RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 9. Students can also read RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 9 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. The why do we fall ill important questions are curated with the aim of boosting confidence among students.
RBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Important Questions Improvement in Food Resources
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Which one is an oil yielding plant among the following?
(a) Lentil
(b) Sunflower
(c) Cauliflower
(d) Hibiscus
Answer:
(b) Sunflower
Question 2.
Which one is not a source of carbohydrate?
(a) Rice
(b) Millets
(c) Sorghum
(d) Gram
Answer:
(d) Gram
Question 3.
To solve the food problem of the country, which among the following is necessary?
(a) Increased production and storage of food grains
(b) Easy access of people to the food grain
(c) People should have money to purchase the grains
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 4.
Weeds affect the crop plants by :
(a) killing of plants in field before they grow.
(b) dominating the plants to grow.
(c) competing for various resources of crops (plants) causing low availability of nutrients.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(c) competing for various resources of crops (plants) causing low availability of nutrients.

Question 5.
Which one of the following species of honey bee is an Italian species?
(a) Apis dorsata
(b) Apis florae
(c) Apis cerana indica
(d) Apis mellifera
Answer:
(d) Apis mellifera
Question 6.
Cattle husbandry is done for the following purposes :
(i) Milk production
(ii) Agricultural work
(iii) Meat production
(iv) Egg production
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Question 7.
Which of the following are Indian cattle?
(i) Bos indicus
(ii) Bos domestica
(iii) Bos bubalis
(iv) Bos vulgaris
Answer:
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (iii)
Question 8.
Which of the following are exotic breeds?
(i) Brawn
(ii) Jersey
(iii) Brown Swiss
(iv) Jersey Swiss
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) (ii) and (iii)
Question 9.
Poultry farming is undertaken to raise following :
(i) Egg production
(ii) Feather production
(iii) Chicken meat
(iv) Milk production
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (i) and (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (iii)

Question 10.
Poultry fowl are susceptible to the following pathogens :
(a) Viruses
(b) Bacteria
(c) Fungi
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 11.
Which one of the following fishes is a surface feeder?
(a) Rohus
(b) Mrigals
(c) Common carps
(d) Catlas
Answer:
(d) Catlas
Question 12.
Animal husbandry is the scientific management of :
(i) animal breeding
(ii) culture of animals
(iii) animal livestock
(iv) rearing of animals
(a) (i), (ii) and (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
Question 13.
Which one of the following nutrients is not available in fertilisers?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Iron
(d) Potassium
Answer:
(c) Iron
Question 14.
Preventive and control measures adopted for the storage of grains include :
(a) strict cleaning
(b) proper disjoining
(c) fumigation
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these

Question 15.
Which of the following is a khdrif crop?
(a) Soyabean
(b) Rice
(c) Maize
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 16.
Plants get hydrogen from :
(a) Air
(b) Water
(c) Soil
(d) Sun
Answer:
(b) Water
Question 17.
Which organism makes vermicompost?
(a) Earthworm
(b) Cockroach
(c) Grasshopper
(d) Bacteria
Answer:
(a) Earthworm
Question 18.
Which of the following is a saline water fish?
(a) Tuna
(b) Rohu
(c) Catla
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Tuna

Question 19.
White revolution is related to :
(a) Milk
(b) Grain
(c) Meat
(d) Fish
Answer:
(a) Milk
Question 20.
Which of the following is not a macro-nutrient?
(a) Potassium
(b) Sulphur
(c) Magnesium
(d) Iron
Answer:
(d) Iron
Question 21.
Which of the following is micronutrient of plants?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Boron
(c) Phosphorus
(d) Potassium
Answer:
(b) Boron
Question 22.
Which of these is the main element in chemical fertilisers?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Phosphorus
(c) Potassium
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 23.
Which species of honey bees is used to increase the production of honey?
(a) Indian bee
(b) Shell be
(c) Little bee
(d) Italian bee
Answer:
(d) Italian bee

Question 24.
Fill in the blanks :
(a) A total of ................... nutrients are essential to plants.
(b) ................... and ................... are supplied by air to plants.
(c) ................... is supplied by water to plants.
(d) Soil supply ................... nutrients to plants.
(e) ................... nutrients are required in large quantity and called as ...................
(f) ................... nutrients are needed in small quantity for plants and are called ...................
Answer:
(a) 16
(b) carbon, oxygen
(c) hydrogen
(d) 13
(e) six, macronutrients
(f) seven, micronutrients
Question 25.
Match the column (A) with the column (B).
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Catla |
(a) Middle-zone feeders |
|
(ii) Rohu |
(b) Bottom feeders |
|
(iii) Mrigal |
(c) Surface feeders |
|
(iv) Fish farming |
(d) Culture fishery |
Answer:
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Catla |
(b) Bottom feeders |
|
(ii) Rohu |
(c) Surface feeders |
|
(iii) Mrigal |
(a) Middle-zone feeders |
|
(iv) Fish farming |
(d) Culture fishery |

