RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Solutions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Financial Statements-I Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Following balances are abstract from the books of Simmi & Vimmi Ltd. Calculate Gross Profit for the year ending as on 31st March 2013.

Solution:
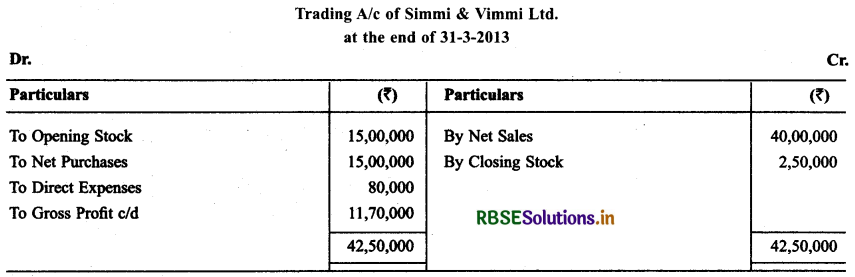

Question 2.
Following balances are abstract from the books of M/s Ahuja & Nanda. Calculate the following amount:
(a) Cost of goods available for sale
(b) Cost of goods sold during the year
(c) Gross Profit

Solution:
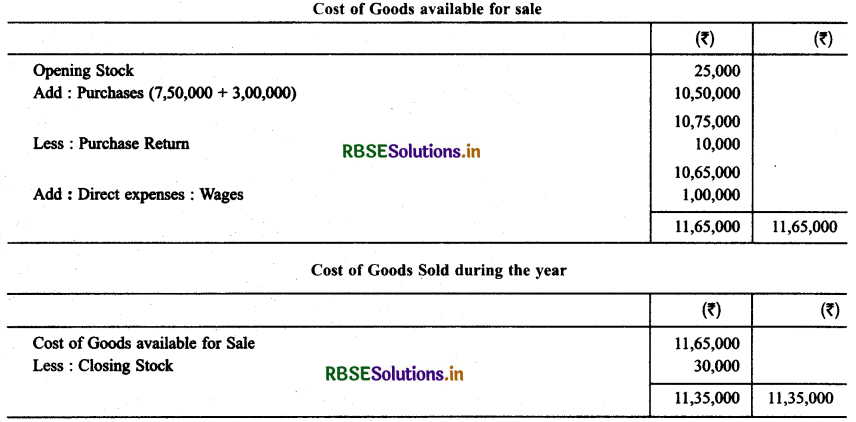
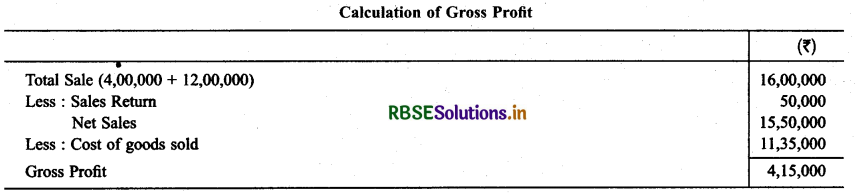

Question 3.
With the help of balances taken from the books of M/s Rajeev & Sons. Calculate Gross profit and operating profit at the end of March 31, 2015.
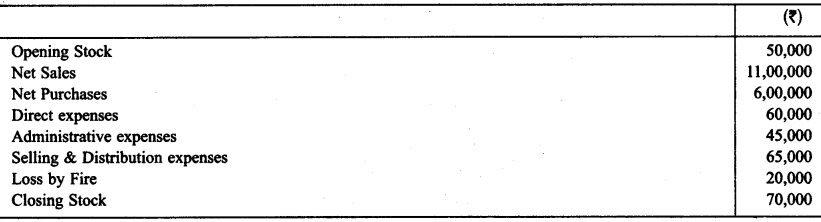
Solution:
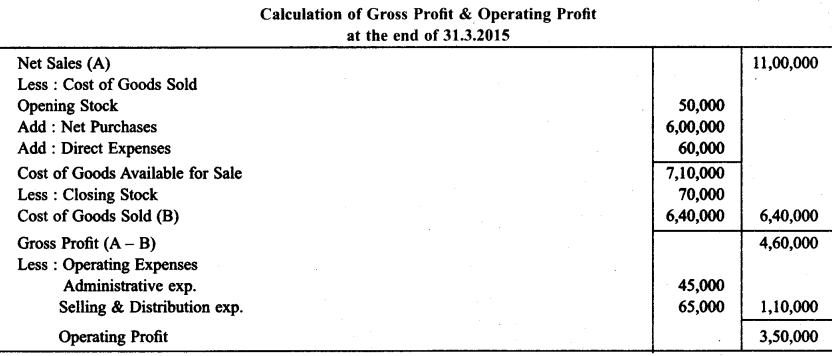
Question 4.
During the year 2005-06, M/s Arora & Sachdeva earn an operating profit of ₹17,00,000. During the year there non operating incomes were ₹ 1,50,000 & Non Operating expenses were ₹ 3,75,000. Calculate net profit earned by the company.
Solution:
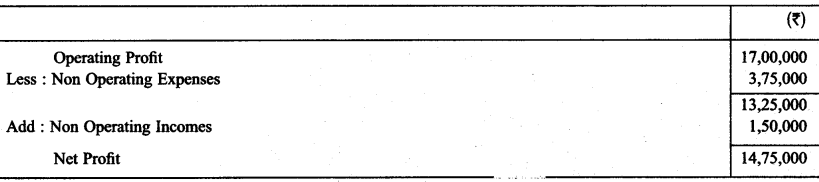
Question 5.
Following balances are abstracted from the trial balance of M/s Bhola & Sons as on March 31, 2015:

