RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 9. Students can also read RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 9 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The why do we fall ill important questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 12 Sound
RBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound InText Questions and Answers
Page No. 162
Question 1.
How does the sound produced by a vibrating object in a medium reach your ear?
Answer:
An object sets the particles of the medium around it vibrating during vibration. The particles in the medium in contact with the vibrating object displace from its equilibrium position. It then exerts force on the adjacent particles. After displacing the adjacent particle, the first particle of medium comes back in its original position. This process continues in the medium till the sound reaches our ear.
Page No. 163
Question 1.
Explain how sound is produced by your school bell.
Answer:
It creates a series of compressions and rarefactions making production of sound, when the bell continues to move forward and backward.
Question 2.
Why are sound waves called mechanical waves?
Answer:
Sound waves need material medium to propagate. Sound waves propagate through a medium because of the interaction of the particles present in that medium.
Question 3.
Suppose you and your friend are on the Moon. Will you be able to hear any sound produced by your friend?
Answer:
No, I will not be able to hear any sound produced by my friend because sound waves need a medium through which they can propagate. Since there is no material medium on the Moon due to absence of atmosphere, therefore, I cannot hear any sound on the Moon.

Page No. 166
Question 1.
Which wave property determines (a) loudness, (b) pitch?
Answer:
(a) Amplitude (b) Frequency
Question 2.
Guess which sound has a higher pitch : guitar or car horn?
Answer:
High the frequency higher is the pitch. So, guitar has a higher pitch than car horn, because sound produced by the strings of guitar has high frequency than that of car horn.
Question 1.
What are wavelength, frequency, time period and amplitude of a sound wave?
Answer:
Wavelength: The distance between two consecutive compressions or two consecutive rarefactions is known as the wavelength. Its SI unit is metre (m).
Frequency: The number of complete oscillations per unit time is known as the frequency of a sound wave. It is measured in hertz (Hz).
Time period: Time taken for one complete oscillation in the density of the medium is called the time period of the sound wave.
Amplitude: The maximum height reached by the crest or trough of a sound wave is called its amplitude.
Question 2.
How are the wavelength and frequency of a sound wave related to its speed?
Answer:
Speed, wavelength and frequency of a sound wave are related by the following equation :
Speed (v) = Wavelength (λ) × Frequency (ν)
v = λ × ν

Question 3.
Calculate the wavelength of a sound wave whose frequency is 220 Hz and speed is 440 m/s in a given medium.
Answer:
Frequency of the sound wave, ν = 220 Hz
Speed of the sound wave, v = 440 ms-1
For a sound wave,
Speed = Wavelength × Frequency; v = λ × ν
∴ λ = \(\frac{v}{ν}=\frac{440}{220}\)
Hence, the wavelength of the sound wave is 2 m.
Question 4.
A person is listening to a tone of 500 Hz sitting at a distance of 450 m from the source of the sound. What is the time interval between successive compressions from the source?
Answer:
The time interval between two successive compressions is equal to the time period of the wave. 11118 time period is reciprocal of the frequency of the wave and is given by the relation : T = \(\frac{1}{\text { Frequency }}=\frac{1}{500}\) = 0.002 s
Question 1.
Distinguish between loudness and intensity of sound.
Answer:
Intensity of a sound wave is defined as the amount of sound energy passing through a unit area per second. Loudness is a measure of the response of the ear to the sound. The loudness of a sound is defined by its amplitude. The amplitude of a sound decides its intensity, which in turn is perceived by the ear as loudness.
Page No. 167
Question 1.
In which of the three media; air, water or iron, does sound travel the fastest at a particular temperature?
Answer:
The speed of sound depends on the nature of the medium. Sound travels fastest in solids. Its speed decreases in liquids and it is the slowest in gases. Therefore, for a given temperature, sound travels fastest in iron.

