RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Solutions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors
RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors Textbook Questions and Answers
Test Your Understanding I.
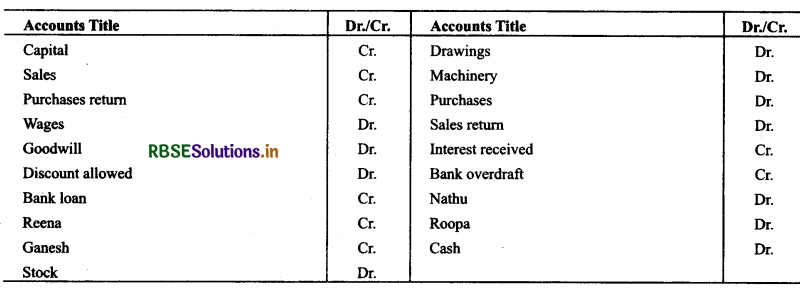
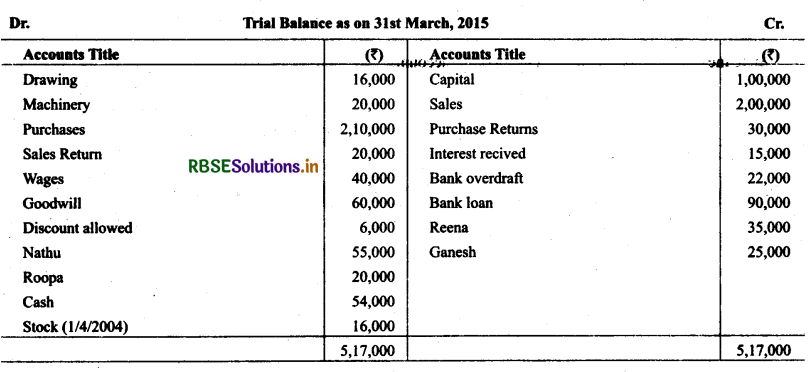
Indicate against each amount whether it is a debit or a credit balance, and prepare a trial balance as at March 31, 2015 based on the following balances:
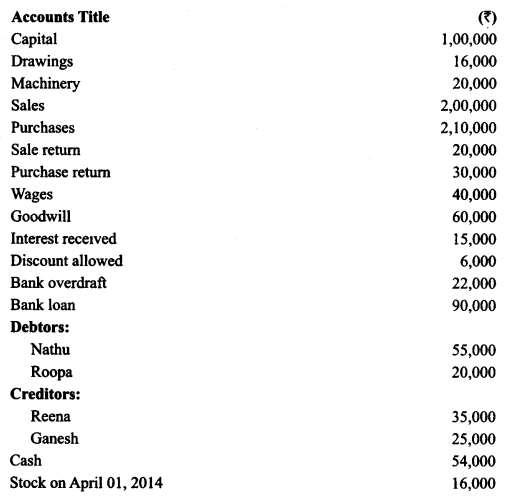
Solution :

Test Your Understanding II
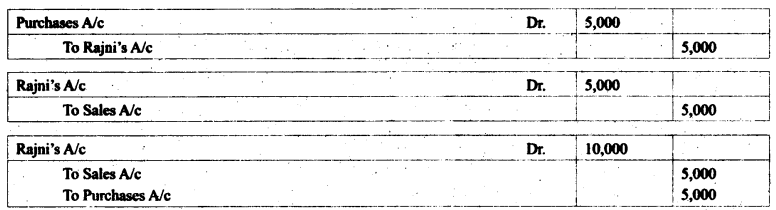
Record the rectification entry for the following transactions:
Question 1.
Credit sales to Rajni ₹ 5,000 recorded in Purchase book:
This is an error of ..................

2. Furniture purchased from M/s Rao Furnishings for ₹ 8,000 was entered into the purchases book.
This is the error of ..................

3. Cash sales to Radhika ₹ 15,000 was shown as receipt of commission in the cash book.
This is the error of ..................

4. Cash received from Karim ₹ 6,000 posted to Nadeem.
This is the error of ..................

Answer:
1. Commission
2. Principle
3. Commission
4. Commission
1.
2.


3.

4.

Test Your Understanding III.
Show the effect through Journal entries:
1. Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 10,000 were posted to his account as ₹ 12,000
This is an ..................

2. Cash paid to Neha ₹ 2,000 was not posted to her account.
This is an error of ...........


3. Sales returns from Megha ₹ 1,600 were posted to her account as ₹ 1,000.
This is an error of ....................

4. Depreciation written off on furniture ₹ 1,500 was not posted to depreciation account.
This is an error of ................
The wrong effect has been:

Answers:
1. Error of Commission

2. Error of Partial Omission


3. Error of Commission

4. Error of Commission

Test Your Understanding IV
Tick the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
Agreement of trial balance is affected by:
(a) One sided errors only
(b) Two sided errors only
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) One sided errors only
Question 2.
Which of the following is not an error of principle?
(a) Purchase of furniture debited to purchases account
(b) Repairs on the overhauling of second hand machinery purchased debited to repairs account
(c) Cash received from Manoj posted to Saroj
(d) Sale of old car credited to sales account
Answer:
(c) Cash received from Manoj posted to Saroj
Question 3.
Which of the following is not an error of commission?
(a) Overcasting of sales book
(b) Credit sales to Ramesh ₹ 5,000 credited to his account
(c) Wrong balancing of machinery account
(d) Cash sales not recorded in cash book
Answer:
(d) Cash sales not recorded in cash book

Question 4.
Which of following errors will be rectified through suspense account?
(a) Sales return book undercast by ₹ 1,000
(b) Sales return by Madhu ₹ 1,000 not recorded
(c) Sales return by Madhu ₹ 1,000, recorded as ₹ 100
(d) Sales return by Madhu ₹ 1,000 recorded through purchases returns book
Answer:
(a) Sales return book undercast by ₹ 1,000
Question 5.
If the trial balance agrees, it implies that:
(a) There is no error in the books
(b) There may be two sided errors in the book
(c) There may be one sided error in the books
(d) There may be both two sided and one sided errors in the books
Answer:
(b) There may be two sided errors in the book
Question 6.
If suspense account does not balance off even after rectification of errors it implies that:
(a) There are some one sided errors only in the books yet to be located
(b) There are no more errors yet to be located
(c) There are some two sided errors only yet to be located
(d) There may be both one sided errors and two sided errors yet to be located
Answer:
(a) There are some one sided errors only in the books yet to be located
Question 7.
If wages paid for installation of new machinery is debited to wages Account, it is:
(a) An error of commission
(b) An error of principle
(c) A compensating error
(d) An error of omission
Answer:
(b) An error of principle
Question 8.
Trial balance is: ..................
(a) An account
(b) A statement
(c) A subsidiary book
(d) A principal book
Answer:
(b) A statement

Question 9.
A Trial balance is prepared:
(a) After preparation financial statement
(b) After recording transactions in subsidiary books
(c) After posting to ledger is complete
(d) After posting to ledger is complete and accounts have been balanced
Answer:
(d) After posting to ledger is complete and accounts have been balanced
Short Answer Type Questions:
Question 1.
State the meaning of a trial balance.
Answer:
It is a statement which shows the arithmetical accuracy of all debits and credits into the ledger accounts.
Question 2.
Give two examples of errors of principle.
Answer:
When some fundamental principle of accountancy is violated while recording a transaction, the error is termed as error of principle. These errors are committed in those cases where a proper distinction between capital and revenue items is not made.
Examples:
(a) Purchase of furniture is treated as an ordinary purchase.
(b) Amount spent on the extension of building is debited to repairs account instead of building account.
(c) The amount spent on the repair of on old machinery is debited to machinery account instead of repairs account
Question 3.
Give two examples of errors of commission.
Answer:
Such type of errors include error due to wrong posting, wrong totaling, wrong, balancing of an account, wrong casting of subsidiary books, and wrong recording of amount in the books of original entry.
Examples:
(a) Sale of goods to Ram on credit for ₹ 420 was entered in the Journal as ₹ 240. (Trial balance will not agree)
(b) Purchase book was undercast by ₹ 30,000. (Trial balance will agree)

Question 4.
What are the methods of preparing trial balance?
Answer:
The following are the various methods of preparing the Trial Balance:
1. Balance Method: Under this method, the balance of each account is taken. This method is very simple, easy to calculate, saves both time and labour.
2. Total Method: Under this method, instead of taking balance of each account, the total of both the sides of each account is taken.
3. Combined Method i.e. Balance and Total Method: Under this method, both the above explained methods i.e. balance as well as total method are shown in a single table. This method is not in use because of wastage of time and labour.
Question 5.
What are the steps taken by an accountant to locate the errors in the trial balance?
Answer:
Steps to locate the errors in the trial balance:
Step 1: Recast the total of trial balance.
Step 2: Find out the difference between the totals of each side.
Step 3: If the difference comes as 10,100,1,000, the casting of the subsidiary books need to be checked.
Step 4: If the difference is divisible by 9, there are chances, mistake could happen due to the transposition of figures. Step 5: If error is not detected, compare the difference of amount with the closing balances of each account in the ledger book.
Step 6: If amount is located, fill the account with amount in the required column of the trial balance, trial balance may agree.
Step 7: If trial balance does not agree, take half or double of the amount of the difference and compare again with the balances of accounts in the ledger.
Step 8: If amount is located, fill the account with amount in the required column of the trial balance, trial balance may agree.
Step 9: If the trial balance does not yet agree, compare the amount of the each account with the closing balance of each account in the ledger book including balances of cash and bank from cash book.
Step 10: If the error is not detected, finally, transfer the balance in suspense account which is gradually closed when all one sided errors are rectified.