Closing Stock was ₹ 3,00,000 on this date. You are required to make. Journal Entries as per need and show these items in the trading & P & L and Balance Sheet of M/s Bhola & Sons.
Solution:
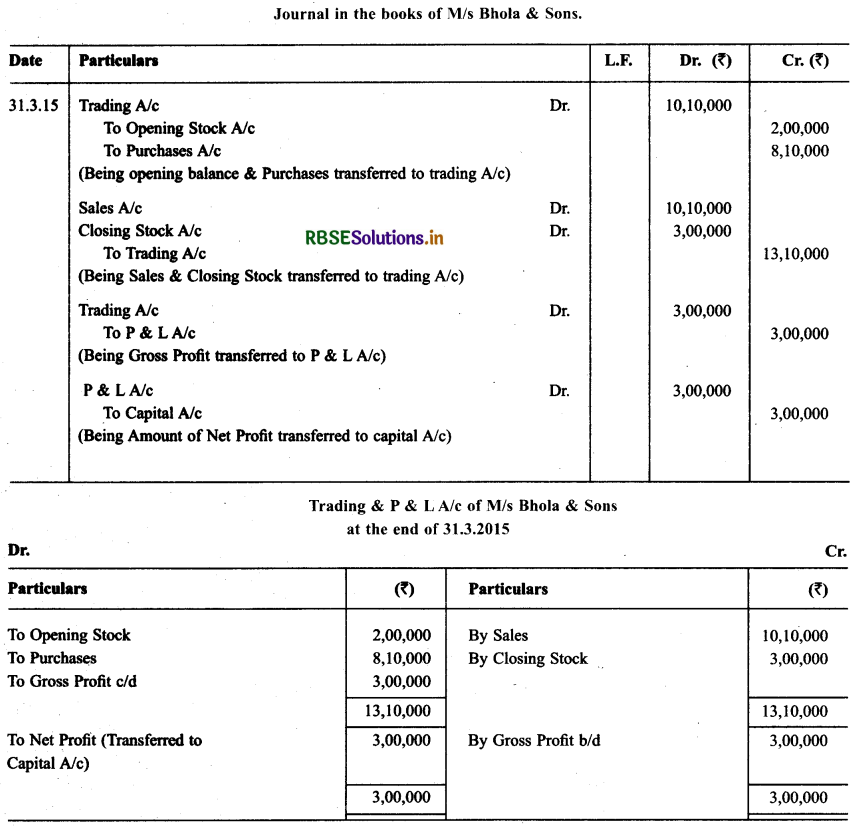
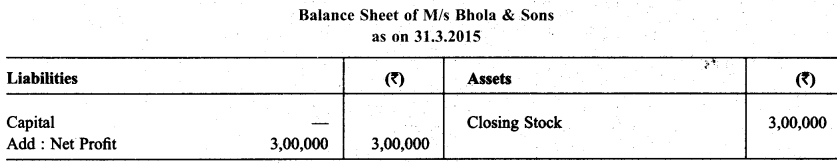

Question 6.
Prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as on March 31, 2015.
Solution:
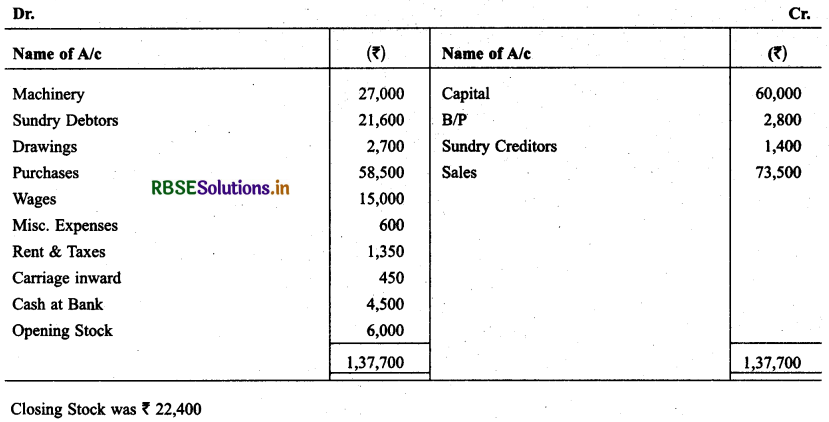
Question 7.