Page No. 168
Question 1.
An echo returned in 3 s. What is the distance of the reflecting surface from the source, given that the speed of sound is 342 m s-1?
Answer:
Speed of sound, u = 342 ms-1
Echo returns in time, t = 3 s
Distance travelled by- sound = v × t = 342 × 3 = 1026 m
In the given time interval, sound has to travel a distance that is twice the distance of the reflecting surface and the source.
Hence, the distance of the reflecting surface from the source = \(\frac{1026}{2}\) m = 513 m.
Page No. 169
Question 1.
Why are the ceilings of concert halls curved?
Answer:
Ceilings of concert halls are curved so that sound after reflection (from the walls) spreads uniformly in all directions.
Page No. 170
Question 1.
What is the audible range of the average human ear?
Answer:
The audible range of an average human ear lies between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Question 2.
What is the range of frequencies associated with :
(a) Infrasound?
(b) Ultrasound?
Answer:
(a) Infrasound has frequencies less than 20 Hz.
(b) Ultrasound has frequencies more than 20,000 Hz.

Page No. 172
Question 1.
A submarine emits a sonar pulse, which returns from an underwater cliff in 1.02 s. If the speed of sound in salt water is 1531 m/s, how far away is the cliff from the submerine?
Answer:
Time taken by the sonar pulse to return, t = 1.02 s
Speed of sound in salt water, υ = 1531 ms-1
Distance of the cliff from the submarine = Speed of sound × Time taken
Distance of the cliff from the submarine = 1.02 × 1531 = 1561.62 m
Distance travelled by the sonar pulse during its transmission and reception in water = 2 × Actual distance = 2d
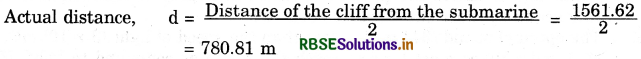
RBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is sound and how is it produced?
Answer:
Sound is a form of energy which gives the sensation of hearing. It is produced by the vibrations caused in air by vibrating objects.
Question 2.
Describe with the help of a diagram, how compressions and rarefactions are produced in air near a source of sound?
Answer:
When a vibrating body moves forward, it creates a region of high pressure in its vicinity. This region of high pressure is known as compression. It creates a region of low pressure in its vicinity when it moves backward. This region is known as a rarefaction. As the body continues to move forwards and backwards, it produces a series of compressions and rarefactions, as shown in below figure.
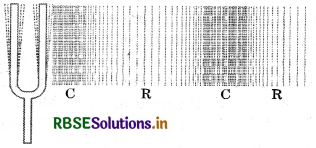
Fig.: A vibrating object creating a series of compressions (C) and rarefactions (R) in the medium

Question 3.
Cite an experiment to show that sound needs a material medium for its propagation.
Answer:
Take an electronic bell and an air tight glass bell jar connected to a vacuum pump. Suspend the bell inside the jar and press the switch of the bell. You will be able to hear the bell ring. Now, pump out the air from the glass jar. The sound of the bell will become fainter and after some time, the sound will not be heard.
This is so bechtise almost all1 air has been pumped out. This shows that sound needs a material medium to travel.
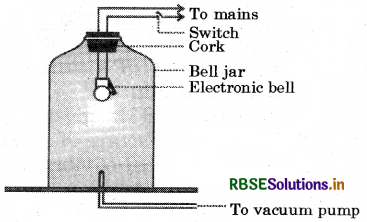
Bell jar experiment showing sound cannot travel in vacuum
Question 4.
Why is sound wave also called a longitudinal wave?
Answer:
The air partiple vibrates parallel to the direction of propagation as sound wave is produced by compressions and rarefactions in the air that is why it is called longitudinal wave.
Question 5.
Which characteristics of the sound help you to identify your friend by his voice while sitting with others in a dark room?
Answer:
The quality or timber of sound enables us to identify our friend by his voice.
Question 6.
Flash and thunder are produced simultaneously. But thunder is heard a few seconds after the flash is seen, why?
Answer:
The speed of sound (344 m/s) is less than the speed of light (3 × 108 m/s). Sound of thunder takes more time to reach the Earth as compared to light. Hence, a flash is seen before we hear a thunder.
Question 7.
A person has a hearing range from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. What are the .typical wavelengths of sound waves in air corresponding to these two frequencies? Take the speed of sound in air as 344 m s-1.
Answer:
For a sound wave,
Speed = Wavelength x Frequency
υ = λ × ν
Speed of sound in air = 344 m/s (Given)
(i) For, ν = 20 Hz
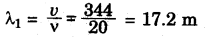
(ii) For, ν = 20000 Hz
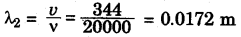
Hence, for humans, the wavelength range for hearing is 0.0172 m to 17.2 m.

Question 8.
Two children are at opposite ends of an aluminium rod. One strikes the end of the rod with a stone. Find the ratio of times taken by the sound wave in air and in aluminium to reach the second child.
Answer:
Velocity of sound in air = 346 m/s
Velocity of sound wave in aluminium = 6420 m/s
Let length of rod be 1 m
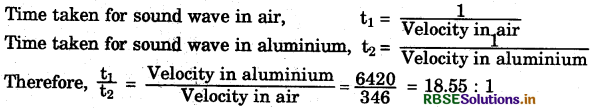
Question 9.
The frequency of a source of sound is 100 Hz. How many times does it vibrate in a minute?
Answer:
Frequency = 100 Hz (given)
This means the source of sound vibrates 100 times in one second.
Therefore, number of vibrations in 1 minute, i.e. in 60 seconds = 100 × 60
= 6000 times.
Question 10.
Does sound follow the same laws of inflection as light does? Explain.
Answer:
Sound follows the same laws of reflection as light does. The incident sound wave and the reflected sound wave make the same angle with the normal to the surface at the point of incidence. Also, the incident sound wave, the reflected sound wave and the normal to the point coincidence all lie in the same plane.
Question 11.
When a sound is reflected from a distant object, an echo is produced. Let the distance between the reflecting surface and the source of sound production remains the same. Do you hear echo sound on a hotter day?
Answer:
An echo is heard when the time for the reflected sound is heard after 0.1 s.
On a hotter day, the velocity of sound is more. If the time taken by echo is less than 0.1 sec it will not be heard.

Question 12.
Give two practical applications of reflection of sound waves.
Answer:
Two practical applications of reflection of sound waves are :
- Reflection of sound is used to measure the distance and speed of underwater objects. This method is known as SONAR.
- Working of a stethoscope is also based on reflection of sound, In a stethoscope, the sound of the patient’s heartbeat reaches the doctor's ear by multiple reflection of sound.
Question 13.
A stone is dropped from the top of a tower 500 m high into a pond of water at the base of the tower. When is the splash heard at the top? Given, g = 10 m s-2 and speed of sound = 340 m s-1.
Answer:
Height of the tower, s = 500 m
Velocity of sound, v = 340 ms-1
Acceleration due to gravity, g= 10 ms-2
Initial velocity of the stone, u = 0 (since the stone is initially at rest)
Time taken by the stone to fall to the base of the tower, t1.
According to the second equation of motion :
S = ut1 + \(\frac{1}{2}\)gt12
500 = 0 × t1 + \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 10 × t12
t12 = 100
t1 = 10 s
Now, time taken by the sound to reach the top from the base of the tower,
t2 = \(\frac{500}{340}\) = 1.47 s
Therefore, the splash is heard at the top after time, t
Where, t = t1 + t2 = 10 + 1.47 = 11.47 s.
Question 14.
A sound wave travels at a speed of 339 m s-1. If its wavelength is 1.5 cm, what is the frequency of the wave? Will it be audible?
Answer:
Speed of sound, υ = 339 m s-1
Wavelength of sound, λ = 1.5 cm = 0.015 m
Speed of sound = Wavelength × Frequency
υ = λ × ν
ν = \(\frac{v}{\lambda}=\frac{339}{0.015}\) = 22600 Hz
The frequency range of audible sound for humans lies between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. Since, the frequency of the given sound is more than 20,000 Hz, it is not audible.
Question 15.
What is reverberation? How can it be reduced?
Answer:
The repeated multiple reflections of sound in any big enclosed space is known as reverberation.
The reverberation can be reduced by covering the ceiling and walls of the enclosed space with sound absorbing materials, such as fibre board, loose woollens, etc.