Question 6.
What is a suspense account? Is it necessary that is suspense account will balance off after rectification of the errors detected by the accountant? If not, then what happens to the balance still remaining in suspense account?
Answer:
Suspense Account: Trial balance is the basis of preparing financial statements which includes income statement and balance sheet. If the trial balance does not match and it is urgent to prepare financial statements, the difference in either side of trial balance is put in ‘Suspense Account’ for the time being.
Balance off of Suspense Account: When all one sided errors are rectified, there remains nil balance in the suspense account and suspense account is automatically closed.
Balance left in Suspense Account: When some balance is left in the suspense account, it means, there are certain one sided errors left to be rectified which may be rectified after the preparation of balance sheet in the next year.
Placing of Balance of Suspense Account: if there is debit balance in the suspense account, it is posted on the assets side and if there is credit balance in the suspense account, it is posted on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Question 7.
What kinds of errors would cause difference in the trial balance? Also list examples that would not be revealed by a trial balance?
Answer:
The kinds of Errors which cause Difference in the Trial Balance
(1) The Errors of Commission: if there is error in casting or error in carrying forwarding of amount or posting of an amount on the wrong side of correct account or posting is done with wrong amount in the correct account, the trial balance does not agree.
(2) Errors Due to Partial Omission: it happens when a transaction is recorded in one account but not in the other account affected.
Example: Sales of ₹ 10,000 to Ram was not recorded in Ram’s account.
The kinds of errors which do not cause difference in the trial balance:
(1) Errors of Commission: if errors occurs due to recording in the correct book or there is the posting of an amount is done in the wrong account but on the correct side.
(2) Errors of Principle: it happens when accounting principles are not adopted while passing journal entries and no distinction between capital item and revenue item is made. Example: Wages paid on the installation of machinery was debited to wages account.
(3) Compensating Errors: Such errors happen when the effect of one error is nullified by another error and the effect of debit and credit is nil. Example: Purchase of ₹ 10,000 was recorded as ₹ 1,000 whereas the sales of ₹ 10,000 was recorded as ₹ 1,000. In this case, debit side was short by ₹ 9,000 in first error whereas credit side was short by ₹ 9,000 in the second error. The second error nullified the effect of first error.
Question 8.
State the limitations of trial balance?
Answer:
Limitations of trial balance:
(1) Error in the Books of Original Entry: If a mistake is committed in writing up the subsidiary books, it will not cause a disagreement of the Trial Balance.
For example: if a. credit purchase of ₹ 465 from Azaruddin is wrongly written as ₹ 564 in the Purchase Book, such an error will not be disclosed by the Trial Balance.
Effect: As the posting on both the debit side of Purchases Account and credit side of Azaruddin’s Account will be with the same wrong amount of ₹ 564, the trial balance will agree.
(2) Omission of an Item in the Books of Original Entry: If an entry is omitted in a subsidiary book such omission will not affect the agreement of the Trial Balance. For example: goods worth ₹ 400 were sold to Mr. Gavaskar and delivered to him, but no entry was passed through the Sales Book.
Effect: The amount will not appear on the debit side of Gavaskar’s A/c, nor will it appear on the credit side of the Sales A/c as it was not recorded in the sales book. Hence, the Trial Balance will tally.
(3) Posting an item to a Wrong Account, but on the Correct Side: Suppose, goods of ₹ 1,000 were bought on credit from Mr. Rakesh Roshan. The transaction may have been correctly entered in the Purchases Book but while posting to ledger, by mistake Rajesh Roshan’s A/c have been credited in place of Rakesh Roshan’s. The Trial Balance will tally but the mistake will be there.

(4) Compensating Errors: While posting entries in subsidiary books two mistakes are committed in such a way that one mistake is compensated by the other, then the Trial Balance will tally, but the mistakes will remain undetected. For example: underposting of ₹ 100 on the debit side of a certain account would be compensated by under posting of ₹ 100 on the credit side of another account and vice-versa.
(5) Errors of Commission: If a transaction is entered in the subsidiary books with wrong amount, it will not have its effect on the totals of Trial Balance.
For example: if goods sold to Sonu on credit for ₹100 are wrongly entered in the sales Book with an amount of ₹ 150, both the debit and credit sides will be in excess of ₹ 50 and hence it will not affect the total of Trial Balance.
(6) Errors in the Original Books: If a mistake is committed while journalising a transaction it will also affect the ledger in the same way.
For example: if the furniture purchased for ₹ 200 from Nitu has been journalised with an amount of ₹ 210, this will raise the amount of furniture account by ₹ 10 in the debit side and will accordingly raise the amount in Nitu’s account by ₹ 10 in the credit side. Thus, it will not affect the totals of Trial Balance.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the purpose for the preparation of trial balance.
Answer:
The following are the purpose of preparing trial balance:
(a) It Helps to Check the Arithmetical Accuracy: The agreements of trial balance ensures that all debit and credit balances have been duly posted in the trial balance and no account is left. If it does not match, it means there are certain one sided errors left which are to be detected and rectified. If such errors can be rectified immediately, it is okay, otherwise, the balance in the suspense account is transferred to a newly opened account known as suspense account.
(b) It Helps to Locate the Errors: If trial balance does not match, it means there are certain one sided errors which are to be rectified. Two sided errors are not disclosed through balance but can be known by analysing the transactions from the books of original entry till the transfer to trial balance.
(c) It helps to Prepare Financial Statements: Trial balance is the basis to prepare final accounts. Final accounts or financial statements consists of trading account, profit & loss account and balance sheet. If trial balance matches, the process to prepare final accounts starts.
Question 2.
Explain errors of principle and give two examples with measures to rectify them.
Answer:
Errors of principle are committed due to ignorance of the fundamental principle of accountancy, eg. a capital expenditure may be treated as a revenue expenditure and vice-versa. Thus, type of error affects two accounts and therefore do not affect the total of the trial balance.
Example 1: Sales of an old type writer for ₹ 800 credited to sales A/c. Rectify the error.

Example 2: Repairs to Building ₹ 60,000 debited to Building Account. Rectify the error.


Question 3.
Explain the errors of commission and give two examples with measures to rectify them.
Answer:
Errors of Commission: When a transaction is incorrectly recorded either wholly or partially it is known an error of commission. Some of these errors may affect the trial balance while some others may not. Errors of commission may be of the following types:
Example 1: Purchase of ₹ 50,000 from Darshan entered in the purchase book as ₹ 5,000 only. Rectify the error by making necessary journal entry.
Please note, here, both purchase account and Darshan accounts have been posted with ₹ 5,000 and balance in both accounts need to be increased. This error will not affect the total of trial balance.


Example 2: Goods sold to Sameer for ₹ 50,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
Please note, here instead of debiting Sameer by ₹ 50,000, his account was credited by ₹ 5,000. To correct his account, we need to debit his account by ₹ 55,000 and credit suspense account as it is a one sided error.