Following trial Balance is taken from the books of M/s Ram as on March 31, 2014. You are required to prepare. Trading & P & L and Balance Sheet on this date.
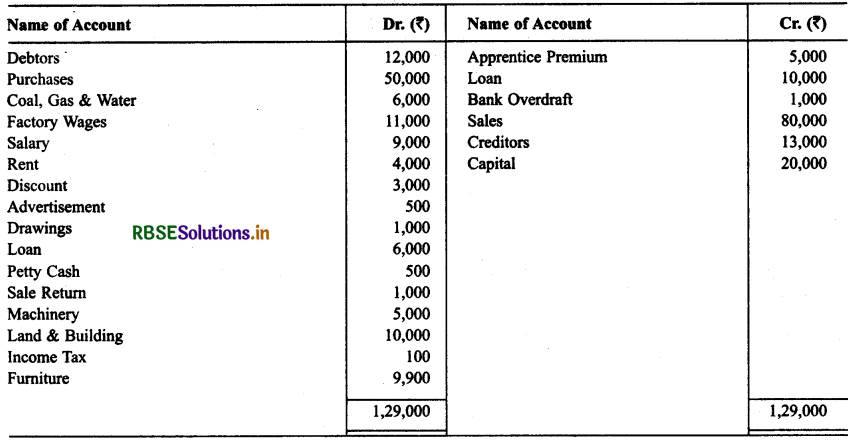
Solution:
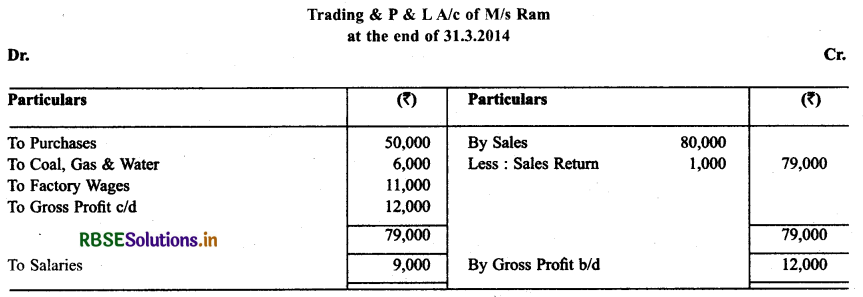
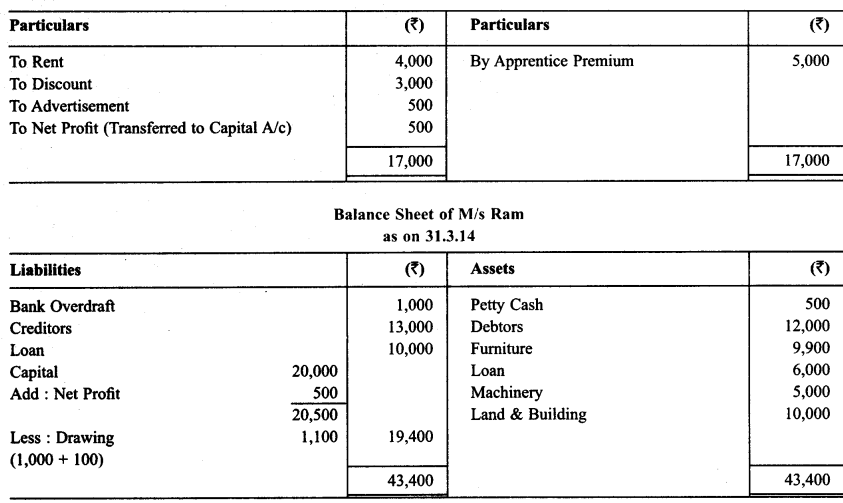
Question 8.
Following Trial Balance of Manju Chawla is taken as on March 31, 2015. You are required to prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as on date.
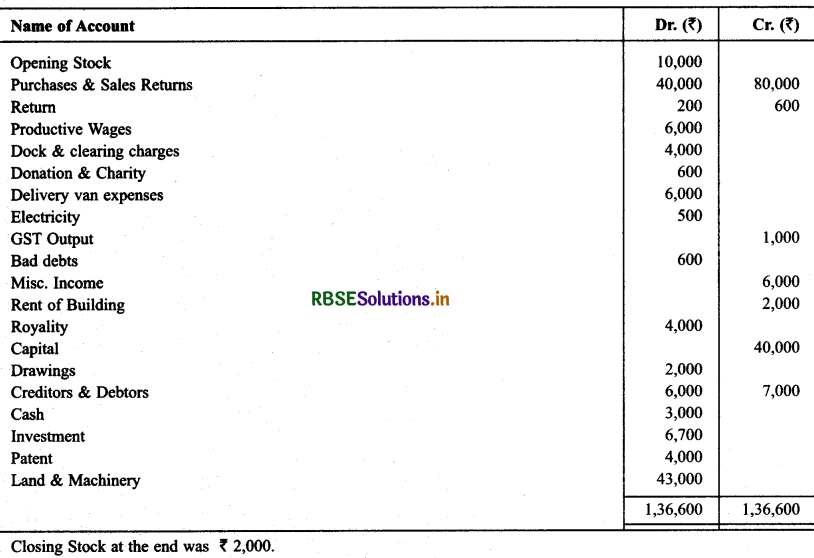
Solution:
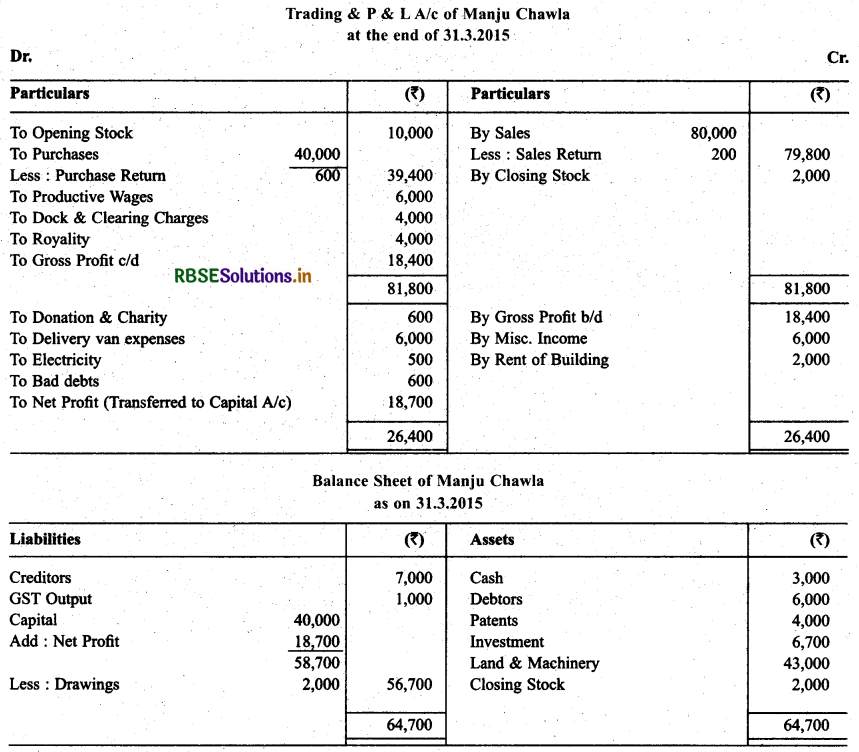