Question 16.
What is loudness of sound? What factors does it depend on?
Answer:
The effect produced in the brain by the sound of different frequencies is called loudness of sound. Loudness depends on the amplitude of vibrations. In fact, loudness is proportional to the square of the amplitude of vibrations.
Question 17.
Explain, how hats use ultrasound to catch a prey.
Answer:
Bats produce high-pitched ultrasonic squeaks. These high-pitched squeaks are reflected by objects such as preys and returned to the bat’s ear. This allows a bat to know the distance of his prey.
Question 18.
How is ultrasound used for cleaning?
Answer:
Objects to be cleaned are put in a cleaning solution and ultrasonic sound waves are passed through that solution. The high frequency of these ultrasound waves detaches the dirt from the objects.
Question 19.
Explain the working and application of a sonar.
Answer:
SONAR is an acronym for Sound Navigation And Ranging. It is an acoustic device used to measure the depth, direction, and speed of underwater objects such as submarines and shipwrecks with the help of ultrasounds. It is also used to measure the depth of seas and oceans.
A beam of ultrasonic sound is produced and transmitted by the transducer (it is a device that produces ultrasonic sound) of the SONAR, which travels through seawater. The echo produced by the reflection of this ultrasonic sound is detected and recorded by the detector, which is converted into electrical signals. The distance (d) of the underwater object is calculated from the time (t) taken by the echo to return with speed (u) is given by 2d = v × t. This method of measuring distance is also known as ‘echo-ranging’.
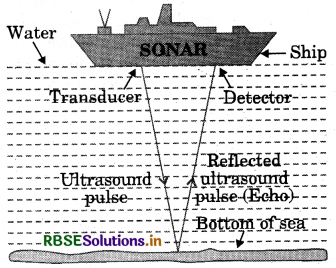
Question 20.
A SONAR device on a submarine sends out a signal and receives an echo 5 s later. Calculate the speed of sound in water if the distance of the object from the submarine is 3625 m.
Answer:
Time taken to hear the echo, t = 5 s
Distance of the object from the submarine, d = 3625 m
Total distance travelled by the SONAR waves during the transmission and reception in water = 2d
Velocity of sound in water, υ = \(\frac{2 d}{t}=\frac{2 \times 3625}{5}\) = 1450 ms-1.

Question 21.
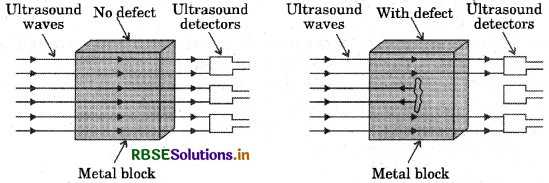
Explain, how defects in a metal block can be detected using ultrasound.
Answer:
Defects in metal blocks do not allow ultrasound to pass through them and they are reflected back. This fact is used to detect defects in metal blocks. Ultrasound is passed through one end of a metal block and detectors are placed on the other end. The defective part of the metal block does not allow ultrasound to pass through it. As a result, it will not be detected by the detector. Hence, defects in metal blocks can be detected using ultrasound.
Question 22.
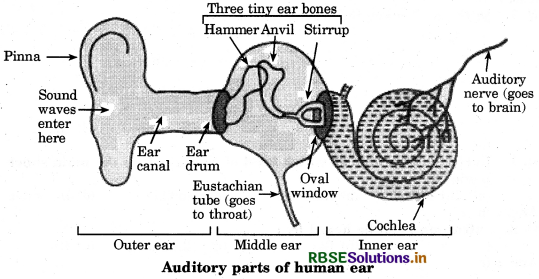
Explain, how the human ear works.
Answer:
The human ear consists of three parts - the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
- Outer ear: This is also called ‘pinna’. It collects the sound from the surrounding and directs it towards auditory canal.
- Middle ear: The sound reaches the end of the auditory canal where there is a thin membrane called eardrum or tympanic membrane. The sound waves set this membrane to vibrate. These vibrations are amplified by three small bones - hammer, anvil and stirrup.
- Inner ear: These vibrations reach the cochlea in the inner ear and are converted into electrical signals which are sent to the brain by the auditory nerve, and the brain interprets them as sound.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 हमारे आस - पास के पदार्थ
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Motion
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 प्राकृतिक सम्पदा
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 10 गुरुत्वाकर्षण
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 गति
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 9 बल तथा गति के नियम
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 हम बीमार क्यों होते हैं