Question 4.
What are the different types of errors that are usually committed in recording business transaction?
Answer:
Types of Errors : On the basis of nature, errors can be classified into four categories:
(a) Errors of Commisions : Such type of errors include error due to wrong posting, wrong totaling, wrong, balancing of an account, wrong casting of subsidiary books, and wrong recording of amount in the books of original entry.
Note: Trial balance agrees if errors occurs due to recording in the correct book or there is the posting of an amount is done in the wrong account but on the correct side.
Trial balance does not agree if there is error in casting or error in carrying forwarding of amount or posting of an amount on the wrong side of correct account or posting is done with wrong amount in the correct account.
(b) Errors of Omission: These errors can be of two types:
(i) Errors due to Complete Omission: It happens when a transaction is not recorded anywhere in the original books of original entry or recorded in the journal book but not recorded in the ledger.
Example: Sales of ₹ 10,000 to Ram not recorded anywhere.
Note: Trial balance agrees.
(ii) Errors due to Partial Omission: It happens when a transaction is recorded in one account.
Example: Sales of ₹ 10,000 to Ram was not recorded in Ram’s account.
Note: Trial balance does not agree.
(iii) Errors of Principle: It happens when accounting principles are not adopted while passing journal entries and no distinction between capital item and revenue item is made.
Example: Wages paid on the installation of machinery was debited to wages account.
Note: Trial balance agrees.
(d) Compensating Errors: Such errors happen when the effect of one error is nullified by another error and the effect of debit and credit is nil.
Example: Purchase of ₹ 10,000 was recorded as ₹ 1,000 whereas the sales of ₹ 10,000 was recorded as ₹ 1,000. In this case, debit side was short by ₹ 9,000 in first error whereas credit side was short by ₹ 9,000 in the second error. The second error nullified the effect of first error. Note: Trial balance agrees.

Question 5.
As an accountant of a company, you are disappointed to learn that the totals in your new trial balance are not equal. After going through a careful analysis, you have discovered only one error. Specifically, the balance of the Office Equipment account has a debit balance of ₹ 15,600 on the trial balance. However, you have figured out that a correctly recorded credit purchase of pendrive for ₹ 3,500 was posted from the journal to the ledger with a ₹ 3,500 debit to Office Equipment and another ₹ 3,500 debit to creditors’ accounts.
Answer each of the following questions and present the amount of any misstatement:
(a) Is the balance of the office equipment account overstated, understated, or correctly stated in the trial balance?
(b) Is the balance of the creditors account overstated, understated, or correctly stated in the trial balance?
(c) Is the debit column total of the trial balance overstated, understated, or correctly stated?
(d) Is the credit column total of the trial balance overstated, understated, or correctly stated?
(e) If the debit column total of the trial balance is ₹ 2,40,000 before correcting the error, what is the total of credit column.
Answer:
(a) The balance of office equipment account is overstated as the cost of pen drive is wrongly debited in office equipment account.
(b) The balance of creditors is understated as debited by amount of pen drive for ₹ 3,500.
(c) The debit side of trial balance is overstated due to addition in value of office equipment for ₹ 3500 by wrongly debited amount of pendrive.
(d) Credit side of trial balance is understated as amount of creditors is decreased by ₹ 3,500.
(e) Total credit side of trial balance is ₹ 2,36,500.
Numerical Questions
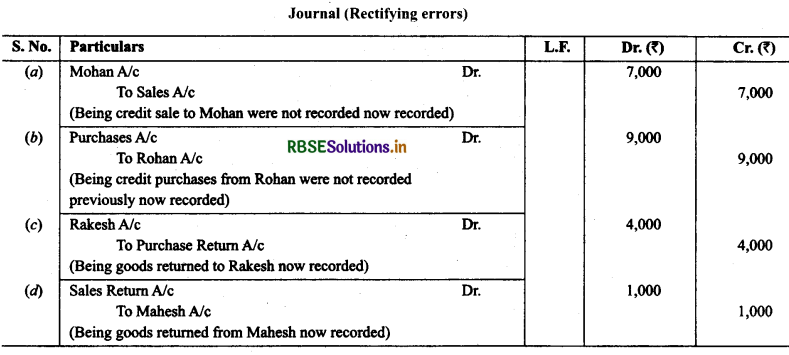
1. Rectify die following errors:
(a) Credit sales of Mohan ₹ 7,000 were not recorded.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were not recorded.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were not recorded.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were not recorded.
Solution:
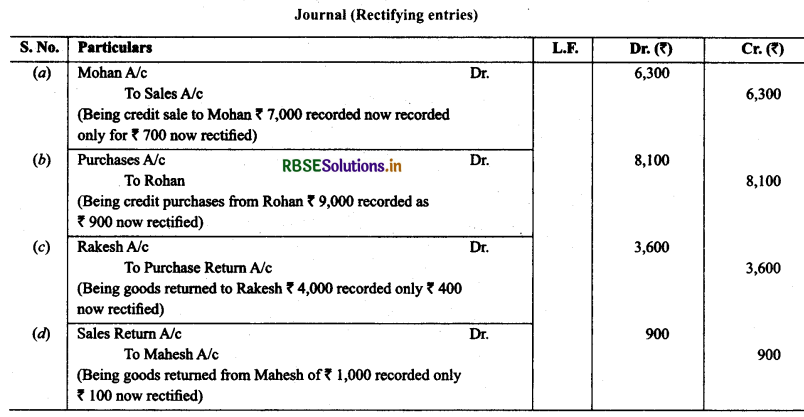
2. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were recorded as ₹ 700.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were recorded as ₹ 900.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded as ₹ 400.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were recorded as ₹ 100.
Solution:
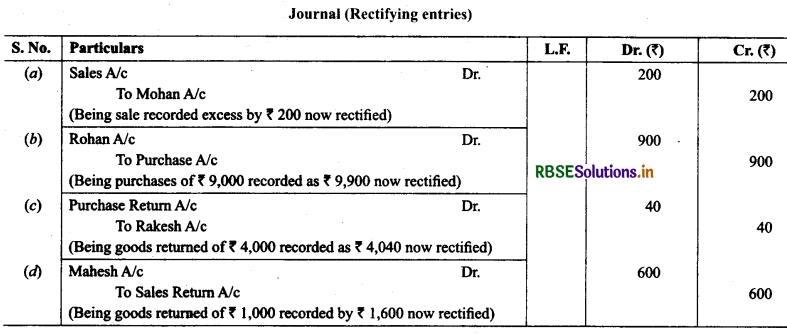
3. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were recorded as ₹ 7,200.
(b) Credit purchased from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were recorded as ₹ 9,900
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded as ₹ 4,040.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were recorded as ₹ 1,600.
Solution:

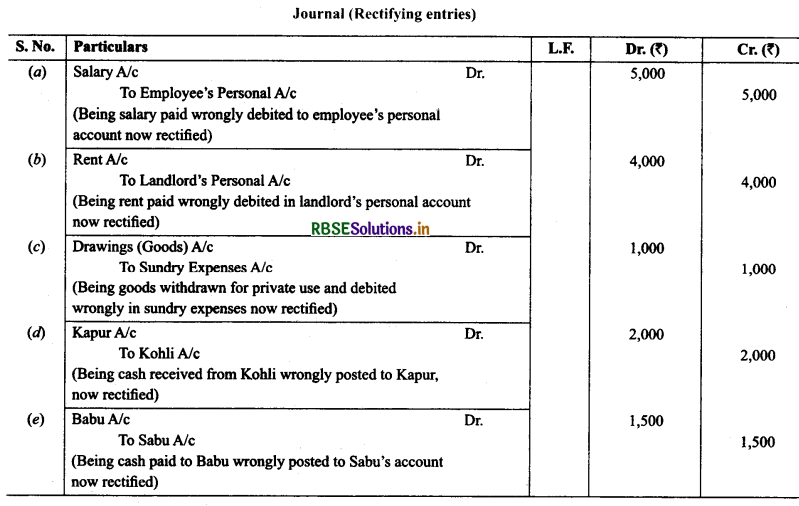
4. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Salary paid ₹ 5,000 was debited to employee’s personal account.
(b) Rent Paid ₹ 4,000 was posted to landlord’s personal account.
(c) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use ₹ 1,000 were debited to sundry expenses account.
(d) Cash received from Kohli ₹ 2,000 was posted to Kapur’s account.
(e) Cash paid to Babu ₹ 1,500 was posted to Sabu’s account.
Solution:
5. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were recorded in purchases book.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 900 were recorded in sales book.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded in the sales return book.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were recorded in purchases return book.
(e) Goods returned from Nahesh ₹ 2,000 were recorded in purchases book.
Solution:
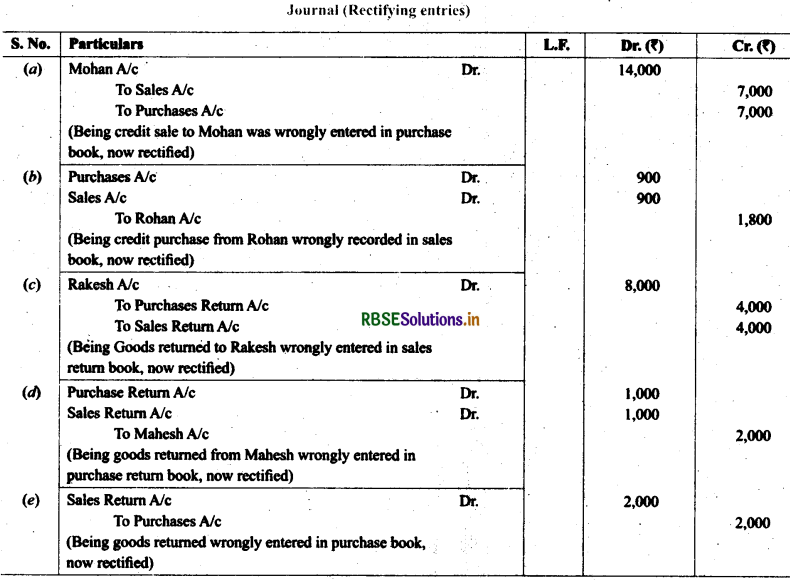
6. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Sales book overcast by ₹ 700.
(b) Purchases book overcast by ₹ 500.
(c) Sales return book overcast by ₹ 300.
(d) Purchase return book overcast by ₹ 200.
Solution:
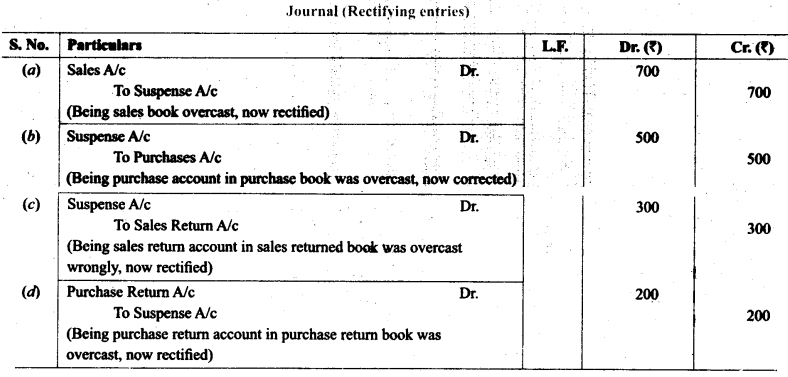
7. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Sales book undercast by ₹ 300.
(b) Purchases book undercast by ₹ 400.
(c) Return Inwards book undercast by ₹ 200.
(d) Return outwards book undercast by ₹ 100.
Solution:
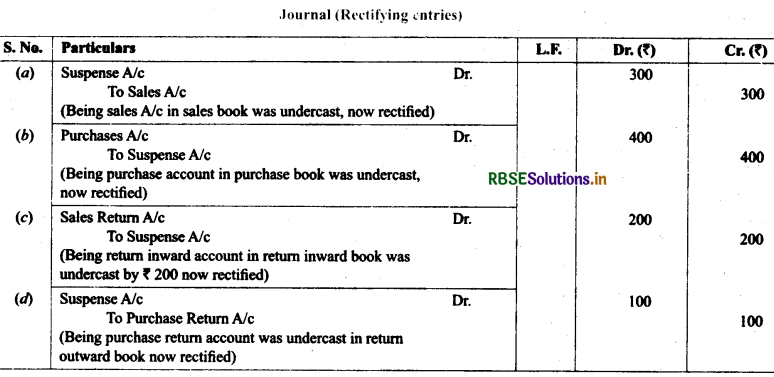

8. Rectify the following errors and ascertain the amount of difference in trial balance by preparing suspense account:
(i) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were not posted.
(ii) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were not posted.
(iii) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were not posted.
(iv) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were not posted.
(v) Cash paid to Ganesh ₹ 3,000 was not posted.
(vi) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were not posted.
Solution:
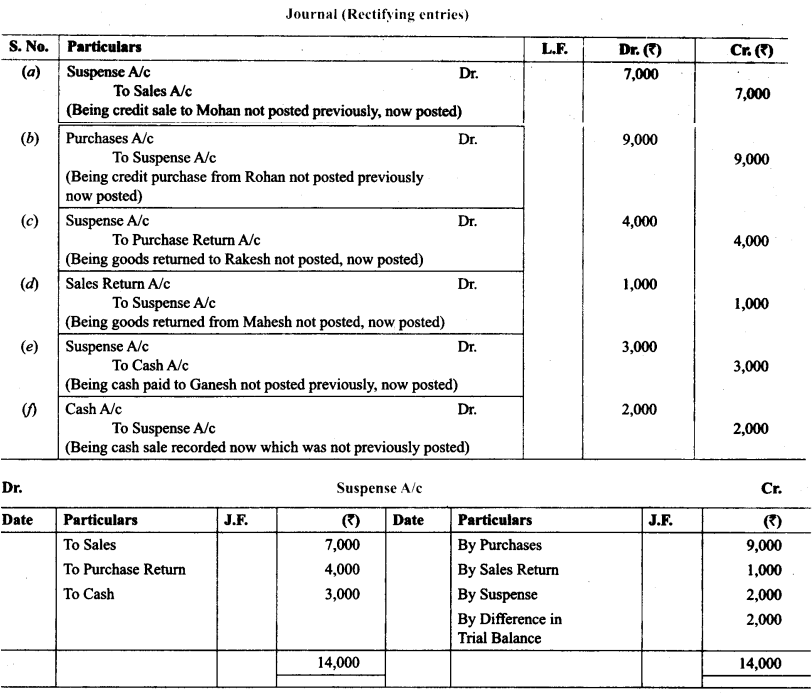
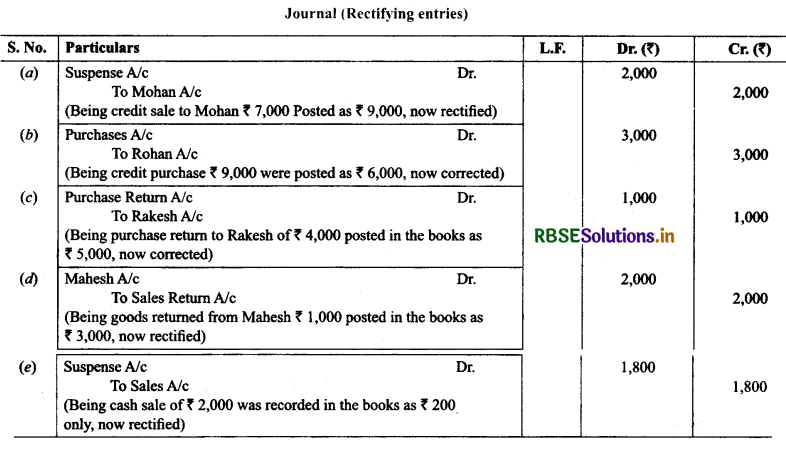
9. Rectify the following errors and ascertain the amount of difference in trial balance by preparing suspense account:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted as ₹ 9,000.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted as ₹ 5,000.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted as ₹ 3,000.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted as ₹ 200.
Solution:
10. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted to Karan.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted to Gobind.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted to Naresh.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted to Manish.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted to commission account.
Solution:
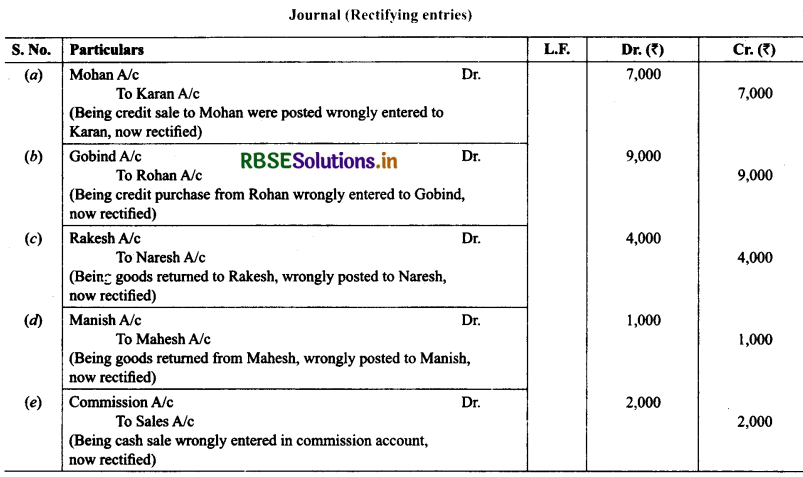
11. Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance.
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted to the debit of his account as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted to the credit of his account.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted to the debit of his account as ₹ 2,000.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted to the debit of sales account as ₹ 5,000.
Solution:
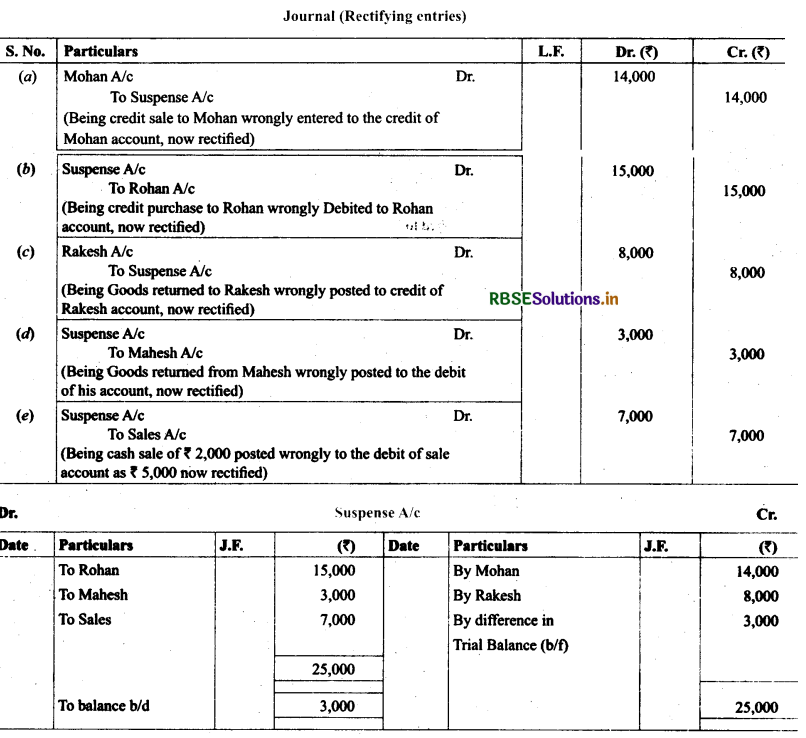

12. Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance.
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were posted to Karan as ₹ 5,000.
(b) Credit purchase from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were posted to the debit of Gobind as ₹ 10,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were posted to the credit of Naresh as ₹ 3,000.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were posted to the debit of Manish as₹ 2,000.
(e) Cash sales ₹ 2,000 were posted to commission account as ₹ 200.
Solution:
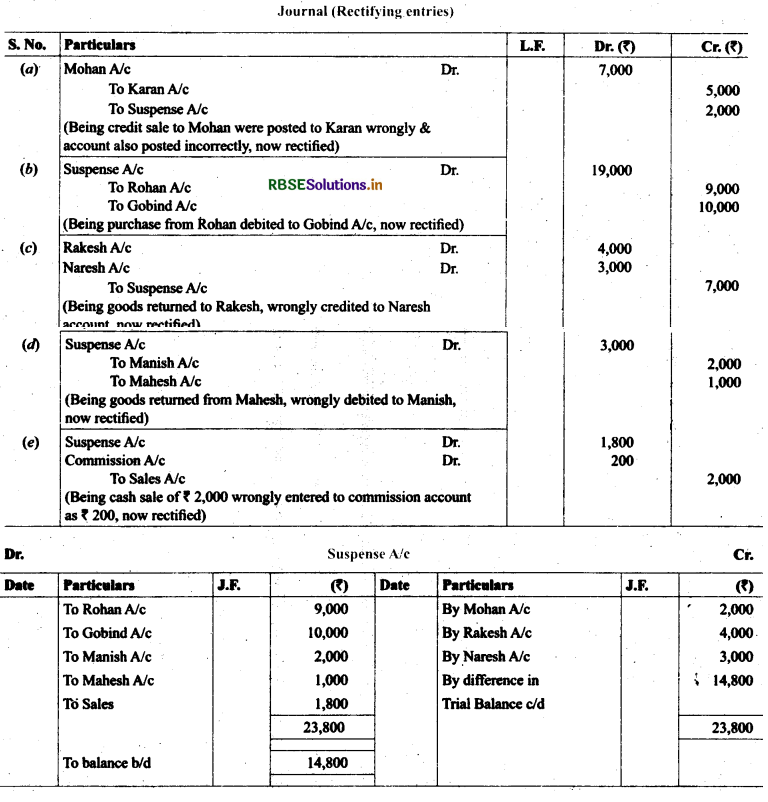
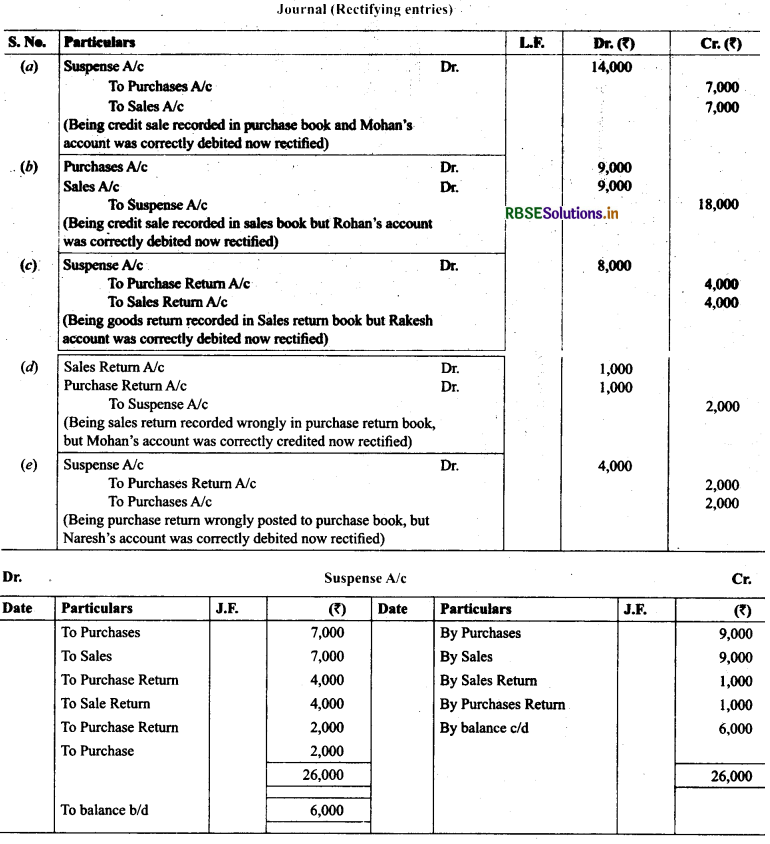
13. Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain die difference in trial balance.
(a) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 7,000 were recorded in Purchase Book. However, Mohan’s account was correctly debited.
(b) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 9,000 were recorded in Sales Book. However, Rohan’s account was correctly credited.
(c) Goods returned to Rakesh ₹ 4,000 were recorded in sales return book. However, Rakesh’s account was correctly
debited.
(d) Goods returned from Mahesh ₹ 1,000 were recorded through purchases return book. However, Mahesh’s account was correctly credited.
(e) Goods returned to Naresh ₹ 2,000 were recorded through purchases book. However, Naresh’s account was correctly debited.
Solution:
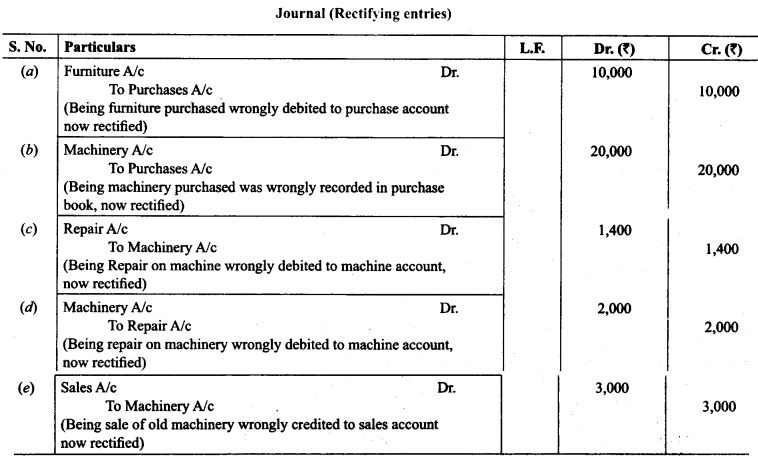
14. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Furniture purchased for ₹ 10,000 wrongly debited to purchases account.
(b) Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for ₹ 20,000 was recorded through purchases book.
(c) Repairs on machinery ₹ 1,400 debited to machinery account.
(d) Repairs on overhauling of second hand machinery purchased ₹ 2,000 was debited to Repairs Account.
(e) Sales of old machinery at book value of ₹ 3,000 was credited to sales account.
Solution:

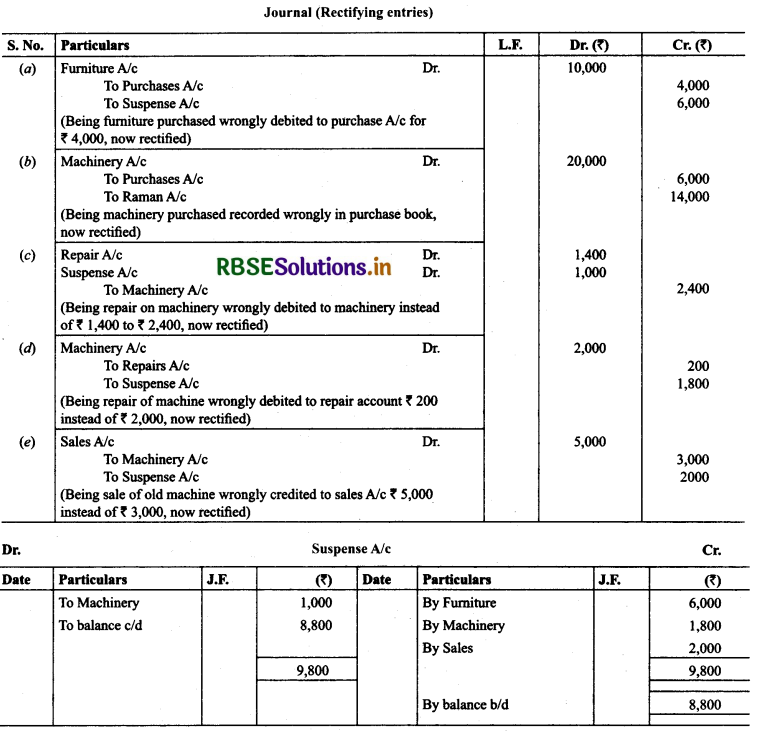
15. Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance,
(a) Furniture purchased for ₹ 10,000 wrongly debited to purchase account as ₹ 4,000.
(b) Machinery purchased on credit from Raman for ₹ 20,000 recorded through Purchases Book as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Repairs on machinery ₹ 1,400 debited to Machinery account as ₹ 2,400.
(d) Repairs on overhauling of second hand machinery purchased ₹ 2,000 was debited to Repairs account as ₹ 200.
(e) Sales of old machinery at book value ₹ 3,000 was credited to sales account as ₹ 5,000.
Solution:
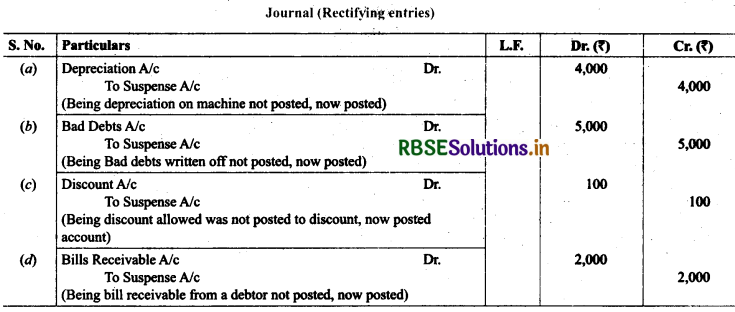
16. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 4,000 was not posted.
(b) Bad debts written off ₹ 5,000 were not posted.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted.
(d) Bill receivable for ₹ 2,000 received from a debtor was pot posted.
Solution:
17. Rectify the following errors:
(a) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 4,000 was posted as ₹ 400.
(b) Bad debts written off₹ 5,000 were posted as ₹ 6,000.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was posted as ₹ 60.
(d) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use ₹ 800 were posted as ₹ 300.
(e) Bill receivable for ₹ 2,000 received from a debtor was posted as ₹ 3,000.
Solution:
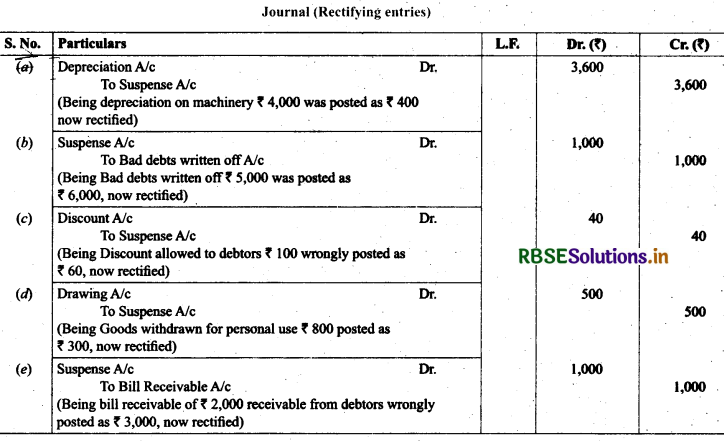

18. Rectify the following errors assuming that a suspense account was opened. Ascertain the difference in trial balance:
(а) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 4,000 was not posted to depreciation account.
(б) Bad debts written-off₹ 5,000 were not posted to debtors account.
(c) Discount allowed to a debtor ₹ 100 on receiving cash from him was not posted to discount allowed account.
(d) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use ₹ 800 were not posted to drawings account.
(e) Bill receivable for ₹ 2,000 received from a debtor was not posted to bills receivable account.
Solution:
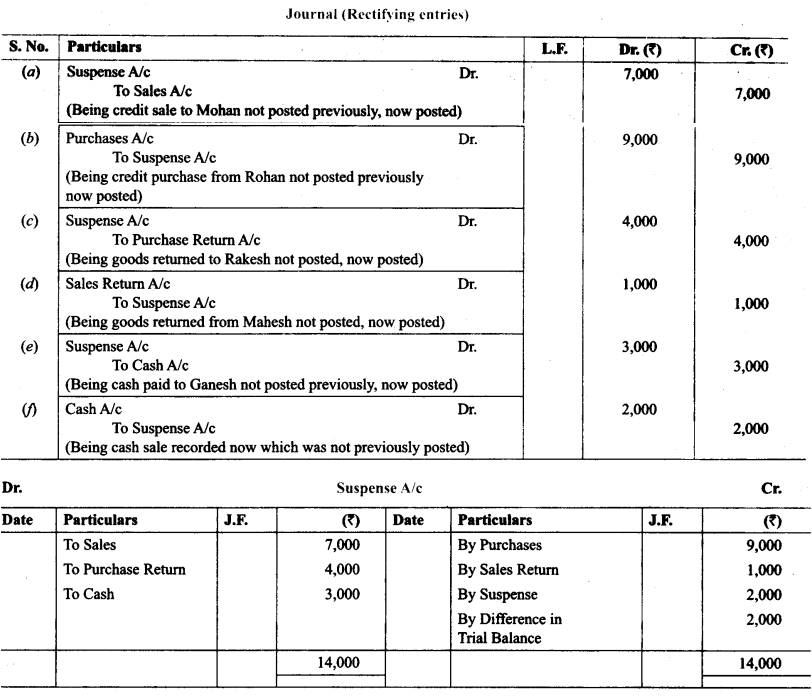
19. Trial balance of Anuj did not agree. It showed an excess credit of ₹ 6,000. He put the difference to suspense account. He discovered the following errors:
(a) Cash received from Ravish ₹ 8,000 posted to his account as ₹ 6,000.
(b) Returns inwards book overcast by ₹ 1,000.
(c) Total of sales book ₹ 10,000 was not posted to Sales account.
(d) Credit purchases from Nanak ₹ 7,000 were recorded in sales Book. However, Nanak’s account was correctly credited.
(e) Machinery purchased for ₹ 10,000 was posted to purchases account as ₹ 5,000. Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Solution:
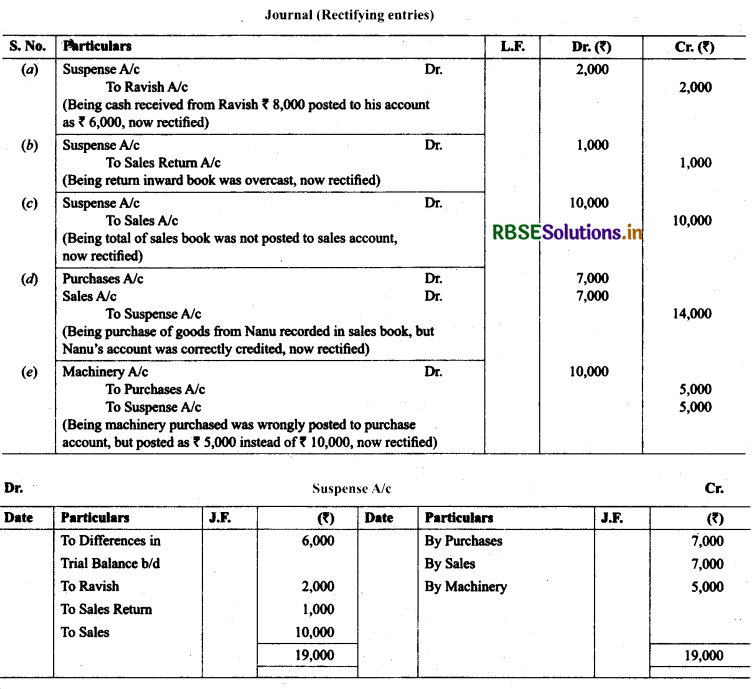
20. Trial balance of Raju showed an excess debit of₹ 10,000. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Depreciation written-off on furniture ₹ 6,000 was not posted to Furniture account.
(b) Credit sales to Rupam ₹ 10,000 were recorded as ₹ 7,000.
(c) Purchases book undercast by ₹ 2,000.
(d) Cash sales to Rana ₹ 5,000 were not posted in sales A/c.
(e) Old Machinery sold for ₹ 7,000 was credited to sales account.
(f) Discount received ₹ 800 from Kanan on paying cash to him was not posted. Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Solution:
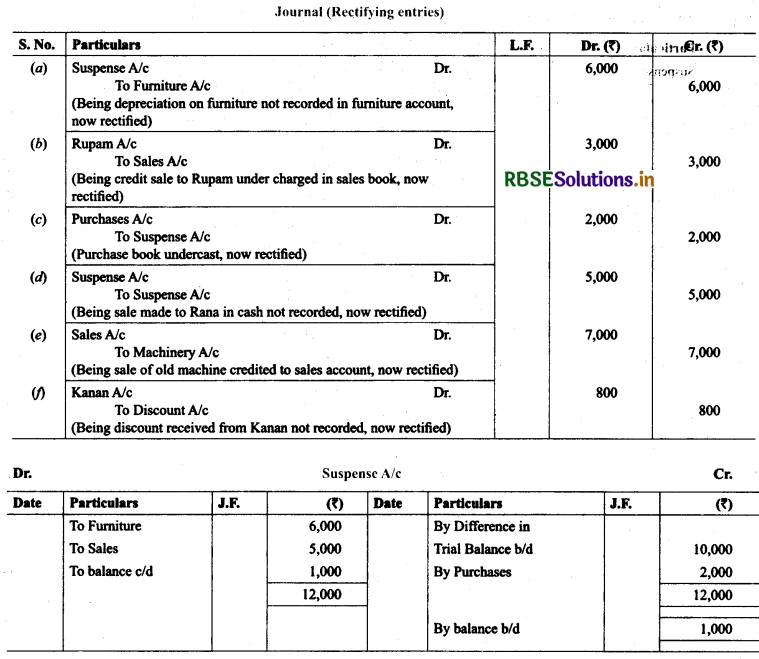

21. Trial balance of Madan did not agree and he put the difference to suspense account. He discover the following errors:
(a) Sales return book overcast by ₹ 800.
(b) Purchases return to Sahu ₹ 2,000 were not posted in Sahu A/c.
(c) Goods purchased on credit from Narula ₹ 4,000 though taken into stock, but no entry was passed in the books.
(d) Installation charges on new machinery purchased ₹ 500 were debited to sundry expenses account as ₹ 50.
(e) Rent paid for residential accommodation of Madan (the proprietor) ₹ 1,400 was debited to Rent account as ₹ 1,000. Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
Solution:

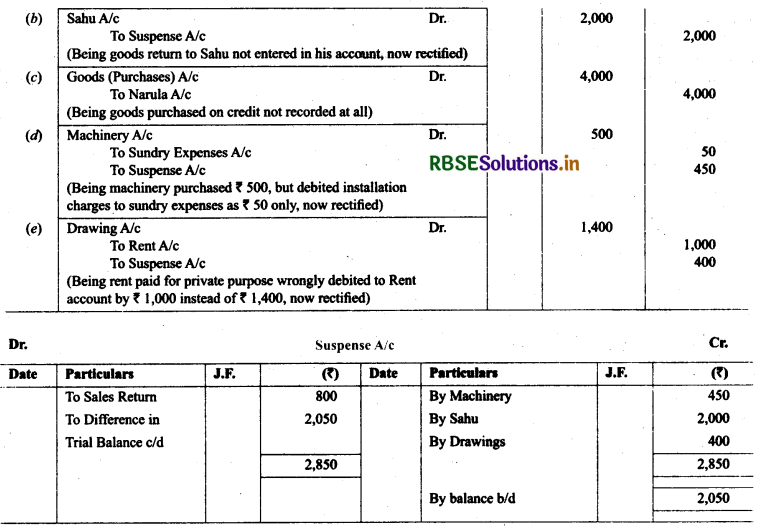
22. Trial balance of Kohli did not agree and showed an excess debit of₹ 16,300. He put the difference to a suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Cash received from Rajat ₹ 5,000 was posted to the debit of Kama! as ₹ 6,000.
(b) Salaries paid to an employee ₹ 2,000 were debited to his personal account as ₹ 1,200.
(c) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use ₹ 1,000 were credited to sales account as ₹ 1,600.
(d) Depreciation provided on machinery ₹ 3,000 was posted to Machinary account as ₹300.
(e) Sale of old car for ₹ 10,000 was credited to sales account as ₹ 6,000. Rectify the errors and prepare suspense account.
Solution:
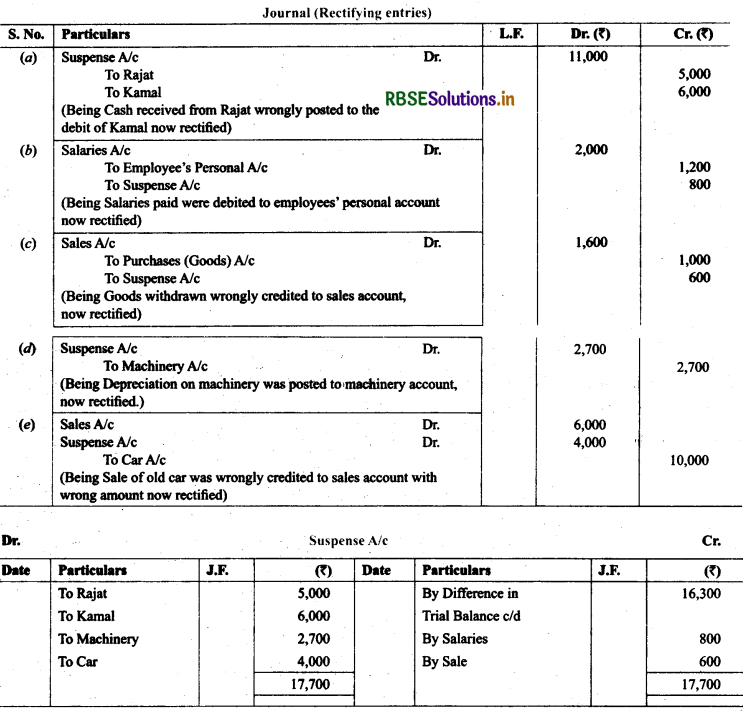
23. Give journal entries to rectify the following errors assuming that suspense account had been opened:
(a) Goods distributed as free sample ₹ 5,000 were not recorded in the books.
(b) Goods withdrawn for personal use by the proprietor ₹ 2,000 were not recorded in the books.
(c) Bill receivable received from a debtor ₹ 6,000 was not posted to his account.
(d) Total of return inwards book ₹ 1,200 was posted to return outwards account.
(e) Discount allowed to Reema ₹ 700 on receiving cash from her was recorded in the books as ₹ 70.
Solution:
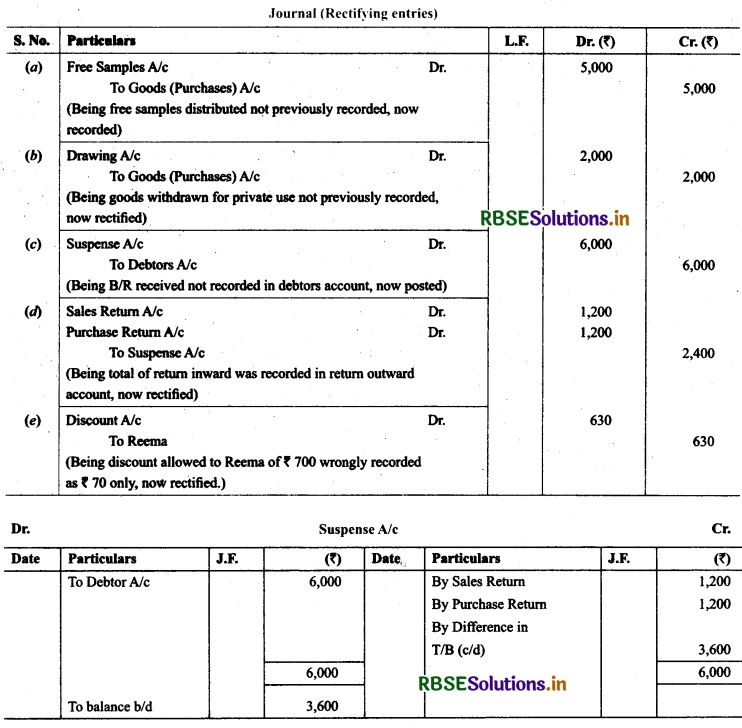
24. Trial balance of Khatau did not agree. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) Credit sales to Manas ₹ 16,000 were recorded in the purchases book as ₹ 10,000 and posted to the debit of Manas as ₹ 1,000.
(b) Furniture purchased from Noor ₹ 6,000 was recorded through purchases book as ₹ 5,000 and posted to the debit of Noor ₹ 2,000.
(c) Goods returned to Rai ₹ 3,000 recorded through the sales book as ₹ 1,000.
(d) Old machinery sold for ₹ 2,000 to Maneesh recorded through sales book as ₹ 1,800 and posted to the credit of Manish as ₹ 1,200.
(e) Total of returns inwards book ₹ 2,800 posted to purchase account. Rectify the above errors and prepare suspense account to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
Solution:
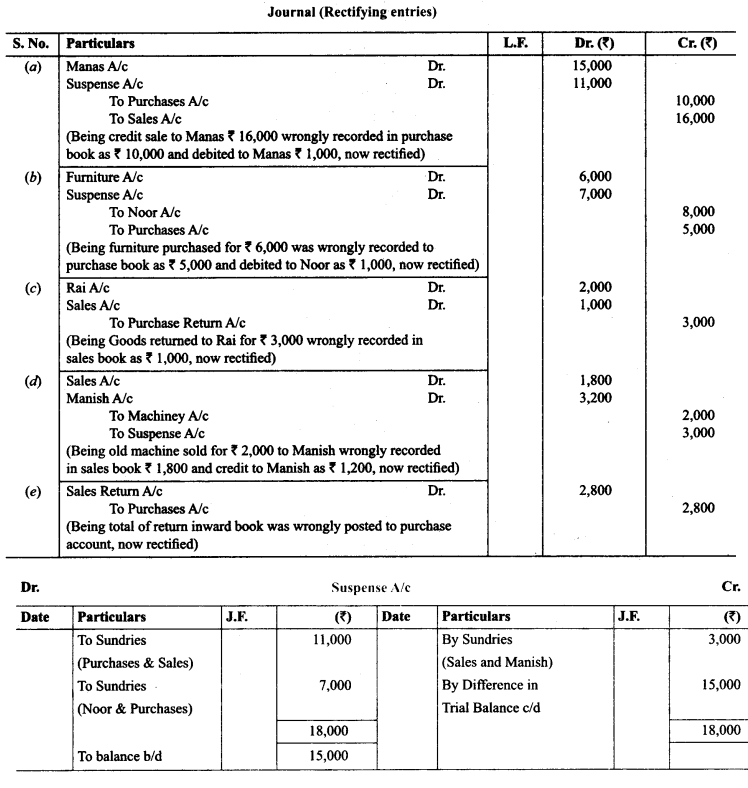