Question 9.
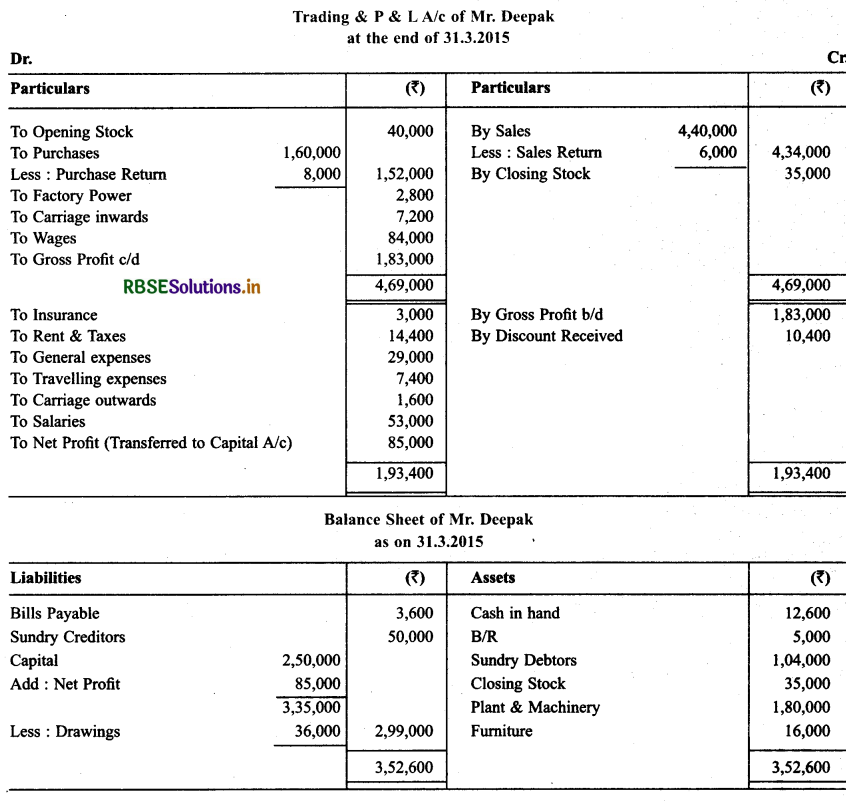
Following is the trial balance of Mr. Deepak as on March 31, 2015. You are required to prepare Trading and P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as on date while closing stock is ₹ 35,000.
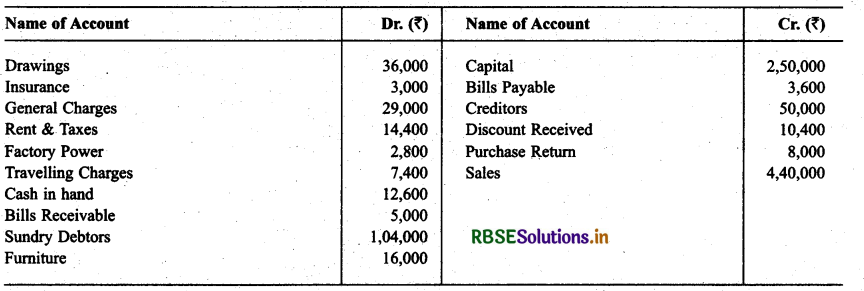
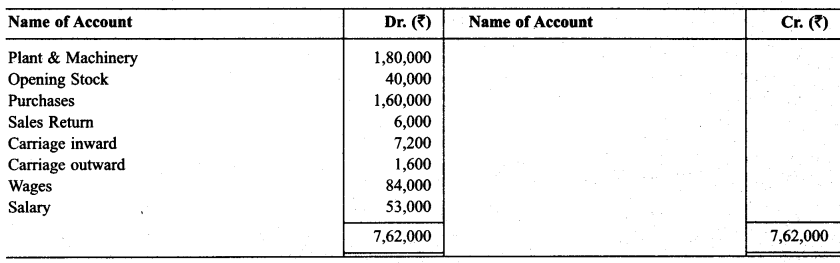
Solution:
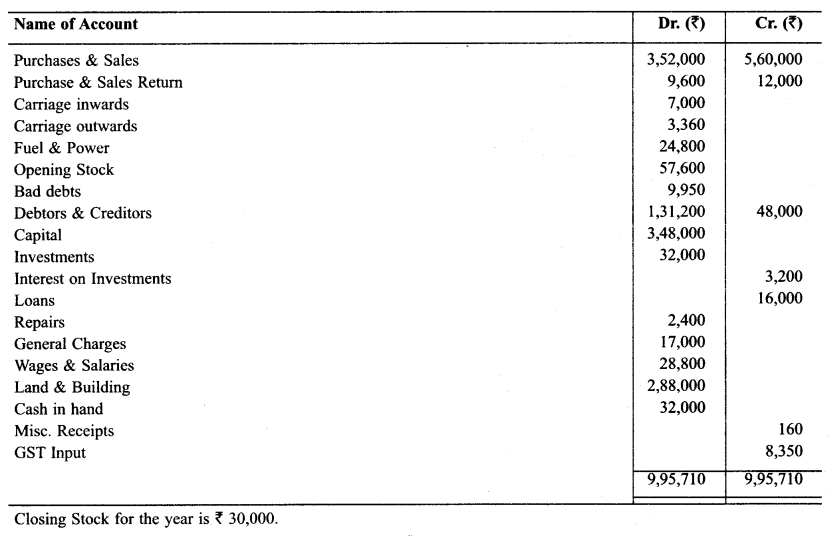
Question 10.
Prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as on March 31, 2013 with the help of following particulars.
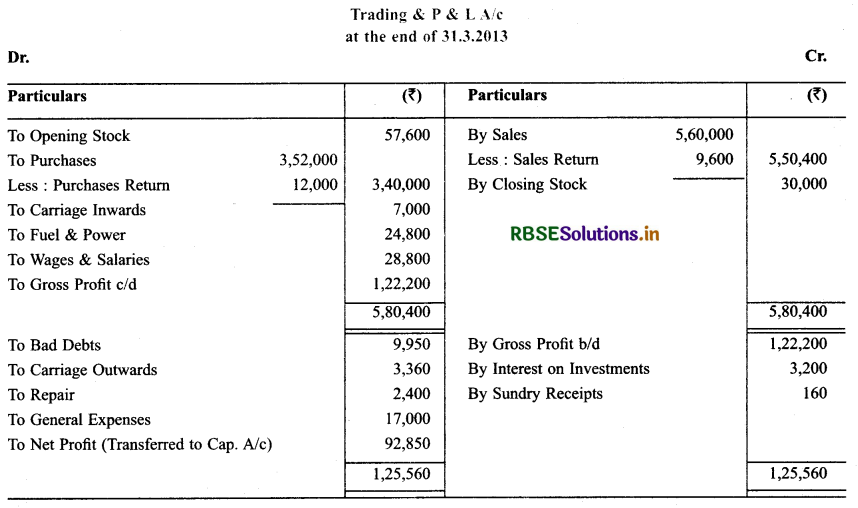
Solution:
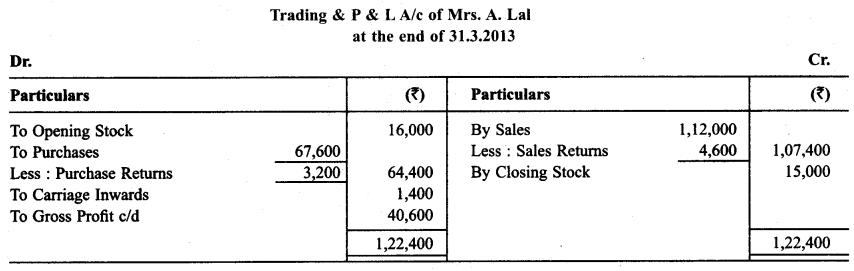
Question 11.
Prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as on March 31,2013 with the help of under mentioned trial balance.)

