RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 12. Students can also read RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemistry in Everyday Life InText Questions and Answers
Question 16.1.
Sleeping pills are recommended by doctors to the patients suffering from sleeplessness but it is not advised to take its doses without consultation with doctors, why?
Answer:
Sleeping pills contain drugs which may be tranquilizers or antidepressants. They affect the nervous system and induce sleep. If they taken in doses higher than recommended may produce harmful effects and act as poison and cause even death. Therefore, it is advisable to take these sleep ing pills under strict supervision of a doctor.

Question 16.2.
With reference to which classification has the statement "ranitidine is an antacid" been given?
Answer:
Renitidine is labelled as antacid since it is quite effective in neutralizing the excess of acidity in the stomach hence this statement refers to the classification of drugs according to pharmacological effect.
Question 16.3.
Why do we require artificial sweetening agents?
Answer:
To reduce calorie intake and to protect teeth from decaying, we need artificial sweeteners.
Question 16.4.
Write the chemcial equation for preparing sodium soap from glycerol oleate and glyceryl palmitate. Structures of these compounds are given below:
(i) (C15H31 COO)3.C3H5 - Glyceryl palmitate
(ii) (C17H33COO)3 C3H5 - Glyceryl Oleate
Answer:
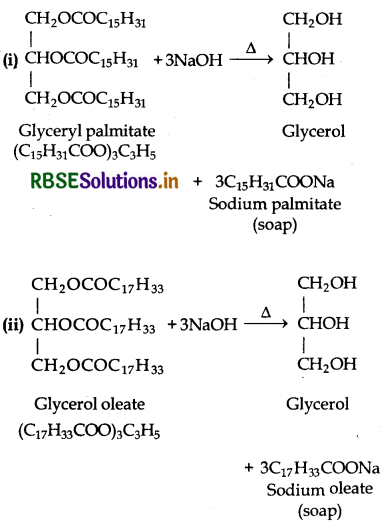
Question 16.5.
Following type of non-ionic detergents are present in liquid detergents, emulsifying agents and wetting agents. Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the molecule. Identify the functional group (s) present in the molecule.
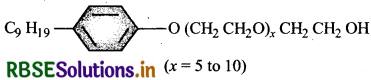
Answer:
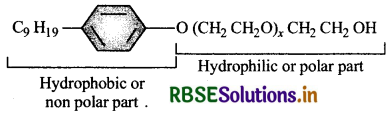
Functional groups present in the detergent molecules are:
- ether and
- primary (1) alcoholic group.
RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chemistry in Everyday Life Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 16.1.
Why do we need to classify drugs in different ways?
Answer:
There are a large variety of drugs for different purpose of diagnosis, prevention, relief or cure of various diseases. These drugs have been classified in different ways on the following basis:
- On the basis of pharmacological effect
- On the basis of drug action
- On the basis of chemical structure and
- On the basis of molecular targets

Question 16.2.
Explain the term, target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry.
Answer:
A knowledge of the physiological function of the drug target in the body helps us to choose a compound which can interact with the target molecule. These compounds are called lead compounds and drugs are designed from these compounds. Drugs interact with biomolecules like proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic ac known as target molecules or drug targets. For example, proteins which act as biocatalysts are called enzymes and those which are involved in communication system are called receptors. Lipids and carbohydrates form structural part of cell membranes and nucleic acids have coded informations in the cell.
Question 16.3.
Name the macromolecules which are chosen as drug targets.
Answer:
Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids.
Question 16.4.
Why should not medicines be taken without consulting the doctors?
Answer:
The drugs or medicines have side effects also. These are caused when a drug binds to more than one receptor site. Furthermore their wrong choice and overdose can cause toxicity and may even cause death. Therefore, it is necessary that the medicines should not be taken without consulting the doctors.
Question 16.5.
Define the term Chemotherapy.
Answer:
The branch of chemistry which deals with the treatment of various diseases using chemical substances is called Chemotherapy.

