RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries Important Questions and Answers.
RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Iron and steel industry is :
(a) Basic industry
(b) Agro based industry
(c) Consumer industry
(d) IT industry
Answer:
(a) Basic industry
Question 2.
Which is the largest producer of raw jute, and jute goods in the world ?
(a) India
(b) Pakistan
(c) Bangladesh
(d) China
Answer:
(a) India
Question 3.
Most of the sugar mills are located in these states of India.
(a) Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
(b) Bihar and West Bengal
(c) Punjab and Haryana
(d) Uttar Pradesh and Haryana
Answer:
(a) Uttar Pradesh and Bihar
Question 4.
Which city is called “The electronic capital city” of India ?
(a) Mumbai
(b) Bangalore
(c) Kolkata
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(b) Bangalore

Question 5.
Which one is a consumer industry?
(a) Sewing Machine
(b) Iron and steel
(c) Copper smelting
(d) Aluminium smelting
Answer:
(a) Sewing Machine
Question 6.
Which of the following fibre is called 'Golden fibre'?
(a) Cotton
(b) Wool
(c) Jute
(d) Silk
Answer:
(c) Jute
Question 7.
Which of the following is a joint sector industry ?
(a) BHEL
(b) SAIL
(c) TISCO
(d) OIL
Answer:
(d) OIL
Question 8.
First place in the world in the production of gur and khandsari of -
(a) China
(b) India
(c) Brazil
(d) Srilanka
Answer:
(b) India

Question 9.
Where was the first cement industry factory in India planted ?
(a) Chennai
(b) Mumbai
(c) Kolkata
(d) Udaipur
Answer:
(a) Chennai
Question 10.
The major solid wastes in India are-
(a) Fly ash
(b) Phospo-gypsum
(c) Iron and steel slags
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Fill in the blanks
1. People employed in the ............. activities manufacture the primary materials into finished goods.
2. The first successful textile mill was established in ............ in 1854.
3. Some quantities of ........, are also required to harden the steel.
4. ................... has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries in India.
5. Every litre of waste water discharged by our industry pollutes ............. the quantity of freshwater.
Answer:
1. Secondary
2. Mumbai
3. Manganese
4. Chhota Nagpur plateau region
5. eight times.

Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which industry is considered as the backbone in general and economic development of a country ?
Answer:
Manufacturing industry.
Question 2.
Name any two industries which are based on minerals ?
Answer:
- Iron and steel industry
- Cement industry
Question 3.
Who helps the manufacturing industries to fulfil their objectives?
Answer:
The National Manufacturing Competitiveness Council (NMCC) has been set up with this objective.
Question 4.
When many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres, it is known as
Answer:
Agglomeration economies.

Question 5.
Name the agency which markets steel for public sector plants.
Answer:
Steel Authority of India Ltd. (SAIL).
Question 6.
Give any two examples of consumer industries.
Answer:
- Sugar Industry
- Paper industry.
Question 7.
Which city is called the “Electronic capital of India” ?
Answer:
Bangalore.
Question 8.
What is meant by agro based industry ?
Answer:
The industry which gets its raw materials from agriculture is known as agro based industry.
e.g., Sugar industry.
Question 9.
Write the classification of industries on the basis of source of raw materials used.
Answer:
(a) Agro based - cotton, jute, rubber, sugar etc.
(b) Mineral based - iron and steel, cement, aluminium

Question 10.
Give two examples of agro based . industries.
Answer:
Cotton industry and silk industry.
Question 11.
What is "white revolution” ?
Answer:
“White revolution” is the programme of increasing the production of milk by modernization.
Question 12.
Write two names of raw materials which are used in making cement.
Answer:
Limestone, silica.
Question 13.
Name the centres of cotton textile industry in India.
Answer:
Ahmedabad, Mumbai, Coimbatore, Kolkata, Nagpur, Kanpur.
Question 14.
Write any two problems of jute industries in India.
Answer:
- The invention of synthetic as a substitute of jute is giving a tough competition to the jute industry.
- International competition, especially from in Bangladesh has also led to the decline of the industry.

Question 15.
When and where was the first cotton textile industry of India established?
Answer:
The first successful cotton textile mill was established in Mumbai in 1854.
Question 16.
Why is the iron and steel industry called a heavy industry ?
Answer:
The iron and steel industry is called a heavy industry because all the raw materials and finished products are heavy and bulky.
Question 17.
What is light industry ?
Answer:
This industry uses light raw materials and makes light weight finished products.
e.g., Electronics, fans.
Question 18.
Which materials are used for making paper ?
Answer:
Bamboo, sawai grass and straw of sugarcane.