Solution:
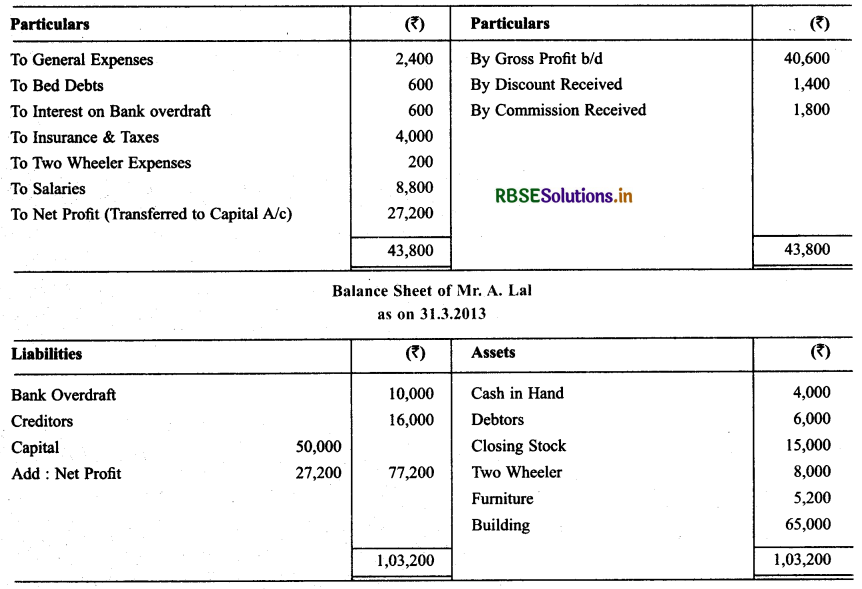

Question 12.
From the following balances of M/s Royal Traders. Prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as on 31.3.2015
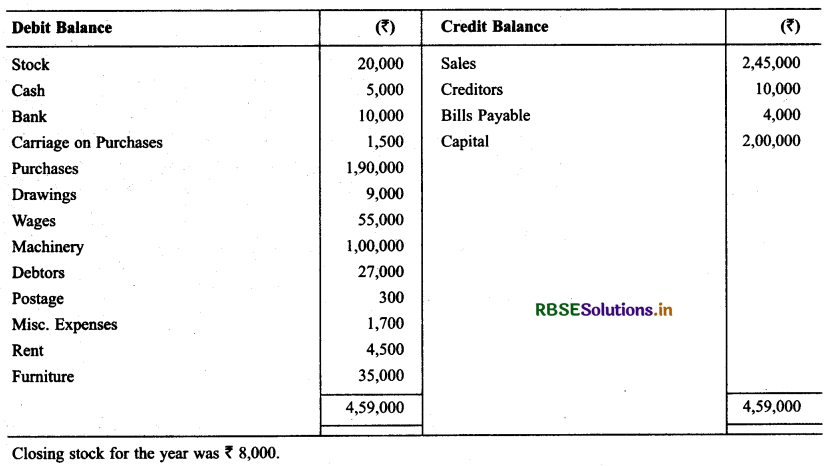
Solution:
Question 13.
Prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet of M/s Neema Traders as on 31.3.2015 from the following particulars.