25. Trial balance of John did not agree. He put the difference to suspense account and discovered the following errors:
(a) In the sales book for the month of January total of page 2 was carried forward to page 3 as ₹ 1,000 instead of ₹ 1,200 and total of page 6 was carried forward to page 7 as ₹ 5,600 instead of ₹ 5,000.
(b) Wages paid for installation of machinery ₹ 500 was posted to wages account as ₹ 50.
(c) Furniture purchased from R & Co. for ₹ 10,000 on credit was entered in Purchase Book as ₹ 6,000 and posted there from to R & Co. as ₹ 1,000.
(d) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 5,000 were recorded in Purchase Book.
(e) Goods returned to Ram ₹ 1,000 were recorded in Sales Book.
(f) Credit purchases from S & Co. for ₹ 6,000 were recorded in sales book. However, S & Co. was correctly credited.
(g) Credit purhases from M & Co. ₹ 6,000 were recorded in Sales Book as ₹ 2,000 and posted there from to the credit of M & Co. as ₹ 1,000.
(h) Credit sales to Raman ₹ 4,000 posted to the Credit of Raghvan as ₹ 1,000.
(i) Bill receivable for ₹ 1,600 from Noor was dishonoured and posted to debit of Allowances account.
(j) Cash paid to Mani ₹ 5,000 against our acceptance was debited to Manu.
(k) Old furniture sold for ₹ 3,000 was posted to Sales account as ₹ 1,000.
(l) Depreciation provided on furniture ₹ 800 was not posted.
(m) Material ₹ 10,000 and wages ₹ 3,000 were used for construction of building. No adjustment was made in the books.
Rectify the errors and prepare suspense to ascertain the difference in trial balance.
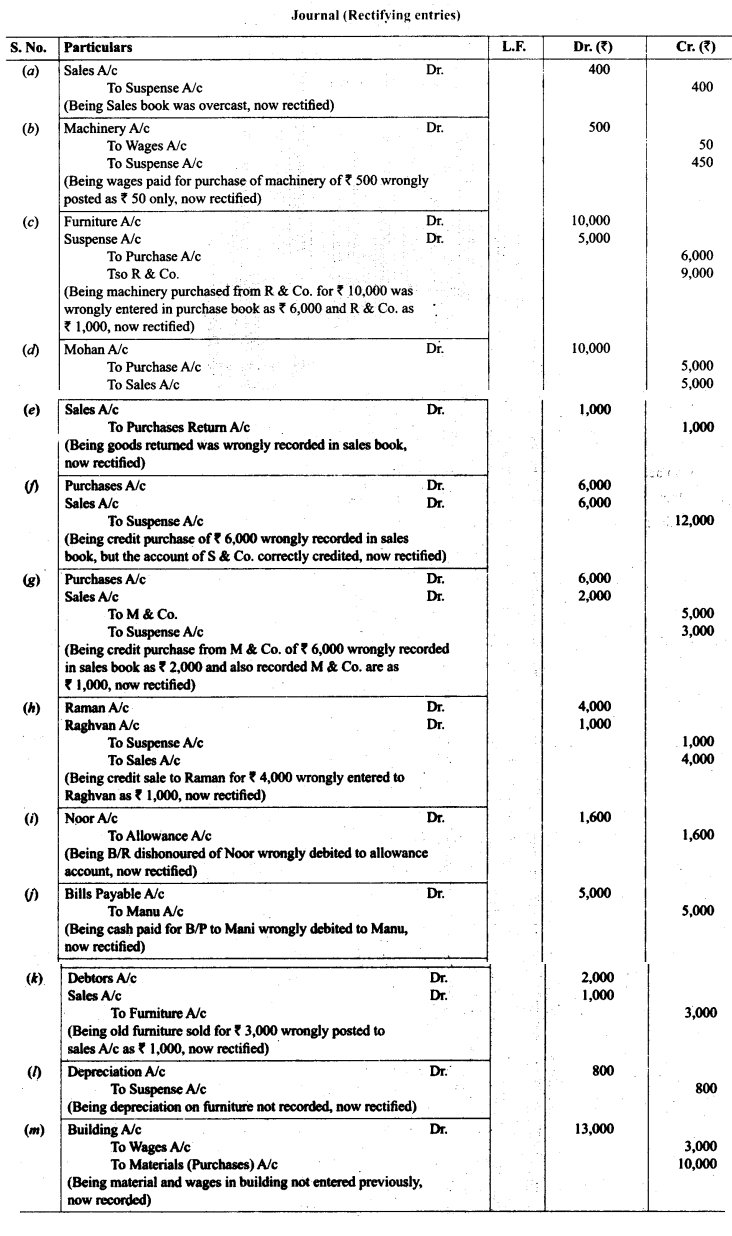
Solution:

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 5 बैंक समाधान विवरण
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 4 लेन-देनों का अभिलेखन-2
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 6 तलपट एवं अशुद्धियों का शोधन
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 4 Presentation of Data
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Applications of Computers in Accounting
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 11 Accounts from Incomplete Records
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 10 Financial Statements-II
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 9 Financial Statements-I
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 7 Depreciation, Provisions and Reserves
- RBSE Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 6 Trial Balance and Rectification of Errors