Question 19.
Write two problems of cotton textile industries of India.
Answer:
- Power supply is erratic.
- Low output of labour.
Question 20.
Write two locational factors of industries.
Answer:
- Availability of raw materials.
- Availability of labour.
Question 21.
What are consumer industries ?
Answer:
These industries provide goods primarily for the consumption of people.
e.g., Sugar industry
Question 22.
In which countries does India export cotton yarns ?
Answer:
USA, England, Russia and France.
Question 23.
Mention two problems of sugar industries in India.
Answer:
- Old and inefficient methods of productions
- Transport delays in carrying canes to factories

Question 24.
Mention two major problems of iron and steel industries.
Answer:
- High cost and limited availability of cooking coal.
- Lower productivity of labour.
Question 25.
Write two uses of aluminium.
Answer:
- For making aeroplanes
- For making utensils.
Question 26.
Write any four centres of automobile industries.
Answer:
Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Kolkata.
Question 27.
How thermal pollution of water occurs ?
Answer:
Thermal pollution of water occurs when hot water from factories and thermal plants is drained into rivers and ponds before cooling.
Question 28.
What is the raw material for sugar industry ?
Answer:
The raw material for sugar industry is sugarcane.

Question 29.
From what is aluminium manufactured ?
Answer:
Aluminium is manufactured form bauxite.
Question 30.
Give any four examples of manufacturing industry.
Answer:
- Steel industry
- Automobile industry
- Textile industry
- Bakery and beverage industry
Question 31.
Economic strength of a country is measured by the development of which industries ?
Answer:
Economic strength of a country is measured by the develoment of manufacturing industries.
Question 32.
What kind of economic development is needed for sustainable development ?
Answer:
The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of economic development with environmental concerns.
Question 33.
Which is the main power supply corporation in India ?
Question 34.
What are the two important requirement of establishing an aluminium industry ?
Answer:
- Regular supply of electricity.
- An assured source of raw material at minimum cost.

Short Answer Type Questions (Type-I)
Question 1.
“Iron and Steel industry could not develop fully in India.” Give any two reasons for this.
Or
Write any four reasons liable for under development of Iron and Steel industry in India.
Answer:
- High costs and limited availability of coking coal.
- Lower productivity of labour.
- Irregular supply of energy.
- Poor infrastructure.
Question 2.
Give two suggestions for the progress of cotton textile industries in India.
Answer:
- More supply of long, staple cotton which we have to import.
- Increase in consumption level of cloth.
Question 3.
Write any four ways of controlling air pollution, emitted by industries in India.
Answer:
- Smoke can be reduced by using oil or gas instead of coal in factories.
- Minimum uses of sources of sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- Controlling smoke and ash from industry's precipitators.
- Industries must be situated far from urban areas.

Question 4.
Write the four causes of decentralization of cotton textile industries in India.
Answer:
Four causes of decentralization of cotton textile industries are:
- Increase in cotton producing area in India and increase in varieties of cotton.
- Making wet climate for cotton cultivation artificially.
- Development of transport and communication facilities.
- Increase of movement of cheap and skilled labours.
Question 5.
In which sector is the iron and steel industry, situated in Jamshedpur on the basis of ownership ? State two reasons for establishing this industry in Jamshedpur.
Answer:
TISCO is owned and operated by individuals (private sector).
Locational factors of TISCO:
- Availability of iron ore, coal and limestone from nearby areas.
- Availability of cheap and skilled labour from Bihar, West Bengal and Odisha.
Question 6.
“Industrialisation and urbanization go hand in hand”. explain.
Answer:
Industrialisation and urbanization goes hand in hand. Cities provide market and also provide services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour etc. Workers need houses and other facilities. The provision of these, facilities can convert a small town into a big city.