Solution:
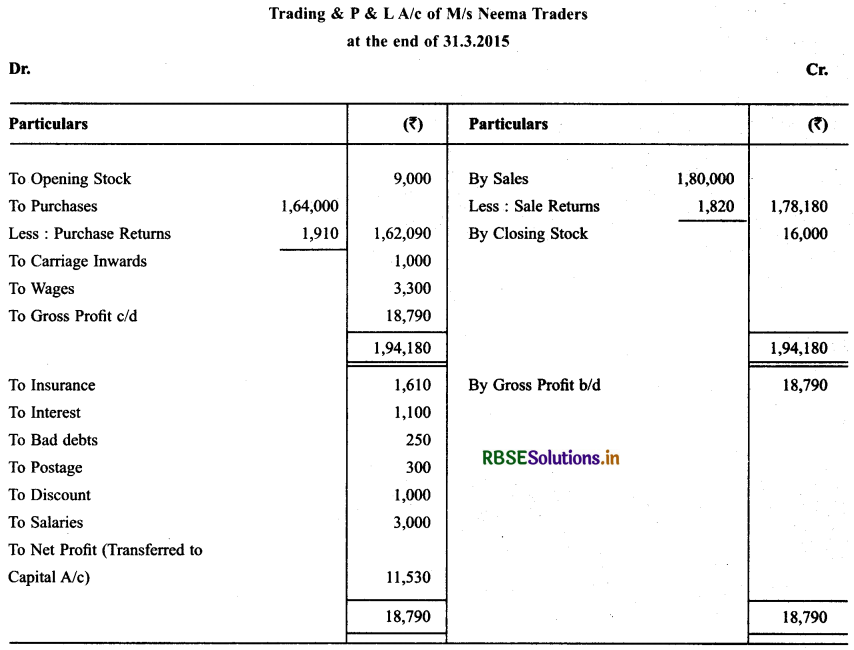
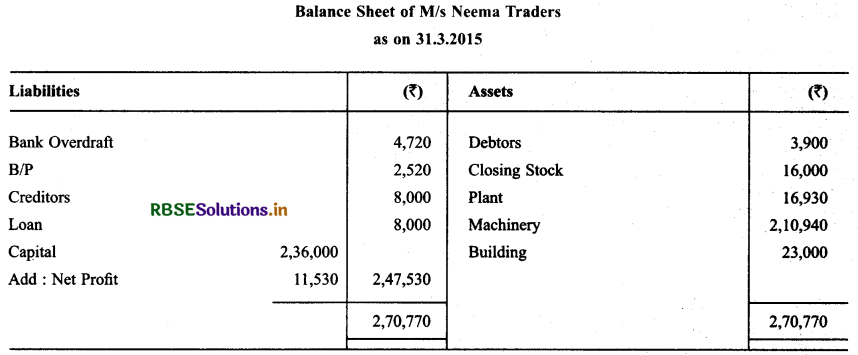
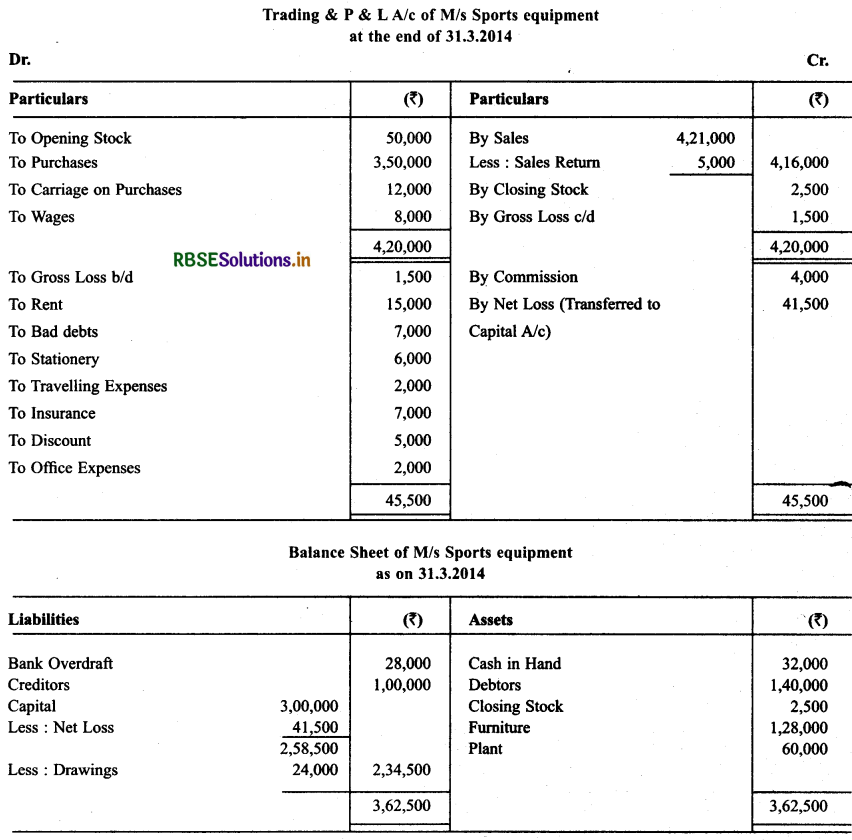
Question 14.
From the following balances of M/s Neelu Saree, prepare Trading & P & L A/c and Balance Sheet as oh March 31,2013.
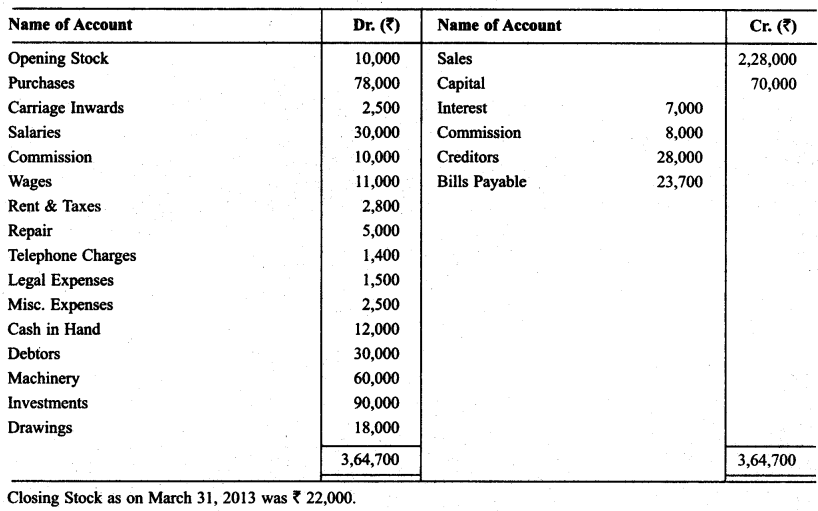
Solution:
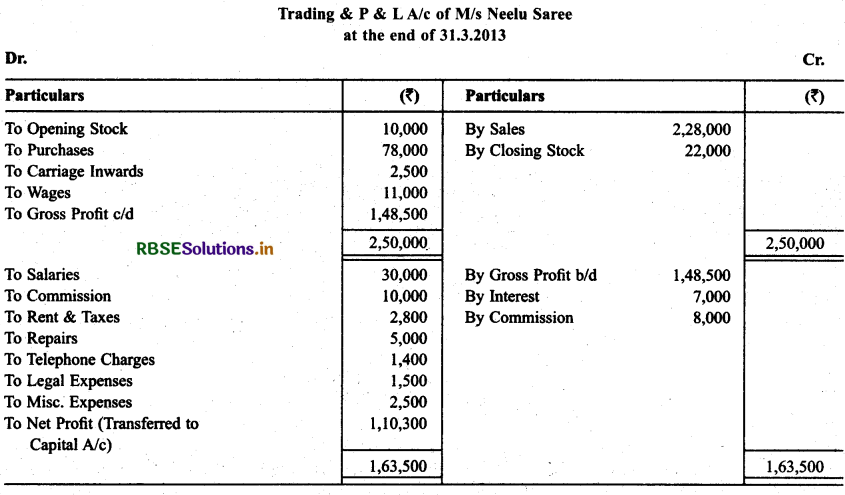

