RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 13 Motion and Time Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 7 science chapter 4 heat extra questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
RBSE Class 7 Science Motion and Time InText Questions and Answers
Page 147
Question 1.
How many seconds there are in a day and how many hours are there in a year.
Answer:
(i) In a day, we have 24 h
We know that 1 h = 3600 s
So, 24 h = 3600 x 24 = 86400 s
(ii) In a year, we have 365 days and 1 day = 24h
So, for 365 days, we have 24 x 365 h = 8760 h

Page 148
Question 2.
Paheli wondered how time was measured when pendulum clocks were not available.
Answer:
When pendulum docks were not available, ancestors noted repeated events in nature occurring after regular intervals to understand the time. Many time measuring devices such as sundials, water docks and sand clocks were used before the pendulum clocks became popular.
Page 150
Question 3.
Boojho wants to know whether there is any device that measures the speed.
Answer:
Speed is measured with the help of a device called speedometer
RBSE Class 7 Science Motion and Time Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Classify the following as motion along a straight line, circular or oscillatory motion:
(i) Motion of your hands while running.
(ii) Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road.
(iii) Motion of a child in a merry - go - round.
(iv) Motion of a child on a see saw.
(v) Motion of the hammer of an electric bell.
(vi) Motion of a train on a straight bridge.
Answer:
(i) Oscillatory motion
(ii) Straight line
(iii) Circular motion
(iv) Oscillatory motion
(v) Oscillatory motion
(vi) Straight line
Question 2.
Which of the following are not correct?
(i) The basic unit of time is second.
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
(iii) Distances between two cities are measured in kilometres.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is not constant.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
Answer:
(i) True
(ii) False
(iii) True
(iv) False
(v) False.
Question 3.
A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Answer:
Time taken to complete 20 oscillations = 32 s
Time taken to complete one oscillation = \(\frac{32}{20}\) = 1.6 s
Time period = 1.6 seconds
Question 4.
The distance between two stations is 240km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Answer:
The distance between two stations = 240 km
Time taken to cover this distance = 4 hours
Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\) = \(\frac{240}{4}\) = 60 km/h
Question 5.
The odometer of a car reads 57321.0 km when the clock shows the time 06:30 AM. What is the distance moved by the car, if at 08:50 AM, the odometer reading has changed to 57336.0 km? Calculate the speed of the car in km/ min during this time. Express the speed in km/h also.
Answer:
Odometer reading at 8:30 AM = 57321.0 km
Odometer reading at 8.50 AM = 57336.0 km
Difference in distance = 57336.0 - 57321.0 = 15 km
Difference in time = 8:50 - 8:30 = 20 min
First Case: To calculate the speed of a car in km/min
Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
=\( \frac{15 \mathrm{~km}}{20 \mathrm{~min}}\)
= \(\frac{3}{4}\) km/min
= 0.75 km/min
Second case: To calculate the speed of a car in km/hour
= 0.75 x 60 (1 hr = 60 min)
= 45 km/h
Question 6.
Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Answer:
Time taken to reach school from home = 15 minutes = 15 x 60 = 900 sec.
Speed of bicycle = 2 m/s
Distance = time x speed
= 900 x 2 = 1800 m
The distance from home to school is 1800 m = 1.8 km
Question 7.
Show the shape of the distance - time graph for the motion in the following cases:
(i) A car moving with a constant speed.
(ii) A car parked on a side road.
Answer:
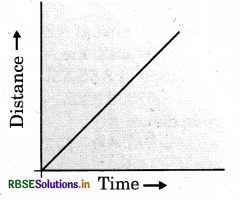
(i) Distance - time graph of a car moving with a constant speed.
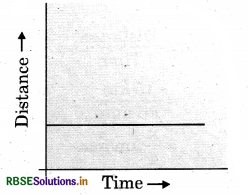
(ii) Distance - time graph of a car parked on a side road.
Question 8.
Which of the following relations is correct?
(i) Speed = Distance x Time
(ii) Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
(iii) \(\text { Speed }=\frac{\text { Time }}{\text { Distance }}\)
(iv) \(\text { Speed }=\frac{1}{\text { Distance } \times \text { Time }} \)
Answer:
(ii) Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
Question 9.
The basic unit of speed is:
(i) km/min
(ii) m/min
(iii) km/h
(iv) m/s
Answer:
(iv) m/s.
Question 10.
A car moves with a speed of 40 km/h for 15 minutes and then with a speed of 60 km/h for the next 15 minutes. Total distance covered by the car is:
(i) 100 km
(ii) 25 km
(iii) 15 km
(iv) 10 km
Answer:
(ii) 25 km.
Speed of a car = 40 km/h and
time = 15 min = 15/60 h.
In first 15 minutes,
Distance covered = Speed x time
= 40 x\( \frac{15}{60} \)= 10 km
In next 15 minutes, Speed of car = 60 km/h
and time = 15 minutes = \(\frac{15}{60} \)h.
Distance covered in next 15 minutes
= 60 x \(\frac{15}{60} \) = 15 km
Total distance covered = 10 km +15 km
= 25 km.

Question 11.
Suppose the two photographs (NCERT textbook shown in figure 13.1 and figure 13.2) had been taken at an interval of 10 seconds. If a distance of 100 metres is shown by 1 cm in these photographs, calculate the speed of the fastest car.
Answer:
Distance covered by the fastest car, which is measured by scale is 2 cm.
It is given that 1 cm is equivalent to 100 m
Therefore, 2 cm = 200 m
Distance travelled by car = 200 m
Time interval between the two photographs = 10 s
Speed = \(\frac{\text { Distance }}{\text { Time }}\)
= \( \frac{200}{10} \) = 20 m/s
Question 12.
Figure shows the distance - time graph for the motion of two vehicles A and B. Which one of them is moving faster?
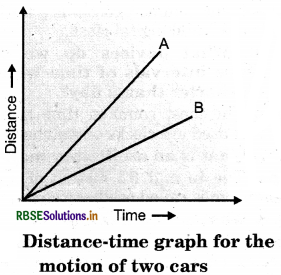
Answer:
Vehicle A is moving faster than vehicle B. Because vehicle A has covered more distance than vehicle B in given time
and \(\text { speed }=\frac{\text { Distance covered }}{\text { Time taken }} \)
Question 13.
Which of the following distance - time graphs shows a truck moving with speed which is not constant?
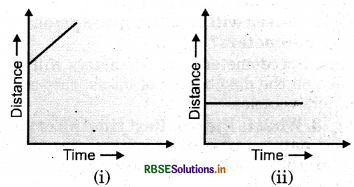
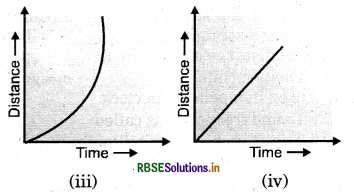
Answer:
(iii)

- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Electric Current and its Effects
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 Motion and Time
- RBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- RBSE Class 6 Science Notes Chapter 8 शरीर में गति
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 18 Wastewater Story
- RBSE Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 17 Forests: Our Lifeline