Question 7.
Write the significance of cotton textile industry in Indian economy.
Answer:
- It is the only industry in the country that is complete and self-sufficient in the rang from raw materials to the highest added value products.
- Being a tropical country, India has wide market, as it has a great demand throughout the country. The industry, by creating demands, support many other industries, such as chemicals, packaging materials and engineering works.
- The textile industry provides employment to a large number of individuals in the country.
Question 8.
Write any four challenges of cotton textile industries in India.
Answer:
- The weaving, knitting and processing units, cannot use much of the high quality yarn that is produced in the country.
- There are some large and modern factories in this segment, but most of the production is in fragmented small units, which cater to the local market.
- Many of our spinners export cotton yarns while apparel or garment manufacturers have to import fabric.
- Power supply is erratic and low output of labour and steep competition with the synthetic fibre industry.
Question 9.
Define the term agglomeration economies.
Answer:
Cities provide markets and also provides services such as banking, insurance, transport, labour etc. to the industries. Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies.
Question 10.
Write the differences between private sector and cooperative sector.
Answer:
|
Cooperative sector |
Private sector |
|
1. These industries are run on a cooperative basis by a group of people (Anand Dairy Firm in Gujarat). |
1. These industries are owned by individuals or firms,(TISCO). |
|
2. The capital is invested by shareholders. |
2. The capital is invested by individuals or firms organized by the individuals |
|
3. The distribution of profit or loss is among the shareholders. |
3. The profit or loss affects the individual or firms. |

Question 11.
Write the base of manufacturing industries in the pre-independence period.
Answer:
In the pre-independence period, most of the manufacturing units were located in places from the point of view of overseas trade such as Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai etc. Consequently, there emerged .certain pockets of industrially developed urban centers surrounded by huge agricultural rural hinterland.
Question 12.
Make a chart of an ideal location of an industry.
Answer:
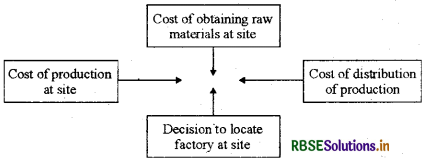
Question 13.
Make a chart of industry-market linkage.
Answer:
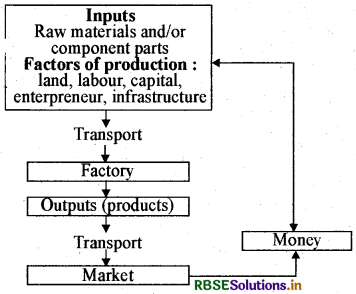
Question 14.
Make a chart of the processes of manufacture of steel.
Answer:
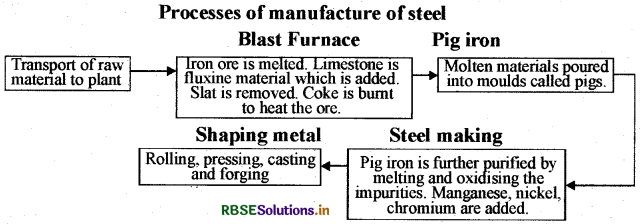
Question 15.
The sugar industry is now shifting from north to south and west. Mention the reason for this.
Answer:
(a) Climate: Sugarcane is a tropical crop. Peninsular India has a tropical climate which gives higher yield per unit area as compared to north India.
(b) Higher sucrose: Due to favourable climatic conditions, the sucrose content is also higher in tropical variety of sugarcane in south and west.
(c) Long crushing period: The crushing season is also much longer in the south than in the north.
(d) The irrigation facilities are higher in south than north.

Question 16.
What is the importance of the IT sector for the Indian economy?
Answer:
- It has provided employment to over · millions of people.
- The industry is a major foreign exchange earner.
- It has helped in the growth of the service .sector.
- It provides employment to innumerable males and females.
Question 17.
Write the classification of industries according to their main roles.
Answer:
(a) Basic or key industries- These industries supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods.
e.e., Iron and steel, copper smelting and aluminium smelting
(b) Consumer industries- These indus. tries produce goods for direct use of consumers.
e.g., Sugar, toothpaste, fans and paper etc.
Question 18.
Write the classification of industries on the basis of capital investment.
Answer:
(a) Small scale industries- These industries employ small number of persons and invest of about rupees one crore.
e.g., Readymade garments etc.
(b) Large scale industries- These industries employ large number of persons in each unit and have large production levels.
e.g., Iron and steel industry and jute industry etc.