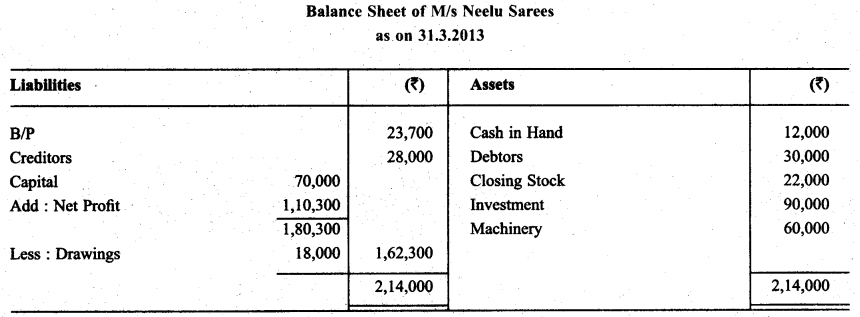

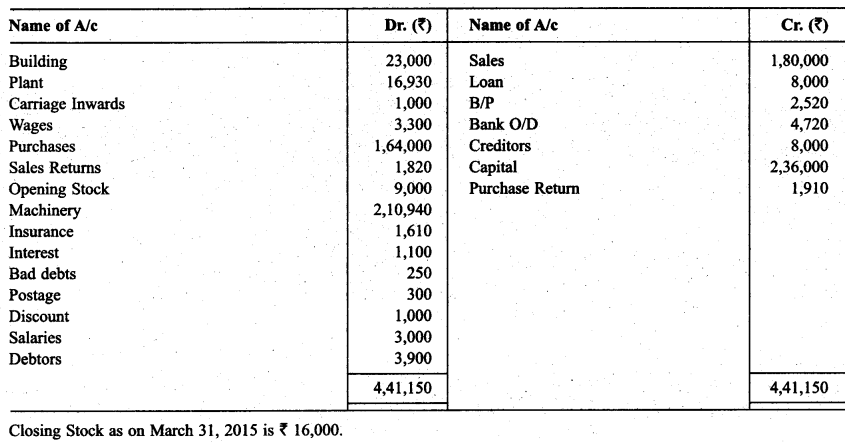
Question 15.
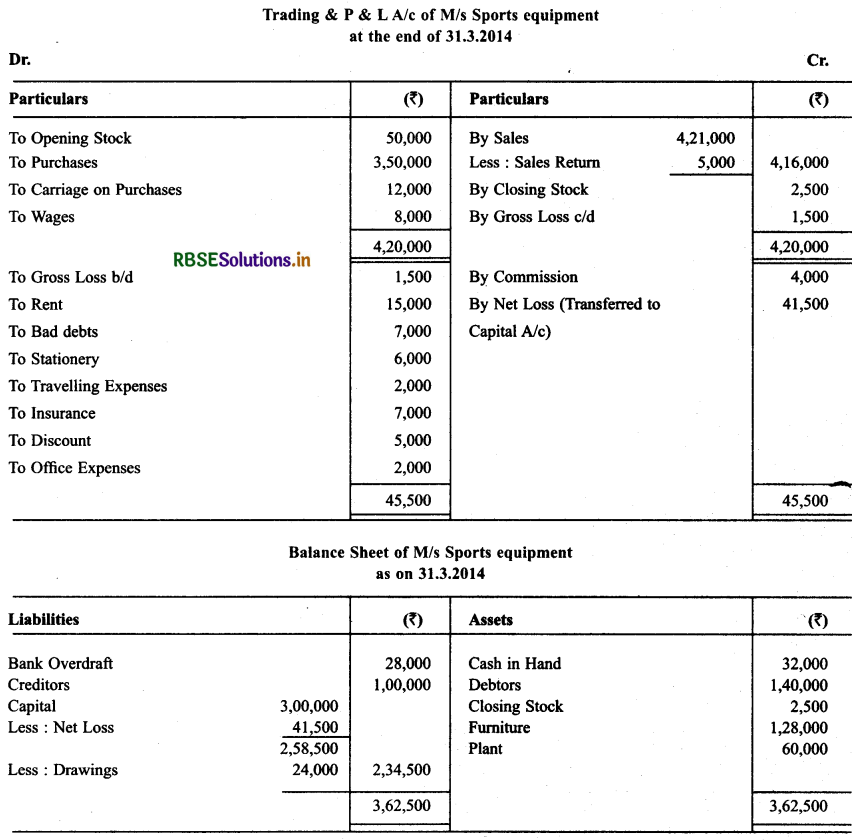
From the following balances of M/s Sports equipment, prepare trading & P & L A/c at the end of March 31, 2014 & Balance Sheet as on that date.
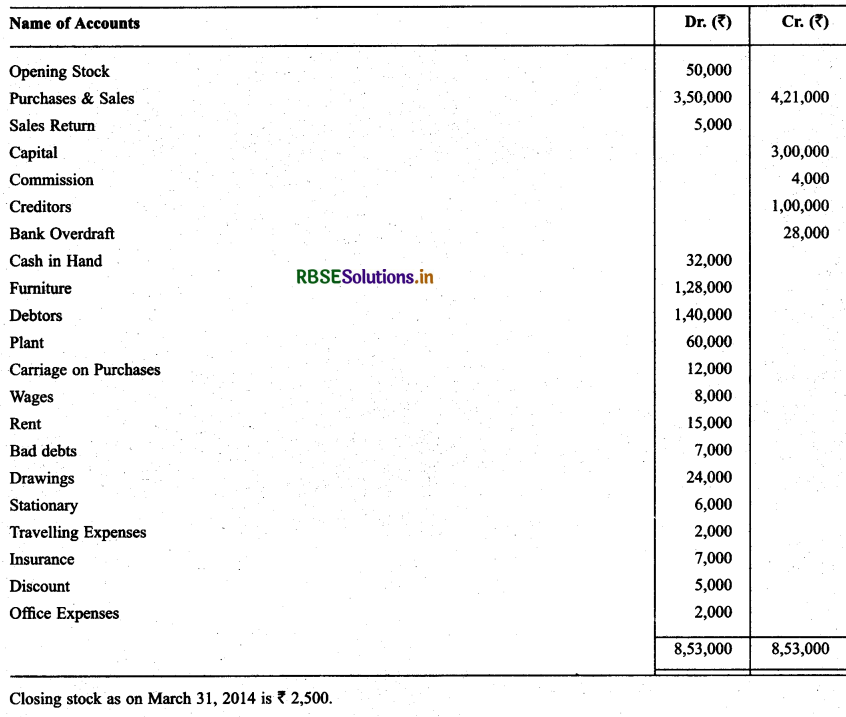
Solution:
Test Your Understanding I.
l. State True or False:
(i) Gross profit is total revenue.
(ii) In trading and profit and loss account, opening stock appears on the debit side because it forms the part of the cost of sales for the current accounting year.
(iii) Rent, rates and taxes is an example of direct expenses.
(iv) If the total of the credit side of the profit and loss account is more than the total of the debit side, the difference is the net profit.
Answers:
I. (i) T
(ii) T
(iii) F
(iv) T
II. Match the items given under ‘A’ with the correct items under ‘B’
(i) Closing stock is credited to -- (a) Trial balance
(ii) Accuracy of book of account is tested by -- (b) Trading account
(iii) On returning the goods to seller, the buyer sends -- (c) Credit note
(iv) The financial position is determined by -- (d) Balance sheet
(v) On receiving the returned goods from the sends -- (e) Debit note buyer, the seller
Answers:
(i) (b) (ii) (a) (iii) (e) (iv) (c) (v) (d)

Test Your Understanding II
Choose the correct option in the following questions:
Question 1.
The financial statements consist of:
(i) Trial balance
(ii) Profit and Loss Account
(iii) Balance sheet
(iv) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
(iv) (i) & (iii)
Question 2.
Choose the correct chronological order of ascertainment of the following profits from the profit and loss account:
(i) Operating Profit, Net Profit, Gross Profit
(ii) Operating Profit, Gross Profit, Net Profit
(iii) Gross Profit, Operating Profit, Net Profit
(iv) Gross Profit, Net Profit, Operating Profit
Answer:
(iii) Gross Profit, Operating Profit, Net Profit
Question 3.
While calculating operating profit, the following are not taken into account.
(i) Normal transactions
(ii) Abnormal items
(iii) Expenses of a purely financial nature (iv) (ii) & (iii)
(v) (i) & (iii)
Answer:
(iii) Expenses of a purely financial nature (iv) (ii) & (iii)
Question 4.
Which of the following is correct:
(i) Operating Profit = Operating profit - Non-operating expenses - Non-operating incomes
(ii) Operating profit = Net profit + Non-operating Expenses + Non-operating incomes
(iii) Operating profit = Net profit + Non-operating Expenses - Non-operating incomes
(iv) Operating profit = Net profit - Non-operating Expenses + Non-operating incomes
Answer:
(iii) Operating profit = Net profit + Non-operating Expenses - Non-operating incomes