Question 16.6.
Which forces are involved in holding the drugs to the active site of enzymes?
Answer:
Hydrogen bonding ionic bonding dipole-dipole interactions or van der Waals interactions.
Question 16.7.
While antacids and antiallergic drugs interfere with the function of histamines, why do these not interfere with the function of each other?
Answer:
They do not interfere with the functioning of each other because they work on different receptors in the body.
Question 16.8.
Low level of noradrenaline is the cause of depression. What type of drugs are needed to cure this problem? Name two drugs.
Answer:
Low level of noradrenaline (neurotransmitter) reduces the signal sending activity to the nerves and the per son suffers from depression. In such cases, the patient needs anti-depressant drugs that inhibit the enzymes which catalyse the degradation of noradrenaline. The two drugs are iproniazid and phenelzine.
Question 16.9.
What is meant by the term broad spectrum antibiotics? Explain.
Answer:
Antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria are said to be broad spectrum antibiotics. For example: tetracycline, chloramphenicol, ofloxacin, etc. They cure many diseases. For example : chloramphinical can be used in case of typhoid, dysentery, acute fever, urinary infections, maningitis, pneumonia, etc.

Question 16.10.
How do antiseptics differ from disinfectants ? Give an example of each.
Answer:
Chemical substances which prevent the growth of microorganisms and even kill them but are safe to be applied to the living tissues are called antiseptics. They are generally used on wounds, cuts, ulcers and diseased skin surfaces. For example: dettol, savlon, furacin, soframycin, etc. Chemical substances which kill microorganisms but are not safe to be applied to the living tissues are called disinfectants. These are generally used to kill microorganisms present in the drains, toilets floors, etc. For example: phenol (21% solution) and chlorine (04 ppm).
Question 16.11.
Why are cimitidine and ranitidine better antacids than sodium hydrogen carbonate or magnesium or aluminimum hydroxide?
Answer:
Both sodium bicarbonates and hydroxides of magnesium or aluminium are very good antacids since they neutralize the excess of HCl and raise the pH value to appropriate level in stomach. But their prolong use can cause the secretion of excessive acid in the stomach. This may quite harmful and may lead to the formation of ulcers. Both cimitidine and ranitidine are better antacids without any side effects.
Question 16.12
Name a substance which can be used as an antiseptic as well as disinfectant.
Answer:
02% solution of phenol acts as antiseptic while its 1% solution acts as disinfectant.

Question 16.13.
What are main constitutents of dettol?
Answer:
Chloroxylenol and a-terpineol in a suitable solvent.
Question 16.14.
What is tincture of iodine? What is its use?
Answer:
Tincture of iodine is a 2-3% solution of iodine in alcohol and water. It is a powerful antiseptic and is applied on wounds.
Question 16.15.
What are food preservatives?
Answer:
Chemical substances which are used to protect food materials against various microorganism i.e.,bacteria, yeasts, moulds etc are konwn as food preserva- tives. For example: sodium benzoate, sodium metabisulphite, p-hydroxybenzoate esters, etc.
Question 16.16.
Why is use of aspartame limited to cold foods and drinks?
Answer:
Aspartame decomposes at cooking or baking temperatures and hence can be used only in cold foods and drinks.
Question 16.17.
What are artificial sweetening agents? Give two examples.
Answer:
Artificial sweeteners are the chemical compounds which give sweetening effect to the food and enhance its odour and colour also. They do not add to calorie intake. For example: Saccharin, aspartame, alitame, sucralose, L- glucose, etc.
Question 16.18.
Name the sweetening agent used in the preparation of sweets for a diabetic patient.
Answer:
Saccharin, aspartame or alitame.

