RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 10. Students can also read RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The class 10 economics chapter 2 intext questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 10 Social Science Solutions Economics Chapter 3 Money and Credit
RBSE Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit InText Questions and Answers
Page-40 (Let's work these out)
Question 1.
How does the use of money make it easier to exchange things ?
Answer:
It is difficult to determine exchange rate in barter system whereas with money price of all goods can be determine and there is no problem of double coincidence of wants and exchange is possible easily.
Question 2.
Can you think of some examples of goods/services being exchanged or wages being paid through barter ?
Answer:
Even today in rural areas barter system is in practice where people complete their needs through barter system and still in villages the payment of wages is made in the form of grains.
Page-42 (Let's work these out)
Question 1.
M. Salim wants to withdraw ₹ 20,000 in cash for making payments. How would he write a cheque to withdraw money ?
Answer:
M. Salim will write cheque in the following manner-
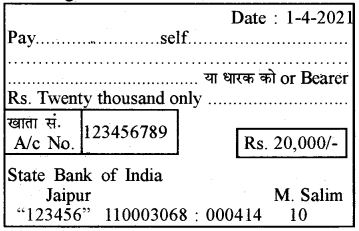

Question 2.
Tick the correct answer.
After the transaction between Salim and Prem,
(i) Salim's balance in his bank account increases, and Prem's balance increases.
(ii) Salim's balance in his bank account decreases, and Prem's balance increases.
(iii) Salim's balance in his bank account increases, and Prem's balance decreases.
Answer:
(ii) Salim's balance in his bank account decreases, and Prem's balance increases.
Question 3.
Why are demand deposits considered as money ?
Answer:
Demand deposits are the same as money because the deposited money in bank can also be withdrawn at the depositor's wish or payment to other can be made by a cheque. So demand deposits are regarded as money.
Page-45 (Let's work these out)
Question 1.
Why do lenders ask for collateral while lending ?
Answer:
If the borrower fails to repay the loan, the lender has the right to sell the asset or collateral to receive payment.
Question 2.
Given that a large number of people in our country are poor, does it in any way affect their capacity to borrow ?
Answer:
Poverty of people affects its capability to take loan. Due to poverty repayment of loan is very painful. And due to lack of collateral they do not get loan easily.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks choosing the correct option from the brackets.
While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. This means ............ (low/ high) interest rates .............. (easy/tough) conditions for repayment, ................ (less/more) collateral and documentation requirements.
Answer:
While taking a loan, borrowers look for easy terms of credit. This means low-interest rate, easy conditions for repayment, less collateral and documentation requirements.

Page-47 (Let's work these out)
Question 1.
List the various sources of credit in Sonpur.
Answer:
There are various sources of credit in Sonpur
- Moneylender
- Businessmen of Sonpur
- Big farmers, and zamindars
- Banks.
Question 3.
Compare the terms of credit for the small farmer, the medium farmer and the landless agricultural workers in Sonpur.
Answer:
In Sonpur small farmers are dependent on money lenders who provide credit to farmers at higher rate of interest and they force them to sell their produce at low rate, Medium farmers arrange loan from banks who provides loan on easy terms. Landless agricultural farmers arrange credit from big farmers and zamindars who provide loans at higher rate of interest and do not provide them wages for work (begaar) for the value of repayment.
Question 4.
Why will Arun have a higher income from cultivation compared to Shyamal ?
Answer:
Arun will have a higher income from cultivation compared to Shyamal due to the following reaons-
- Arun has 7 acres of land while Shyamal has only 1.5 acres.
- Arun has taken a loan from the bank, whose interest rate is 8.5% per annum. While Shyamal has taken a loan from the agricultural trader of the village for 36% per annum.
- Arun can sell his crop to anyone, while Shyamal has also promised to sell the crop to the agricultural trader from whom he has taken loan.
Question 5.
Can everyone in Sonpur get credit at a cheaper rate ? Who are the people who can ?
Answer:
All the people in Sonpur cannot avail credit at cheaper rate. Only those people who have collateral can arrange loan from bank at cheaper rate of interest.
Question 6.
Tick the correct answer. (i) Over the years, Rama's debt.
- will rise.
- will remain constant.
- will decline.
(ii) Arun is one of the few people in Sonpur to take a bank loan because
- other people in the village prefer to borrow from the moneylenders
- banks demand collateral which everyone cannot provide.
- interest rate on bank loans is same as the interest rate charged by the traders.
Answer:
(i) will rise.
(ii) banks demand collateral which everyone cannot provide.