Short Answers Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the objectives of preparing Financial Statements?
Solution:
Objectives of preparing financial statements:
- Help to determine financial position
- Help to Determine Gross Profit and Gross Loss
- Help to Determine Net Profit and Net Loss
- Comparison with Previous Year’s Profit
- Analysis of Individual items
- Details of Direct and Indirect Expenses
Question 2.
What are the main purpose of preparing Trading A/c?
Solution:
The purposes of preparing Trading and Profit & Loss Account:
- Trading account of a business concern is prepared to calculate the Gross Profit or Gross Loss.
- Trading account helps us to find out cost of goods sold.
- It helps in comparing the stock of current year and previous year.
- It shows direct costs.
The purposes of preparing Trading and Profit & Loss Account:
- Profit and loss account of a business concern is prepared to calculate Net Profit or Net Loss.
- It shows indirect expenses and indirect incomes.
- It also helps us to know operating and non-operating items.
Question 3.
Explain the concept of ‘Cost of Goods Sold’.
Solution:
Cost of goods sold: It is cost of those goods (including all direct expenses) which are sold in the current year.
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Net Purchases + All Direct Expenses - Closing Stock
Question 4.
What is a Balance Sheet? What are its characteristics?
Solution:
Balance Sheet: The last step in the preparation of final accounts is the preparation of Balance Sheet. It is a classified summary of the balances remaining open in a set of books. It is a “SHEET’ of all those ledger “BALANCES” relating to the assets owed and liabilities owed by the business on a particular date. It is a statement containing all the unclosed balances of “Real” and “Personal” accounts.

Characteristics of balance sheet:
- Balance Sheet is a snapshot of the financial position of the business
- It is a statement and not an account
- This is the last step in the process of the preparation of final accounts
- There will always be an agreement in the totals of the two sides of a correct Balance Sheet
- This statement is prepared at the end of the accounting period
- It consists of all real accounts and personal accounts
- The Balance Sheet consists of two sides namely, Liabilities and Assets.
- The total value of liabilities (liabilities to outsiders and capital of the proprietor) is always equal to the total value of the assets. Assets = Liabilities + Owners equity
Question 5.
Distinguish between capital and revenue expenditure and state whether the following statements are items of capital or revenue expenditures:
(a) Expenditure incurred on repairs and whitewashing at the time of purchase of an old building in order to make it usable.
(b) Expenditure incurred to provide one more exit in a cinema hall in compliance with a government order.
(c) Registration fees paid at the time of purchase of a building.
(d) Expenditure incurred in the maintenance of a tea garden which will produce tea after four years.
(e) Depreciation charged on a plant.
(f) The expenditure incurred in erecting a platform on which a machine will be fixed.
(g) Advertising expenditure, the benefits of which will last for four years.
Answer:
Difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure
|
Basis |
Capital expenditure |
Revenue expenditure |
|
Earning capacity |
To increase earning capacity |
To maintain revenue capacity |
|
Purpose |
To acquire fixed assets |
To conduct day to day conduct of business |
|
Nature |
Non-recurring in nature |
Recurring in nature |
|
Period of benefit |
Its benefit extends for more than one year |
Its benefit accrues within an accounting year |
Nature of expenditures in transactions
(a) Capital expenditure
(b) Capital expenditure
(c) Capital expenditure
(d) Capital expenditure
(e) Revenue expenditure
(f) Capital expenditure
(g) Deferred Revenue Expenditure

Question 6.
What is operating Profit?
Solution:
Operating profit is earned with the help of normal business (operating) activities. Operating profits are the excess of operating income over operating expenses. Financial expenses and abnormal items are not included in operating expenses.
Operating profit = Gross profit - Other Operating expenses + Other Operating Incomes
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are financial statements? What information do they provide?
Solution:
Meaning: Financial statement refer to the end results of financial transactions taken place during a particular period. The end results are in the form of profit or loss and financial statements.
Types of financial statements:
(a) Trading, Profit and Loss Account: It is prepared to find out gross profit, net profit and operating profit for the year ended.
(b) Balance Sheet: It is prepared to know financial position in the form of assets and liabilities at the end of the year.
Question 2.
What are closing entries? Give four examples of closing entries.
Solution:
Closing Journal Entries: When the nominal accounts are closed by transferring to either trading account, profit and loss account, such entries are called closing entries which are made in the Journal proper.
Note: No entries are passed for real accounts and personal accounts. They are directly transferred to balance sheet.
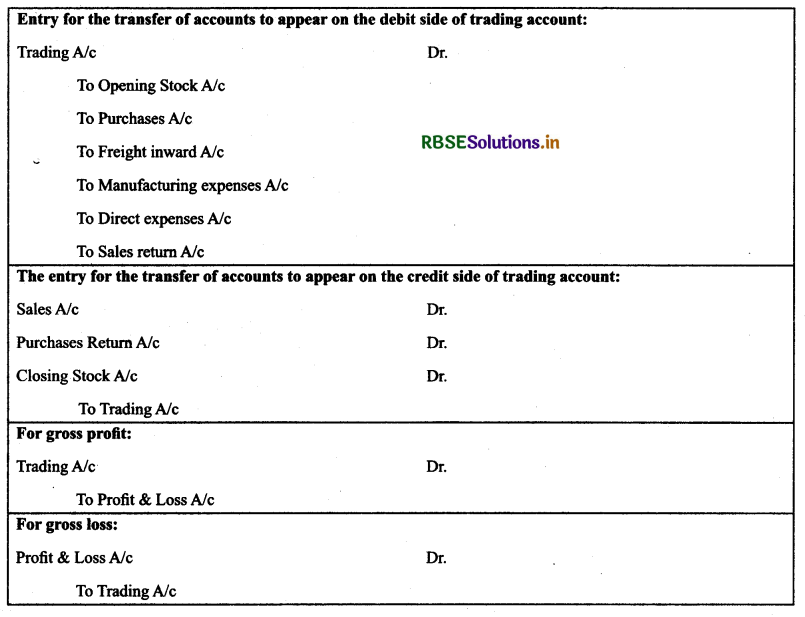
Question 3.
Discuss the need of preparing a balance sheet.
Solution:
Balance sheet is a statement of all assets and liabilities at the end of an accounting year. Need of preparing balance sheet:
- It depicts financial statement in the form personal accounts and real accounts.
- It shows sources of funds in the form of liabilities and application of funds in the form of assets.
- It helps the investors take decision on investment in an enterprise.
- It helps the management prepare strategies how to improve financial position.

Question 4.
What is meant by Grouping and Marshalling of assets and liabilities? Explain the ways in which a balance sheet may be marshalled.
Solution:
Marshalling of assets and liabilities refers to styles of preparing balance sheet. There are two ways to prepare balance sheet:
(a) Order of Liquidity: Under liquidity order assets which are realisable in cash most easily are shown first and the assets which are most difficult to realise are shown in the end.
(b) Order of Permanence: On the basis of this order, fixed assets such as Land & Buildings, Plant & Machinery, Furniture, etc., are shown first, and these are followed by floating assets such as stock, debtors etc. The item which has practically no permanence is cash and it is shown at the end.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors