) On the debit side of profit and loss account
(c) As deduction from the capital in the balance sheet
(d) On the assets side of balance sheet
Answer:
(c) As deduction from the capital in the balance sheet