Question 19.
Write a short note on mini steel plants.
Answer:
Mini steel plants are smaller, have electric furnaces, use steel scrap and sponge iron. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots. as well. They produce mild and alloy steel of given specifications.
Question 20.
Write any four names of agro based industries.
Answer:
Names of four agro based industries-
- sugar industry
- cotton industry
- jute industry
- vegetable oil industry etc.
Question 21.
Draw and illustrate value addition in the textile industry.
Answer:
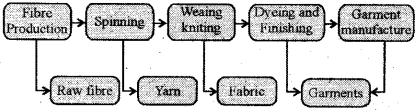

Question 22.
There is an increase in value at each stage in the textile industry. Explain by giving examples.
Answer:
There is an increase in value at each stage in the textile industry, for example-Suppose that yarn is sold at ₹ 85 per kg. If it sold as a trouser it fetches ₹ 800 per kg. Value is added at every stage from fibre to yarn to fabric and to garment.
Question 23.
What is the reason for most of the iron and steel industries being concentrated in the area of Chhota Nagpur plateau in India.
Answer:
- The area of Chhota Nagpur plateu in India has more favourable relative advantages for the development of iron and steel industry
- These include, low cost of iron ore, high grade raw materials in proximity, cheap labour and vast growth potential in the home market.
Short Answer Type Questions (Type-II)
Question 1.
Answer the following questions-
(i) Fill in the blanks in the following table. Place 1 and 2 showing industrymarket linkage.
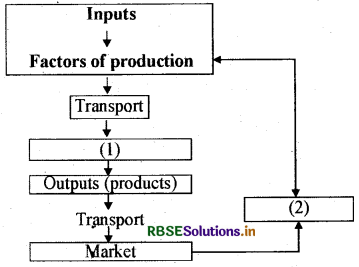
(ii) What is the significance of the golden .quadrilateral super highways?
Answer:
(i) (1) Factory, (2) Money.
(ii) The major objective of these super highways is to reduce the time and the distance between the mega cities of India. These highway projects are being implemented by the National Highways Authority of India.

Question 2.
How is the National Thermal Power Corporation helping to reduce environmental pollution ?
Answer:
NTPC is a major power providing corporation in India. This corporation controls the environmental pollution by these ways :
- Optimum utilization of equipments adapting latest techniques and upgrading the existing equipments.
- Minimizing wastes generation by maximizing ash utilization.
- Providing green belts for nurturing ecological balance and addressing the question of special purpose vehicles for afforestation.
- Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system and liquid waste management.
- Ecological monitoring, reviews and online database management for all its power stations.
Question 3.
Write a short note on aluminium smelting in India.
Answer:
Aluminium smelting is the second most important metallurgical industry in India.
It is light, a good conductor of heat, malleable and becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals.
It is used to manufacture aircrafts, utensils and wires. It has gained popularity as a substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in a number of industries.
Distribution: There are eight aluminium smelting plants in the country located in Odisha (NALCO and BALCO), West Bengal, Kerala, U.P., Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu.
Question 4.
Write a short note on automobile industry in India.
Answer:
Automobiles provide vehicles for quick transport of goods services and passengers.
Trucks, buses, cars, motorbikes, scooters, 3wheelers etc. are manufactured in India at various centres. After the liberalization, the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market which led to the healthy growth of the industry. This industry has experienced a quantum jump in less than 15 years.
Foreign direct investment brought a new technology and aligned the industry with global development. Currently, new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for vehicles in the market, which led to the healthy growth of the industry including passenger cars, two and three-wheelers.
The industry is located around Delhi, Gurgaon, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Bangalore etc.

Question 5.
The cement industry is expanding at a fast rate - mention the factors responsible.
Answer:
- Decontrol of price.
- Decontrol of distribution
- High demand due to government's stress on infrastructure.
- There are 125 big and 332 small cement factories in India which are producing different types of cement.
- Increase in export especially to Middle East, African and South Asian countries.
Question 6.
Distinguish between large scale and small scale industries.
Answer:
|
Large scale industries |
Small scale industries |
|
1. Any industry in which investment is more than 1 crore is known as a large scale industry. e.g. iron and steel, cotton etc. |
1. Any industry in which investment limit is less than 1 crore is known as small scale industries. E.g. garments industry, soap industry etc. |
|
2. As more capital is required, so it is a capital intensive industry. |
2. As less capital is required, so it is a labour intensive industry |
|
3. Women workers are not .generally employed in this industry. |
3. Women workers are employed in a large number in this industry. |
Question 7.
Write the significance of cotton textile industry for the Indian economy.
Answer:
(a) The close association with agriculture- This industry has close links with agriculture and provide livelihoods to farmers, cotton ball pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing.
(b) Demand creative- It is a demand creative industry. It supports many other industries such as chemicals, dyes, packaging materials and engineering works.
(c) Employment- The industry provides employment to a large number of skilled as well as unskilled workers. The hand spun Khadi provides large scale employment to weavers to their homes.
(d) Decentralization- The industry helps in decentralization as 90% of the weaving, cutting and processing is in decentralized sector.
Question 8.
Write a short note on cement industry.
Answer:
Cement is essential for construction activity such as building houses, factories, bridges, roads, airports, dams and for other commercial establishments. This industry requires bulky and heavy raw materials like limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum. Coal and electric power are needed apart from rail transportation.
Development : The first cement plant was set up in Chennai in 1904. After independence, the industry expanded. Decontrol of price and distribution since 1989 and other policy reforms let the cement industry to make raid strides in capacity, process, technology and production. There are several large and mini cement plants in which India produces a variety of cements. Cement is exported mainly to Middle East, African and South Asian countries.

Question 9.
Write a short note on NTPC.
Answer:
NTPC is a major power providing corporation in India. It has ISO certification for EMS (environment management system 14001). The corporation has a proactive approach for preserving the natural environment and resources like water, oil, gas and fuel in places where it is setting up power plants. This has been possible through :
- Optimum utilization of equipments adapting latest techniques and upgrading the existing equipments.
- Minimizing wastes generation by maximizing ash utilization.
- Providing green belts for nurturing ecological balance and addressing the question of special purpose vehicles for afforestation.
- Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system and liquid waste management.
- Ecological monitoring, reviews and online database management for all its power stations.
Question 10.
Describe information technology and electronics industry.
Answer:
Currently, the importance of this industry is increasing in the whole world. Information technology and electronics industry has developed a lot in India too. The description of this industry is clear in the following points-
- In India, the electronics industry covers transistor sets to television, telephones, cellular telecom, telephone exchange, radars, computers and many other equipments required by the telecommunication industry.
- Bengaluru has emerged as the electronic capital of India.
- Other important centres for electronic goods are Mumbai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow and Coimbatore. The major industry concentration is at Bengaluru, Noida, Mumbai, Chennai, Hyderabad and Pune.
- The continuing growth in the hardware and software is the key to the success of IT industry in India.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the importance of manufacturing industries ?
Answer:
(i) Employment: Manufacturing industry is the main source of employment for a large number of skilled as well as unskilled workers.
(ii) Foreign exchange: Export of manufactured goods brings foreign exchange to Indía.
(iii) Reduction of pressure on land: Manufacturing industry reduces pressure on land by providing employment to workers.
(iv) Daily needs: Manufacturing industries produces products of daily needs and helps the common people to fulfil their basic needs.
(v) Utilization of natural resources: Utilisation of natural resources has become possible with the development of industries in the country.

Question 2.
Classify the industries on the basis of ownership.
Answer:
Industries can be divided into four categories on the basis of ownership.
(i) Public sector: The industry which is controlled and owned by the government is known as public sector. e.g., Durgapur Steel Plant.
(ii) Private sector :
- These industries are owned by individuals or firms (TISCO).
- The capital is invested by individuals or firms organized by the individuals.
- The profit or loss affects the individual or firms.
(iii) Co-operative sector :
- These industries are run on a cooperative basis by a group of people (Coir industry in Kerala).
- The capital is invested by shareholders.
- The distribution of profit or loss is among the shareholders.
(iv) Joint sector: Joint sector industries are industries which are jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals.
E.g. Oil India Limited (OIL) is jointly owned by public and private sectors.
Question 3.
Write the factors that affect the location of industries.
Answer:
(i) Availability of raw material: To set up an industry, the first requirement is raw material. Availability of iron ore and coal in the Chhota Nagpur plateau has led to the coming up of iron and steel industry there.
(ii) Labour: Cheap labour in northern part of India is responsible for the growth of sugar industry.
(iii) Means of transport, communication and export facilities: These are responsible for the growth of industries, in Maharashtra.
(iv) Favourable climate: The equitable climate which is favourable for cotton production is available in Maharashtra and Gujarat area.
(v) Availability of capital: Availability of capital which gains from market is one of the main factors of progress of industry.
(vi) Government policies: Many a times government announces special privileges to the industries for establishment of their business at identified areas. So government policies also determine the location of industries.
Question 4.
Write a geographical essay on cotton textile industry in India.
Answer:
Development: In ancient India, cotton textiles were produced with hand spinning and handloom weaving techniques. After the 18th century, power loom's came into use. Our traditional industries suffered a setback during the colonial period because they could not compete with the mill made cloth from England.
We have a large share in the world trade of cotton yarn. It accounts for about one-fourth of total international trade. The weaving, knitting and processing units cannot use much of the light quality yarn that is produced in the country. As a results many of our spinners export cotton yarn while apparel/garment manufactures have to import fabric.
Locational factors: In the early years the cotton textile industry was concentrated in the cotton growing belts of Maharashtra and Gujarat. Availability of raw cotton, market, transport, labour, moist climate etc. contributed towards its localization. This industry has close links with agriculture and provide livelihoods to farmers, cotton ball pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing. It is a demand creative industry. It supports many other industries such as chemicals, dyes, packaging materials and engineering works.
While spinning continues to be centralized in Maharashtra, Gujarat and Tamil Nadu, weaving is highly decentralized to provide scope for incorporating traditional skills and designs of weaving in cotton, silk, zari, embroidery etc.
Trade : India exports yarn to Japan, USA, UK, France, Nepal, Singapore, Sri Lanka and African countries.

Question 5.
Describe the jute textile industry in India.
Answer:
Development: India is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods and stands at the second place as an exporter after Bangladesh. In the year 2010-11, there were about 80 jute mills in India. Most of them are located in West Bengal, mainly along the banks of the Hooghly river in a narrow belt. The first jute mill was set up near Kolkata in 1855 at Rishra and indirectly provides employment to millions of people.
Factors responsible for jute industry: Factors responsible their location in the Hooghly basin are proximity of the jute producing areas, inexpensive water transport supported by a good network of railways, waterways and roadways to facilitate movement of raw materials to the mills, abundant water for processing raw jute, cheap labour from West Bengal, Bihar, Odisha and providing banking and insurance facilities of Kolkata and port facilities for export of jute goods.
Challenges: Challenges faced by the industries include stiff competition in the international market from synthetic substitutes and from other competitors like Bangladesh, Thailand etc.
Trade: The main markets are USA, Canada, Russia, Saudi Arab, UK. and Australia.
Question 6.
Describe the iron and steel industry in India.
Answer:
Iron and steel is a mineral based industry. This is the basic industry since all the other industries - heavy, medium and light, depend on it for their machinery.
Development: Steel is required to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction materials, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods.
Production and consumption: Production and consumption of steel is often regarded as the index of a country's development. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials as well as the finished goods are heavy and bulky entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore, cooking coal, limestone are required in the ratio of approximately 4 : 2 : 1. Some quantities of manganese are also required to harden the steel.
In 2018 with 106.5 million tonnes of steel production. India ranked second among the world crude steel producers. In 2018 per capita consumption of steel in the country was only around 70.9 kg per annum.
Iron and steel plants: Presently there are 10 primary integrated and many mini steel plants in India. All public sector undertakings market their steel through Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL) while TISCO, markets its produce through Tata Steel.:
Location: Chhota Nagpur plateau region has the maximum concentration of iron and steel industries. These industries are found in West Bengal, Odisha, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
We import good quality steel from other countries. The overall production of steel is sufficient to meet our dometic demand.
Possibiļities- Still liberalisation and Foreign Direct Investment have given a boost to the industry with the efforts of private entrepreneurs. There is a need to allocate resources for reserach and development to produce steel more competitively.
Question 7.
Write short note on the importance of basic infrastructure industries.
Answer:
Basic industries are the industries which supply their products or raw materials to manufacture other goods. e.g., iron and steel industry.
(i) Development and prosperity: Countries that transform their raw materials into wide variety of furnished goods of higher value are considered prosperous. India's prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as soon as possible.
(ii) Eradication of unemployment and poverty: Industrial development is a precondition for eradication of unemployment and poverty from our country.
(iii) Expansion in trade and commerce: Export of manufactured goods expands trade and commerce, and brings in much needed foreign exchange.
(iv) Less burden on agriculture.

Question 8.
Why does the Chhota Nagpur plateau region have the maximum concentration of iron and steel industry ?
Answer:
- The Chhota Nagpur plateau is famous for iron ores. The states of Bihar, West Bengal and Jharkhand are provided raw materials.
- Coal, which is used as a fuel, is another important input, and is available in this region in plenty
- Because of more population in this region, cheap labour is also available.
- The Damodar Valley Corporation provides power to these plants.
- The export and import facilities are provided by Kolkata port.
Question 9.
Describe the chemical industry in India.
Answer:
The chemical industry in India is fast growing and diversifying. It contributes approximately 3% of the GDP.:
It comprises both large and small scale manufacturing units.
It is the third largest industry in Asia and occupies 25th place in the world in terms of its size.
Rapid growth has been recorded in both organic and inorganic sectors. Inorganic chemicals include sulphuric acid (fertilizers, plastics etc.), nitric acid, alkalize, soda ash (soaps, detergents etc.).
The chemical industry is the largest consumer of its own. Basic chemicals undergo processing to produce other chemicals that are used for industrial application, agriculture or directly for consumer markets.
Significance of this industry :
- Employment-Chemical industry is one of the major sources of employment for a large number of skilled as well as unskilled workers.
- Foreign exchange-Export of chemicals and chemical products bring foreign exchange to India.
- Reduction of pressure on land-This industry reduces pressure on land by providing employment to workers.
- Development of agriculture-This industry supplies pesticides for the crops which controls harmful insects and weeds.
Question 10.
Describe fertilizer industry of India.
Answer:
The fertilizer industry is centered around the production of nitrogenous fertilizers (urea). Phosphetic fertilizers and ammonium phosphate and complex fertilizers which have a combination of nitrogen, phosphate and potash. The potash is entirely imported as the country does not have any reserves of commercially usable potash or potassium compound in any form.
Production : India is one among the major countries in the world in the production of nitrogenous fertilizers (several fertilizer units). some for urea and some for producing ammonium sulphate as a bi-product and some other small units produce single super phosphate.
Producing areas : After the Green Revolution, the industry expanded to several other parts of the country. Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, U.P., Punjab, Kerala, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Goa, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka etc. are the main producing area of fertilizers.

Question 11.
Write the classification of industries in different aspects.
Answer:
Classification of Industries
(i) On the basis of source of raw materials used :
a. Agro based: The industry which gets its raw materials from agriculture is known as agro based industry. e.g. Sugar industry.
(b) Mineral based: The industry in which mineral products are processed and turned into finished goods. e.g., iron and steel industry.
(ii) According to their main roles :
(a) Basic industry: The industries which lay the foundation of rapid development of other industries is known as basic industry. e.g. Iron and steel.
(b) Consumer industry: These industries provide goods primarily for the consumption of people..e.g. Sugar industry.
(iii) On the basis of capital investment :
(a) Small scale industries: These industries employ small number of persons and invest of about 1 crore. e.g: Readymade garments etc.
(b) Large scale industries: These industries employ large number of persons in each unit and have large production levels.e.g. Iron and steel industry, jute industry etc.
(iv) On the basis of ownership :
(a) Public sector: The industry which is controlled and owned by the government is known as public sector. e.g., Durgapur Steel Plant.
(b) Private sector: These industries are owned by individuals or firms. E.g., TISCO.
(c) Cooperative sector: These industries are run on a cooperative basis by a group of people. E.g., Coir industry in Kerala.
(d) Joint sector: Joint sector industries are industries which are jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. E.g., Oil India Limited (OIL).
(v) Based on the bulk and weight of raw materials and finished goods :
(a) Heavy industries: These industries use heavy raw materials and manufacture finished products. e.g., Iron and steel industry.
(b) Light industries: These industries use light raw materials and make light finished products in weight. E.g., electronics and fans.

Question 12.
Describe sugar industry in India.
Answer:
Sugar industry is an agro based industry. India stands second in the world as a producer of sugar but occupies the first place in the production of gur and khandsari. The raw material used in this industry is bulky, and in haulage its sucrose content reduces.
Development: There were sugar mills in the country spread over U.P., Bihar, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh and Gujarat and along with Punjab, Haryana and Madhya Pradesh. 60% mills are in UP and Bihar. Most of the mills are in cooperative sector.
Due to climate higher sucrose and long crushing period, there is a tendency of sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states of India.
Challenges: Major challenges include the seasonal nature of the industry, old and inefficient method of production, transport delay in carrying canes to factories and the need to maximize the use of baggase.