Question 16.19.
What problem arises in using alitame as artificial sweetener?
Answer:
Alitame is a high potency artificial sweeteners. Therefore it is very difficult to control the sweeteners of the food article to which it is added.
Question 16.20.
How are synthetic detergents better than soap?
Answer:
Synthetic detergents can be used in hard water as well as in slightly acidic medium. The reason being that sulphonic acids and their calcium and magnesium salts are water soluble while the fatty acids and their calcium and magnesium salts are insoluble in water.
Question 16.21.
Explain the following terms with suitable examples:
(a) cationic detergents
(b) anionic detergents
(c) neutral detergents.
Answer:
(a) cationic detergents:
Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with anions as acetates, chlorides or bromides . The cationic part consists of a long hydrocarbon chain and a positively charge Nitrogen atom. The centre ammonium sulphate is positively charged. Fabrics can easily absorb cationic detergents.
example: quaternary ammonium compounds, benzalkonium chloride and cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide.
(b) anionic detergents:
Anionic Detergents are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons. They have anions at the soluble ends of the chains. E.g: Sodium Lauryl sulphate and sodium n-dodecyl benzene sulphonate.
(c) neutral detergents:
Multi-Purpose Neutral Cleaner EKO-PLUS Lalema. Safeblend, Neutral Cleaner, Orange Fragrance Safeblend. Fragrance Free All-Purpose Neutral Cleaner NEUTRAC Lalema. All-Purpose Low Foam Neutral Cleaner OPTINET Lalema. High Performance General Purpose Cleaner GP Forward Solution Center Diversey

Question 16.22.
What are biodegradable and non-biode- gradable detergents ? Give one example of each.
Answer:
Synthetic detergents having straight hydro- carbon chains are easily degraded by microorganisms are called biodegradable detergents. For example, sodium lauryl sulphate, sodium 4-(1-dodecyl) benzene sulphonate and sodium 4-(2-dodecyl) benzene sulphonate. On the other hand, detergents containing branched hydrocarbon chains are not easily degraded by microor- ganisms are called non-biodegradable detergents. For ex- ample, sodium 4-(1, 3, 5, 7 tetramethyloctyl) benzene sul- phonate.
Question 16.23.
Why do soap not work in hard water?
Answer:
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. Therefore soaps produce curdy white precipitate of calcium and magnesium salts of fatty acids which being insoluble in water stick to the clothes as gummy mass.
Question 16.24.
Can you use soaps and synthetic detergents to check the hardness of water?
Answer:
Soaps get precipitated as insoluble calcium or magnesium salts of fatty acids but detergents do not. There- fore, soaps but not synthetic detergents can be used to check the hardness of water.
Question 16.25.
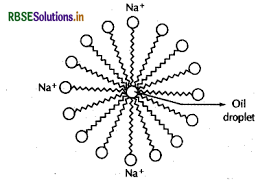
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer:
Cleansing action of soaps :
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the crustel. These micelles remain suspended in the water. Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.

Question 16.26.
If water contains dissolved calcium hydro- gen carbonate (or Ca2+ ions) out of soaps and synthetic detergents, which one will use for cleansing clothes?
Answer:
Calcium carbonate makes water hard. Soaps will give curdy precipitate with hard water and therefore can not be used for cleaning clothes. On the other hand, a syn- thetic detergent does not give precipitate in hard water be- cause its calcium salt is water soluble. Therefore, synthetic detergents can be used for cleansing clothes in such water.
Question 16.27.
Label the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts in the following compounds.
(a) CH3(CH2)10 CH2OSO3- Na+
(b) CH3(CH2)15 - N(CH3)3 Br-
(c) CH3(CH2)16 COO(CH2CH2O)n CH2CH2OH
Answer:
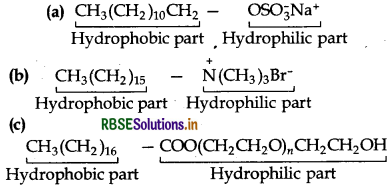

- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 16 दैनिक जीवन में रसायन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 15 बहुलक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 14 जैव-अणु
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 13 ऐमीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 12 ऐल्डिहाइड, कीटोन एवं कार्बोक्सिलिक अम्ल
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 11 ऐल्कोहॉल, फीनॉल एवं ईथर
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 10 हैलोऐल्केन तथा हैलोऐरीन
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 9 उपसहसंयोजन यौगिक
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 8 d- एवं f-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 7 p-ब्लॉक के तत्व
- RBSE Class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 6 तत्वों के निष्कर्षण के सिद्धांत एवं प्रक्रम