Page-50 (Let's work these out)
Question 1.
What are the differences between formal and informal sources of credit ?
Answer:
Points of difference:
|
Points of difference |
Formal source |
Informal source |
|
1. Loan provider |
It includes loans from banks, co-operatives and self and help groups. |
It includes traders, employers, moneylenders, relatives friends. |
|
2. Rate of interest |
Formal sector provides loans at cheaper rate of interst. |
Informal sector charge higher rate of interest on laons. |
|
3. Exploitation of Borrowers |
Borrowers are not exploited in this sector. |
It leads to exploitation of borrowers. |
Question 2.
Why should credit at reasonable rates be available for all ?
Answer:
Credit at reasonable rates should be available for all so that through loans people can increase their income and make repayment on time.
Question 3.
Should there be a supervisor, such as the Reserve Bank of India, that looks into the loan activities of informal lenders ? Why would its task be quite difficult ?
Answer:
Informal sector provides loans to borrowers on high rate of interest and borrowers are exploited in different ways so to control the activities of informal sector there should be a supervisor like Reserve Bank of India. But informal sector is quite huge and scattered and this sector does not complete the documentation so it is difficult to control informal sector.
Question 4.
Why do you think that the share of formal sector credit is higher for the richer households compared to the poorer households ?
Answer:
The share of richer households is higher in formal sector credit compared to poorer households because richer household have collateral to avail loan and their repayment capacity is also high than poor households because their income is high.

RBSE Class 10 Social Science Money and Credit Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In situations with high risks, credit might create further problems for the borrower. Explain.
Answer:
If a person borrows in difficult situation, it may be possible that situations become more difficult for him because in these situations, income of the person is uncertain. If he borrows for work and he is not successful, it is difficult for him to repay loan and again he has to take new loan or sell some part of his assets. Therefore here credit has created problems for the borrower as he falls into debttrap.
Question 2.
How does money solve the problem of double coincidence of wants ? Explain with an example of your own.
Answer:
Money solves the problem of double coincidence of wants by acting as a medium of exchange. If a shoe manufacturer wants to sell shoes in a market and buys rice under barter exchange, both parties have to agree to sell and buy each other's commodities and this creates a problem which is referred to as double coincidence of wants. This problem is overcome by introduction of money. Money has separated the sale and purchase of commodity. Here the shoe manufacturer will first exchange shoes that he has produced for money and then exchange the money for rice.
Question 3.
How do banks mediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money ?
Answer:
Banks accept deposits from people After keeping a portion of deposits as reserves, bank lends to people who demand money as loan. Thus banks intermediate between those who have surplus money and those who need money.
Question 4.
Look at a 10 rupee note. What is written on top? Can you explain this statement ?
Answer:
A ten rupee note has “Reserve Bank of India” written on the top, followed by a statement, “Guaranteed By The Central Government”, and below this it is written as “I promise to pay the bearer the sum of ten rupees.”
It means that it is a promissory note and on behalf of the government of India. It is issued by Reserve Bank of India and it is a promise to public that the bearer of '10 will be paid for 10 in every situation. It creates credibility in public.

Question 5.
Why do we need to expand formal sources of credit in India ?
Answer:
The loan is provided by the formal and informal sectors in India, but informal sector has many shortcomings. Informal sector provides loan at higher rate of interest and people are exploited in many ways. By taking loans from informal sector people fall in debt-trap whereas in formal sector loan is provided at cheaper rate of interest and on easy terms. It will help in reducing debt and avoid to fall in debt trap. It would lead to higher income of the people. So it is required to develop formal sources of credit in India.
Question 6.
What is the basic idea behind the SHGs for the poor? Explain in your own words.
Answer:
The basic idea behind the SHGs is to save poor from the clutches of money lenders, zamindars and big farmers.
- It helps in pooling the savings of the members, who are poor women.
- Members can get timely loans for a variety of purposes at a reasonable rate of interest.
- It helps the borrowers overcome the problem of lack of collateral.
- It also provides a platform to discuss variety of social issues of their concern.
Question 7.
What are the reasons why the banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers ?
Answer:
While giving loan, the lender specifies certain terms and conditions relating to the loan to be followed by the borrower which is known as terms of credit. It includes-
- Interest rate
- Collateral
- Documentation required
- The mode of repayment etc.
Before giving loan a bank ensures about the financial capacity of the borrower to repay the loan. If bank is not satisfied with the paying capacity of a person and if a person does not submit anything to be considered as collateral, then banks might not be willing to lend to certain borrowers.
Question 8.
In what ways does the Reserve Bank of India supervise the functioning of banks ? Why is it necessary ?
Answer:
Reserve Bank of India supervises the functioning of formal sector through its monetary policies. Reserve Bank determines bank rate, cash reserve ratio, statutory liquidity ratio, repo rate etc. Through its monetary policy R.B.I. controls the money supply in an economy.
It is necessary as if R.B.I. does not control the formal sector, there may be imbalance between demand and supply of money and it will negatively affect economy of the nation. Due to lack of control, banks will try to increase their profit and start exploitation of public. So R.B.I. is required to control financial and banking institutions.

