RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
The northern portion of the north-south Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways is-
(a) Srinagar
(b) Mumbai
(c) Chennai
(d) Kolkata
Answer:
(a) Srinagar
Question 2.
Another name of National Highways No.1 is-
(a) Delhi-Jaipur National Highway
(b) Sher Shah Suri National Highway
(c) Jaipur-Mumbai National Highway
(d) Mahatma Gandhi National Highway
Answer:
(b) Sher Shah Suri National Highway
Question 3.
The Indian Railways first started between these two stations-
(a) Mumbai to Kolkata
(b) Mumbai to Thane
(c) Mumbai to Chennai
(d) Mumbai to Surat
Answer:
(b) Mumbai to Thane
Question 4.
After Independence, the sea port developed in India is-
(a) Kandla
(b) New Mangalore
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Mumbai
Answer:
(a) Kandla

Question 5.
Name the road which links a state capital with different district headquarters.
(a) National Highways
(b) State Highways
(c) District Highways
(d) Border roads
Answer:
(b) State Highways
Question 6.
Pipeline transport falls into which of the following classes ?
(a) Air transport
(b) Water transport
(c) Land transport
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Land transport
Question 7.
When was Border Roads Organisation formed ?
(a) 1950
(b) 1952
(c) 1956
(d) 1960
Answer:
(d) 1960
Question 8.
Which is the cheapest means of transportation ?
(a) Road transport
(b) water transport
(c) Air transport
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) water transport

Question 9.
Which is the oldest artificial port of India ?
(a) Haldia port
(b) Mumbai port
(c) Chennai port
(d) Vishakhapatnam port
Answer:
(c) Chennai port
Question 10.
To facilitate quick delivery of mails, how many mail channels have been introuced recently ?
(a)Three
(b) Four
(c) Five
(d) Six
Answer:
(d) Six
Fill in the Blanks
1. Transport, communication and trade are ................. to each other.
2. Golden Quadrilateral highway project are being implemented by the ........... of India (NHAI).
3. Kandla port is a ............... port.
4. The air transport was nationalised in ................
5. The .............. of a country is the difference between its export and import.
Answer:
1. complementary
2. National Highway Authority
3. tidal
4. 1953
5. balance of trade.

Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In how many classes are the roads classified in India ?
Answer:
In six classes.
Question 2.
Classify landways.
Answer:
- Roadways
- Railways
- Pipelines.
Question 3.
National Highways No. 6 which connects Delhi to Kolkata and Chennai to Mumbai and Delhi, falls in which type of project?
Answer:
Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways.
Question 4.
To which places the Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways connect ?
Answer:
It connects in Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata and Delhi.

Question 5.
Which national highways is found in between Delhi and Amritsar ?
Answer:
Sher Shah Suri Marg (National Highway No. 1).
Question 6.
Which is the highest road in India ?
Answer:
The road connecting Manali and Leh.
Question 7.
What is trade ?
Answer:
It is an act of exchange of goods and services between two parties such as people, states and countries.
Question 8.
After Independence, which sea port was made to cover the loss of Karachi port ?
Answer:
Kandla sea port.
Question 9.
Which type of transport network is a new arrival in the transportation map of India?
Answer:
Pipeline transport.

Question 10.
Who are traders ?
Answer:
They are known traders who provide the products to the consumers by transportation.
Question 11.
What is transport?
Answer:
Transport is an act of carrying goods and passengers from one place to another.
Question 12.
What are the main objectives of The Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways?
Answer:
The major objective of Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India.
Question 13.
What is the meaning of Pradhan Mantri Gramin Sarak Yojana ?
Answer:
Under this scheme, special provisions are made so that every village in the country is linked to a major town in the country by an all season motorable road.
Question 14.
Which is the last station of the corridor of north to south and east to west ?
Answer:
Srinagar to Kanyakumari - north to south.
Porbandar to Silchar - cast to west.

Question 15.
Name the stations of north, east, west and south of Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways.
Answer:
North - Delhi
East - Kolkata
South - Chennai
West - Mumbai
Question 16.
Name four important international airports in India.
Answer:
- Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose, Kolkata,
- Chhatrapati Shivaji, Mumabi,
- Indira Gandhi, Delhi,
- Minambakkam, Chennai.
Question 17.
Which gas pipeline is the longest gas pipeline in India?
Answer:
Hazira-Vijaypur-Jagdishpur
Question 18.
When was the border roads of India established and for which purpose ?
Answer:
Border Roads Organisation was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the northern and North-eastern border areas.
Question 19.
Write the 3 names of National Waterways of India.
Answer:
- The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia - N.W. No. 1
- The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri - N.W. No. 2
- The West Coast Canal in Kerala - N.W. No. 3
Question 20.
What is the main aim of trade ?
Answer:
The main aim of trade is the exchange of goods and services among people, states and countries.

Question 21.
What is the benefit of tourism ? Write any two.
Answer:
- Promotes national integration
- Provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
Question 22.
Write the important means of mass communication.
Answer:
Television, radio, press, films are the major means of mass communication.
Question 23.
What is considered as the economic barometer of a country ?
Answer:
Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. So it is considered the economic barometer of a country.
Question 24.
What is the meaning of favourable balance of trade ?
Answer:
It is a situation in which the value of exports is more than import.
Question 25.
Which are the viable Indian waterways where navigation is possible ?
Answer:
Ganga, Brahmaputra, Godavari, Krishna, Mahanadi, Narmada, Tapi.

Question 26.
Which is the largest public sector undertaking in the country ?
Answer:
The Indian Railways.
Question 27.
Why is the railway network well established in the northern plains ?
Answer:
(a) Vast level lands, (b) High population density, (c) Rich agricultural resources, (d) High amount of resources.
Question 28.
Write the names of one natural port and one artificial port.
Answer:
- Natural port - Mumbai
- Artificial port - Chennai
Question 29.
Name an inland riverine port of India.
Answer:
Kolkata tidal port.

Short Answer Type Questions (Type-I)
Question 1.
Match the following :
|
Metropolitan city |
Airport |
|
I. Delhi |
(A) Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose |
|
II. Mumbai |
(B) Meenam Bakkam |
|
III. Kolkata |
(C) Indira Gandhi International |
|
IV. Chennai |
(D) Chhatrapati Shivaji |
Answer:
|
Metropolitan city |
Airport |
|
I. Delhi |
(C) Indira Gandhi International |
|
II. Mumbai |
(D) Chhatrapati Shivaji |
|
III. Kolkata |
(A) Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose |
|
IV. Chennai |
(B) Meenam Bakkam |
Question 2.
Transport, communication and trade are complimentary to each other - explain.
Answer:
Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport. With the development in science and technology, the area of influence of trade and transport has expanded far and wide. Transport has been availed to achieve this with the help of equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport communication and trade are complimentary to each other.

Question 3.
Write the significance of radio as the form of mass communication in India.
Answer:
Radio:
- It is the cheapest and most effective means of communication.
- Besides entertainment, it also provides information and promotes social education.
Question 4.
Write the significance of television as the form of mass communication in India.
Answer:
Television:
- It is one of the largest and essential network in India.
- It provides entertainment and keeps the viewers well informed about the world.
Question 5.
Write any four problems related to road transportation in India.
Answer:
- The national highways are too inadequate
- Inadequate road networks keeping in view the volume and traffic and passengers.
- The roads are highly congested in cities.
- Most of the highways lack side amenities like telephone booths, emergency health services, police station etc.
Question 6.
Make a chart showing different types of means of transport.
Answer:
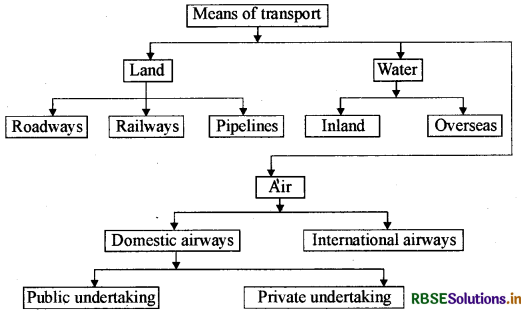
Question 7.
What are national highways ?
Answer:
The main roads which are constructed and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (C.P.W.D.) are known as national highways. These roads connect the state capitals, big cities and important ports.

Question 8.
Write importance of national highways ?
Answer:
Importance:
- The national highways maintain the availability of essential products. The state to state trade is possible because of the national highways.
- All the essential products like the raw materials, finished products, vegetables, food grains etc. are transported through these roads.
Question 9.
What are state highways ? Name the agency responsible for their construction and maintenance.
Answer:
Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are klown as state highways.
These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (S.P.W.D.) in the states and union territories.
Question 10.
Write short note on border roads in India.
Answer:
- The Border Roads Organization, a government of India undertaking constructs and maintain roads in the border areas of the country.
- This organisation was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the northern and north-eastern border areas.
- These roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain.
- These roads have helped in the economic development of these areas.
Question 11.
Write the main disadvantages of Indian Railways.
Answer:
- Many passengers travel without tickets.
- Thefts and damaging of railway properties have not yet stopped completely.
- People stop the trains, pull the chain unnecessarily and these cause heavy damage to the railways.
- Railway transport is unsuitable and uneconomical for short distance and small traffic of goods.
- Another disadvantage of railway transport is its inflexibility. Its routes and timings cannot be adjusted to individual requirements.

Question 12.
Write the significance of waterways in India.
Answer:
- It is the cheapest means of transport.
- It is most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
- It is fuel efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
- More than 95% of the country's trade volume is moved by the sea.
- The maintenance cost of waterways is also negligible.
- With the development of the National Waterways, it has become the main source of transportation for the national trade.
Question 13.
Write a short note on Kandla sea port.
Answer:
Kandla in Kutchh was the first port developed after independence to ease the volume of trade on the Mumbai port, in the wake of loss of Karachi port to Pakistan after the partition. Kandla is a tidal port. It caters to the convenient handling of the exports and imports of highly productive granary and industrial belts stretching across the states of J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat.
Question 14.
Write a short note on Kolkata port.
Answer:
Kolkata port is an inland riverine port.
This port serves a very large and rich hinterland of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.
Being a tidal port, it requires constant dredging of Hooghly.
Haldia port was developed as a subsidiary port, in order to receive growing pressure on the Kolkata port.
Question 15.
Write the importance of airways in India.
Answer:
- The air travel is the fastest, m st comfortable and prestigious mode of transport in India.
- It can cover very difficult terrains like high mountains, deserts, dense forests and also long oceanic stretches with great ease.
- The airways also helps in increasing the trade specially that of perishable products.
- Air travel has made access easier.

Question 16.
Write the special features of telecommunications in India.
Answer:
- India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia.
- Excluding urban places, more than two third of the villages in India have already been covered with Subscriber Trunk Dialing (S.T.D) facility.
- In order to strengthen the flow of information from the grass route to the higher level, the government has made special provisions to extend 24 hours STD facility to every village in the country.
- There is a uniform rate of STD facility all over India.
Question 17.
Why is international trade considered as the economic barometer of the country?
Answer:
International trade is considered as the economic barometer of the country because:
- No country can survive without international trade because resources are space bound.
- It is through international trade that we earn much of our foreign exchange which is required for importing many essential goods.
- Foreign trade helps in transfer of technology.
- Foreign trade leads to cultural exchange.
Question 18.
What is balance of trade ? When is this favourable and when is this unfavo-urable?
Answer:
Export and import are the components of trade.
The balance of trade of a country is the difference between its export and import.
- When the value of export exceeds the value of imports, it is called a favourable balance of trade.
- If the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, it is termed as unfavourable balance of trade.
Question 19.
Why do the foreign tourists like to visit India?
Answer:
Foreign tourists visit India for (1) heritage tourism, (2) eco-tourism, (3) adventure tourism, (4) cultural tourism, (5) medical tourism and (6) business tourism.

Short Answer Type Questions (Type-II)
Question 1.
Mention the major communication network of government of India and write a short note on their spread and density.
Answer:
Communication: Personal communication and mass communication including television, radio, press, films, etc. are the major means of communication in India. The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communicaitons.
India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia: Excluding urban places more than two thirds of the villages in India have already been covered with Subscriber Trunk Dialling (STD) telephone facility.
Mass communication provides entertainment and creates awareness among people, about various national programmes and policies. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and films.
India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually. Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects. India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films; video feature films and video short films.
Question 2.
What are the advantages of roads over the railways?
Answer:
- Roadways require less investment as compared to the railways.
- These can be built at higher altitudes and at any place.
- Maintenance cost is also low.
- Road transportation is easy and is within the reach of the common man. It is available for 24 hours.
- Road transportation provides door to door services.
Question 3.
Write a short note on International Trade.
Or
What is an International Trade? What is the role of international trade in development of a country?
Answer:
The trade between two countries is called international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes. Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. So, it is considered as the economic barometer of the country.
Role of international trade in development of a country:
- No country can survive without international trade because resources are space bound.
- It is through international trade that we earn much of our foreign exchange which is required for importing many essential goods.
- Foreign trade helps in transfer of technology
- Foreign trade leads to cultural exchange.

Question 4.
What are the factors of distribution pattern of railway network in India ?
Answer:
The distribution pattern of the railway network in the country has been largely influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors.
Physiographic factors: The northern plains with their vast lands, high population density and rich agricultural resources provided the most favourable condition for their growth.
A large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide beds posed some obstrucles.
Economic factors: The Himalayan mountainous regions are too unfavorable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
Question 5.
What is the importance of means of communication and transport in the dustrial development ?
Answer:
Radio, television, telephone, e-mail, telegraph etc. are the main means of communication, whereas railways, airways, buses, trucks, cars etc. are the main means of transportation.
- Transportation is the lifeline of a country. This connects one part of the country with another part and helps in providing essential products to all places and people.
- These help the industries to get raw material and its finished products are transported by railways and roadways. Agriculture also depends greatly on transportation.
- Transport network makes the coming and going of workers, labourers and administrators possible.
- Means of communication help the traders to have links with other traders and means of transport provide essential products.
- Means of communication act like nervous system in the human body. We can know what is happening in other parts of nation and world only through this media.
Question 6.
Write the main features of international trade of India.
Answer:
Main features of international trade of India are as follows :
- India's 95% of international trade is done by the sea routes.
- India has trade relations with all the major trading blocks and all geographical regions of the world.
- The commodities exported from India to other countries include gems and jewellery, chemicals and related products, agriculture and alltied products, etc.
- The commodities imported to India include petroleum crude and products, gems and jewellery, chemicals and related products, base metals, electronic items, machinery, agriculture and allied products.
- India has emerged as a software giant at the international level and it is earning large foreign exchange through the export of information technology.

Question 7.
Write a short note on the importance of Tourism in International Trade.
Or
Describe the importance of Tourism industry in India.
Answer:
There is a very important place of tourism industry in India's international trade :
- Tourism is an important source of foreign exchange for India.
- 57.8 lakh foreign tourists visited India in 2010 and contributed ₹ 64,889 crore of foreign exchange.
- More than 150 lakh people are directly engaged in the tourism industry in India.
- Tourism provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
- It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage.
- Foreign tourists visit India for heritage tourism, eco-tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism.
Question 8.
Write the classification of means of transportation.
Answer:
There are three types of means of transportation :
(i) Landways-
- Roadways-car, truck,
- Railways.
- Pipelines.
(ii) Waterways-
- Inland,
- Overseas.
(iii) Airways-
- Domestic (public undertaking, private airlines)
- International
Question 9.
Describe the problems of road network and roads in India.
Answer:
Road network in India India has one of the largest road networks in the world, aggregating to about 56 lakh km.
Problems of roadways in India:
- The road network is inadequate in India compared to demand and volume of traffic.
- The conditions of most of the roads are very poor, these become muddy during the rainy season.
- They are highly congested in cities.
- Most of the highways lack side amenities like telephone booths, emergency health services, police station etc.
- Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow.

Question 10.
Write a note on air transport facilities in India?
Answer:
The air travel is the fastest, most comfortable and prestigious mode of transport in India.
The air transport was nationalized in 1953.
Air India provides international air services. Pawan Hans Helicopters Ltd. provides helicopter services to Oil and Natural Gas Commission in its offshore operations, to inaccessible areas and difficult terrace like the north eastern states and the interior parts of J&K, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
In India air travel is not within the reach of the common people. It is only in the north-eastern states that special provisions are made to extend the services to the common people.
Question 11.
Write a note on postal network in India.
Answer:
The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications. Cards and envelopes are considered first class mails and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air. The second class mail includes book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals. They are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport. To facilitate quick delivery of mails in , large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently. They are called Rajdhani channel, Metro channel, Green channel, Business channel, Bulk channel, Periodical channel.
Question 12.
What are the roles of newspapers, magazines and films as means of mass communication in India?
Answer:
As a mode of mass communication, newspapers, magazines and films create awareness among people about various national programmes and policies.
India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually. They are of different types depending upon their periodicity. Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects. The largest number of newspapers published in the country are in Hindi, followed by English and Urdu.
India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films, video feature films, video short films. The Central Board of Film Certification is the authority for certifying both Indian and foreign films.

Question 13.
Write the importance of pipelines in transportation.
Answer:
- Transportation through pipelines rules ouť delay and transportation losses. Many fertilizer plants and thermal stations are benefitting by the supply of gas through pipelines.
- It maintains a continuous supply of gas and oil.
- The pipelines can be laid through difficult terrains as well as under the sea.
- The initial cost of laying pipelines is high, but the running cost is very low.
- The far inland locations of important refineries like Barauni, Mathura, Panipat etc. could be thought of only because of the pipelines.
Question 14.
Distinguish between transport and communication.
Answer:
|
Transport |
Communication |
|
1. Transport is a system in which passengers and goods are carried from one place to another. |
1. Communications refers to all those means and methods by which views, information, commercial agreements etc. are exchanged. |
|
2. The transport system is considered as the basic artery of economic development. |
2. Communication leads to economic as well as social development of the society. |
|
3. There are usually three means of transportation- land, water, air. |
3. Postal services, telegrams, telephones, mobiles etc. are the main means of communication. |
|
4. Railways, trucks, buses, cars and aeroplanes are the main sources of transportation. |
4. There are two types of communication- personal (letters) and mass communication (radio). |
Question 15.
What is trade ? Classify it.
Answer:
Trade- The exchange of goods and services among people, states and countries is referred as trade. The market is the place where such exchanges take place.
Types- There are three types of trade :
(i) Local trade Local trade is carried in cities, towns and villages.
(ii) State level trade- It is carried between two or more states.
(iii) International trade- The trade between two countries is called international trade. It may take place through sea, air or land routes. Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity. So it is considered the economic barometer of a country.

Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Classify and discuss Indian roads according to their capacity.
Answer:
In India, roads are classified into the following six classes according to their capacity.
(i) Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways: The government has launched a major road development project linking DelhiKolkata-Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi by a 6 lane superhighway. The north-south corridors linking Srinagar (J&K),and Kanyakumari (T.N.) and east-west corridor connecting Silchar (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat) are part of this project. The major objective of Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways is to reduce the time and distance between the megacities of India. These highway projects are being implemented by the National Highways Authority of India (N.H.A.I).
(ii) National Highways: The main roads which are constructed and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (C.P.W.D.) are known as national highways. These roads connect the state capitals, big cities and important ports. The historical Sher Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No.1 between Delhi and Amritsar.
(iii) State highways: Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as state highways. These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (S.P.W.D.) in the states and union territories.
(iv) District roads: These roads connect the district headquarters with other places of the district. These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
(v) Border roads: The Border Roads Organization, a government of India undertaking constructs and maintain roads in the border areas of the country. This organisation was established in 1960 for the development of the roads of strategic importance in the northern and northeastern border areas. These roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain. These roads have helped in the economic development of these areas.
(vi) Other roads: Rural roads which link rural areas with villages and towns are classified under this category. These roads receive special importance under the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Sarak Yojana. Under this scheme, special provisions are made so that every village in the country is linked to a major town by an all season motorable road.
Question 2.
Explain about the development of railways in India.
Answer:
(a) Indian Railways as a mode of transportation: Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India. Railways also make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, site seeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over long distances. The Indian Railway network runs on multiple gauge operations extending over 68,442 km. In this Broad Gauge is 63,491 km, metre gauge is 3200 km and narrow gauge is 1751 km.
(b) Role of railways in the development of agriculture, industries and economical condition of India: Indian Railways play a vital role in the development of agriculture, industries and economical condition of India.
(c) Factors of distribution pattern of the railway network: The distribution pattern of the railway network in the country has been largely influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors. The northern plains with their vast lands, high population density and rich agricultural resources provide the most favourable condition for their growth. A large number of rivers requiring construction of bridges across their wide beds pose some obstacles. The Himalayan mountainous regions are too unfavorable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities. It was difficult to lay the railway tracks on the sandy plains of western Rajasthan, swarms of Gujarat, forested tracks of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Jharkhand. The continuous stretch of Sahyadri could only be crossed through gaps or passes (ghats).
(d) Challenges: Today, the railways has become more important in our national economy than all other modes of transports put together. Indian Railways suffer from certain problems as well--many passengers travel without tickets. Thefts and damaging of railway properties not yet stopped completely. People stop the trains, pull the chain unnecessarily and these cause heavy damage to the railways.
In recent times, the development of the konkan railway along the west coast has facilitated the movement of passengers and goods in this most important economic region of India. It has also faced a number of problem such as sinking of track in some stretches and landslides.

Question 3.
Write a geographical note on pipeline transport in India.
Answer:
Pipeline transport network is a new arrival on the transportation map of India. In the past, these were used to transport water to cities and industries. Now, these are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power plants. Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into slurry. The far inland locations of important refineries like Barauni, Mathura, Panipat etc. could be thought of only because of the pipelines. The initial cost of laying pipelines is high, but the running cost is very low.
There are three important networks of pipeline transportation in the country.
- From oil fields in upper Assam to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh), via Guwahati, Barauni and Prayagraj. It has branches from Barauni to Haldia, via Rajbandh, Rajbandh to Maurigram and Guwahati to Siliguri.
- From Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in Punjab, 'via Viragram, Mathura, Delhi and Sonipat. It has branches to connect Koyali (near Vadodara, Gujarat), Chakshu and other places.
- Gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat connects Jagdishpur in Uttar Pradesh, via Vijaipur in Madhya Pradesh. It has branches to Kota in Rajasthan, Shahjahanpur, Babrala and other places in Uttar Pradesh.
Question 4.
Discuss in detail the waterways and seaports in India.
Answer:
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods. It is a fuel efficient and environment friendly mode of transport.
Waterways, as a cheapest mode: India has inland navigation waterways of 14500 km in length. Out of this only 5685 km are navigable by mechanized boats. The following waterways have been declared as the national waterways by the government.
- The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia - N.W. No. 1
- The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri - N.W. No. 2
- The West Coast Canal in Kerala - N.W. No. 3
The other viable inland waterways include the Godavari, Krishna, Barak, Sunderbans, Buckingham cannal, Brahmani, East-west canal and Damodar Valley Corporation canal.
Major seaports: India is dotted with 12 major and 200 medium and minor ports. The length of Indian coastline is 7516.6 km. The important seaports are -
(i) Kandla: Kandla in Kutchh was the first port developed after independence to ease the volume of trade on the Mumbai port, in the wake of loss of Karachi port to Pakistan after the partition.
Kandla is a tidal port. It caters to the convenient handling of the exports and imports of highly productive granary and industrial belts stretching across the states of J&K, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat. It is also known as Deendayal Port.
(ii) Mumbai: Mumbai is the biggest port with a specious, natural and well sheltered harbour. The Jawaharlal Nehru port is planned with a view to decongest the Mumbai port and will serve as a high port for this region.
(iii) Marmagaon: Marmagaon port is a premier iron ore exporting port.
(iv) New Mangalore: New Mangalore port located in Karnataka caters to the export of iron ore concentrates from Udarmukh mines.
(v) Kochi: Kochi is the extreme southwestern port, located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbour.
(vi) Tuticorin: This port has a natural harbour and rich hinterland. It has a flourishing trade handling of a large variety of cargoes to our neighboring countries like Sri Lanka, Maldives etc. and the coastal regions of India.
(vii) Chennai: Chennai is one of the oldest artificial ports of the country which is ranked next to Mumbai in terms of the volume of trade and cargo.
(viii) Vishakhapatnam: It is the deepest land locked and well protected port.
(ix) Paradeep: This port, located in Odisha, specializes in the export of iron ore.
(x) Kolkata: It is an inland riverine port which serves a very large and rich hinterland of Ganga-Brahmaputra basin.

Question 5.
Describe the internal waterways of India.
Or
Describe the terrestrial navigational waterways of India.
Answer:
Internal waterways in India India has inland navigation waterways of 14,500 km in length. Out of these only 5685 km are navigable by mechanised vessels.
The following waterways home been declared as the National Waterways by the Government.
- The Ganga river between Prayagraj and Haldia (1620 km) N.W. No-1
- The Brahmaputra river between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km) N.W. No.-2
- The West-Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapurma-Kollam, Udyogamandal and Champakkara canals-205 km). N.W. No-3.
- Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna rivers along with Kakinada Puducherry stretch of canals (1078 km). N.W. No.-4.
- Specified stretches of river Brahmani along with Matai river, delta channels of Mahanadi and Brahmani river and East Coast Canal (588 km) N.W. No. 5.
There are some other inland waterways on which water transportation takes place in which Mandavi, Zuari and Cumberjua, Sunderbans, Barak and backwaters of Kerala are the main.
Question 6.
Write a detailed note on mass communication in India.
Answer:
As a mode of mass communication, newspapers, magazines, films, radio and television create awareness among people about various national programmes and policies.
(i) All India Radio: All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country.
(ii) Doordarshan: Doordarshan, the national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports etc. for people of different age groups.
(iii) Newspapers: In India a large number of newspapers and periodicals are published annually. They are of different types depending upon their periodicity. Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects. The largest number of newspapers published in the country are in Hindi, followed by English and Urdu.
(iv) Films: India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films, video feature films, video short films. The Central Board of Film Certification is the authority for certifying both Indian and foreign films.