Question 9.
Analyse the role of credit for development.
Answer:
The growth of an economy depends on the availability of cheap credit. Through loans, borrowers fulfil their productive needs which lead to increase their income. By taking loans businessmen invest in various industries which increase employment opportunities in the country and gross domestic product and national income increases. Through loans financial help is available to small scale and cottage industries. Credit encourages agricultural activities. Farmers borrow to meet their initial requirements of investment such as seeds, fertilizers and implements. Credit encourages the growth of non-farming sectors like animal husbandry fishing, poultry etc. This leads to increase in income of rural people.
Question 10.
Manav needs a loan to set up a small business. On what basis will Manav decide whether to borrow from the bank or the moneylender ? Discuss.
Answer:
Manay needs a loan to set up a small business. Various factors like-
- collateral
- rate of interest
- easy availability
- period of loan plays an important role on his decision.
(1) If Manav have a collateral he will get loan from bank. If he lacks collateral he will have to go to money-lender.
(2) If Manav wants loan at low rate of interest he has to approach formal sector.
(3) Loans will be available easily through money-lender because bank requires proper documentation which takes time.
(4) If Manav wants loan for longer period he should approach a bank.
Question 11.
In India, about 80 percent of farmers are small farmers, who need credit for cultivation.
(a) Why might banks be unwilling to lend to small farmers?
(b) What are the other sources from which the small farmers can borrow ?
(c) Explain with an example how the terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer.
(d) Suggest some ways by which small farmers can get cheap credit.
Answer:
(a) Banks might be unwilling to lend to small farmers because small farmers usually lack proper documents and collateral or asset.
(b) The other sources from which small farmers can borrow are money-lenders or friends, self-help groups and cooperative banks.
(c) The terms of credit can be unfavourable for the small farmer if he has an unhealthy crop, he is either forced to surrender his collateral or sell off a part of his land in order to repay his loan.
(d) Self-help groups and cooperative banks do not require collateral as a guarantee, hence, they can provide cheap credit to the small farmers.
Question 12.
Fill in the blanks :
(i) Majority of the credit needs of the .............. households are met from informal sources.
(ii) ....................... costs of borrowings increase the debt-burden.
(iii) ................ issues currency notes on behalf of the Central Government.
(iv) Bariks charge a higher interest rate on loans than what they offer on ............
(v) ..................... is an asset that the borrower owns and uses as a guarantee until the loan is repaid to the lender.
Answer:
(i) poor
(ii) high
(iii) Reserve Bank of India
(iv) deposits
(v) collateral.

Question 13.
Choose the most appropriate answer-
(i) In a SHG most of the decisions regarding savings and loan activities are taken by :
(a) Bank
(b) Members
(c) Non-government organisation
Answer:
(b) Members.
(ii) Formal sources of credit does not include :
(a) Banks
(b) Cooperatives
(c) Employers
Answer:
(c) Employers.

- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions History Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions History Chapter 2 Nationalism in India
- RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 Sectors of Indian Economy
- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions History Chapter 4 औद्योगीकरण का युग
- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Economics Chapter 5 उपभोक्ता अधिकार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 5 उपभोक्ता अधिकार
- RBSE Class 10 Social Science Important Questions Economics Chapter 4 वैश्वीकरण और भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था
- RBSE Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Economics Chapter 4 वैश्वीकरण और भारतीय अर्थव्यवस्था