Question 26.
Match the column (A) with the column (B).
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Cattle used for tilling and carting |
(a) Local breed of cattle animals |
|
(ii) Indian breed of chicken |
(b) Broiler |
|
(iii) Sahiwal, Red Sindhi |
(c) Milk producing female |
|
(iv) Milch |
(d) Drought |
|
(v) Chicken better fed for obtaining meat |
(e) Aseel |
Answer:
|
Column (A) |
Column (B) |
|
(i) Cattle used for tilling and carting |
(c) Milk producing female |
|
(ii) Indian breed of chicken |
(e) Aseel |
|
(iii) Sahiwal, Red Sindhi |
(d) Drought |
|
(iv) Milch |
(a) Local breed of cattle animals |
|
(v) Chicken better fed for obtaining meat |
(b) Broiler |

Question 27.
Read the statements carefully and identify whether they are True or False-
1. Italian bees have highest honey collection capacity.
2. Wheat, gram, peas and mustard are kharif crops.
3. Manure is partially decomposed organic matter derived from plants and animal waste.
4. The level of vitamin A and C are kept high in poultry feed.
5. Prevention and control measures are used before storage of grains.
Answer:
1. True
2. False
3. True
4. False
5. True
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name any two fodder crops.
Answer:
Berseem and Sudan grass are raised as food for the livestock, called fodder crops.
Question 2.
What do you understand by photoperiod of sunlight?
Answer:
Photoperiod are related to the duration of sunlight required for plant growth.
Question 3.
Name two kharif and two rabi crops.
Answer:
Karif crops: Paddy and soyabean.
Rabi crops: Wheat and gram.

Question 4.
Define hybridisation.
Answer:
Hybridisation refers to crossing between genetically dissimilar plants, to obtain better variety of crops.
Question 5.
What are genetically modified crops?
Answer:
A gene with required characters can introduce into a crop for its improvement is called genetically modified crop.
Question 6.
Name different types of crop production practices involved in India.
Answer:
They are (a) no cost production, (b) low cost production and (c) high cost production.
Question 7.
What is mariculture?
Answer:
The culture of marine fish in sea water is called mariculture.
Question 8.
What are macro-nutrients?
Answer:
The nutrients required by plants in larger quantity is called macro-nutrients. They are nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium and sulphur.

Question 9.
Name the nutrients that plant obtains from air and water.
Answer:
Air - Carbon and oxygen,
Water - Hydrogen and oxygen.
Question 10.
Name any two weeds.
Answer:
Parthenium and Xanthium.
Question 11.
What causes disease in plants?
Answer:
It is caused by pathogens such as bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Question 12.
Name two Indian cattle.
Answer:
Bos indicus - cows
Bos bubalis - buffaloes

Question 13.
How does Bos indicus differ from Bos bubalis?
Answer:
Bos indicus is a cow while Bos bubalis is a buffalo.
Question 14.
State the meaning of capture fishing and culture fishing.
Answer:
Capture fishing: It is done from natural resources.
Culture fishing: It is done by fish farming.
Question 15.
Name four marine fish varieties.
Answer:
Pomphret, mackerel, tuna and sardines.
Question 16.
What is apiculture?
Answer:
Keeping bee for obtaining honey commercially is called apiculture.

Question 17.
Name the products obtained from apiculture.
Answer:
Honey and wax both are obtained from apiculture.
Question 18.
What is meant by bee-keeping?
Answer:
Rearing of bees for the production of honey on a large scale is called bee-rearing.
Question 19.
From where do plants get nutrients?
Answer:
Air, water and soil provides nutrients to plants.
Question 20.
Name two exotic breeds of cattle.
Answer:
Jersey and Brown Swiss.
Question 21.
In what way broilers, feed is different from layers?
Answer:
Broilers feed is protein rich with adequate fat. The level of vitamins A and K is kept high in the poultry feeds.

Question 22.
What type of shelter is provided to broiler and layers?
Answer:
Broilers do not require much space and lighting.
Question 23.
Why should weeds be constantly removed from cultivated fields?
Answer:
Weeds take up nutrients and reduce the growth of the crop.
Question 24.
State one demerit with composite fish culture system.
Answer:
Fish breed only during monsoon and lack of availability of good quality seeds.
Question 25.
State one importance of photoperiod in agriculture.
Answer:
Photoperiod in agriculture provide adequate light for flowering.
Question 26.
Name one micronutrient and one macronutrient which plants take from the soil.
Answer:
Macronutrients are : Calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg) and Micronutrients are : Boron (B), Chlorine (Cl).

Question 27.
What is pisciculture?
Answer:
The production and management of fish is called pisciculture.
Question 28.
What are the harmful effects of fertiliser?
Answer:
Continuous use of fertiliser can cause of soil and water pollution and also destroy soil fertility.
Question 29.
How does bombay duck differ from common carp?
Answer:
Bombay duck is a marine fish, while common carp is a freshwater fish.
Question 30.
Name the two vitamins which are added in the poultry feed.
Answer:
Vitamins A and K
Question 31.
State the reason of introducing Italian bee variety in bee farms.
Answer:
An Italian bee variety, Apis mellifera, has also been brought in to increase yield of honey.
Question 32.
Which nutrients are supplied by cereals and pulses?
Answer:
Carbohydrate is supplied by cereals and protein is supplied by pulses.

Question 33.
Define animal husbandry.
Answer:
Animal husbandry is the management and care of farm animals by humans for profit.
Question 34.
Give technical term for milk producing females and farm labour animals.
Answer:
Milk-producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals), while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals.
Question 35.
Why do we eat pea and groundnut?
Answer:
Pea (matar) provides us protein whereas groundnut provide us necessary fats.
Question 36.
Mention two examples of mixed cropping.
Answer:
Some combinations of mixed cropping are : wheat and mustard, groundnut and sunflower.
Question 37.
(i) Name an exotic variety of honey bee grown in India.
(ii) What is called the rearing of fish on a large scale?
Answer:
(i) Apis cerana indica
(ii) Pisciculture

Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the different ways/methods of hybridisation?
Answer:
Hybridisation can be :
(i) Intervarietal - between different varieties of crops
(ii) Interspecific - between two species of same genus
(iii) Intergeneric - between two different genera
Question 2.
What are the main characters required in a crop during its improvement practices?
Answer:
The useful characters that are required in a crop during its improvement:
- Disease resistance
- Response to fertiliser
- Product quality
- High yield
Question 3.
State the difference between macro-nutrients and micro-nutrients.
Answer:
|
Macro-nutrients |
Micro-nutrients |
|
1. These are required by crops in larger amount. |
1. These are required by crops in very small quantity. |
|
2. Six macro-nutrient: nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur. |
2. Seven micro-nutrients: iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum and chlorine. |

Question 4.
State the difference between manure and fertiliser.
Answer:
|
Manure |
Fertiliser |
|
1. Consist of organic matter |
1. Consist of inorganic matter |
|
2. Formed by animal excreta and plant waste |
2. Formed commercially by chemicals |
|
3. No pollution |
3. Soil and water pollution |
Question 5.
What is organic farming?
Answer:
Farming method in which no chemical fertilizers, pesticides or herbicides are used. Instead of using chemical, farmer uses all organic matter for growth of crops. Example : Manure, neem leaves as pesticides and for grain storage.
Question 6.
State the preventive and control measures used before grains are stored.
Answer:
- Cleaning of the grains.
- Keep seeds in sunlight to provide moisture.
- Using chemicals that kills pest.
Question 7.
What is the advantage of composite fish culture?
Answer:
The camposition of six species of fish in composite fish is highly advantageous because:
- these fishes do not compete for food among themselves:
- they have different food habit.
- food in all parts of pond is utilised due to different food habits.

Question 8.
Why Apis mellifera is adopted for domestication to produce honey?
Answer:
The Italian species of honey bee, i.e. Apis mellifera is adopted for its many good qualities. They :
- sting less.
- have good honey collection capacity.
- produce with less swarming.
- have ability to protect itself from enemy.
- stay in beehives for a long time.
Question 9.
Give difference between apiculture and aquaculture.
Answer:
Domestication of honeybees or production of honey and wax on commercial bases is called apiculture. Farming and management of fish and other aquatic animals and plants in water is called aquaculture.
Question 10.
What are the factors for which variety improvement of crop is done?
Answer:
- Higher yield: It increases production of crop.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance: Crop should be resistant to biotic factors like diseases, insects, pests and abiotic factors like drought, salinity, heat, etc.
- Change in maturity duration: Short-duration maturity allows farmer to grow more crops in a year with short duration maturity and reduces the crop production cost.
- Wider adaptability: Crop should be able to adapt to changing environmental
- conditions.
- Desirable agronomic characteristics: Crop should have tallness and dwarfness as per need. Dwarfness is required for cereals, so that few nutrients are consumed.
Question 11.
Name the sources and the nutrients supplied by them to the plants.
Answer:
|
Source |
Nutrients |
|
Air |
Carbon, oxygen |
|
Water |
Hydrogen, oxygen |
|
Soil |
Nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur (Macro-nutrients) |
|
|
Iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, chlorine (Micro-nutrients) |

Question 12.
What are manures? Give its classification.
Answer:
Substance rich in organic matter and also supplies small quantities of nutrients to soil is called manure. Manure is classified based on the kind of biological material used to make it as:
(i) Compost, (ii) Vermi-compost, (iii) Green manure.
(i) Compost: The manure prepared by decomposing farm waste, livestock excreta, plant waste, etc. in a pit is known as compost.
(ii) Vermi-compost: When the above given matter is allowed to decompose in the pit along with some earthworms to fasten the process of decomposition is called vermi-composting.
(iii) Green manure: Some plants like sun-hemp are used to prepare manure by mulching them into soil by plough is known as green manure.
Question 13.
What are fertilisers? Excess use of fertilisers is not advisable, explain.
Answer:
Fertilisers are commercially produced plant nutrients. They supply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. They are used to ensure good vegetative growth, giving rise to healthy plants.
Excessive use of fertilisers are not advisable as :
- It leads to soil and water pollution.
- It can destroy the fertility of soil.
Question 14.
How do insect pests attack the plant and affect it?
Answer:
Insect pests attack the plants and reduce yield in three ways :
- They cut the root, stem and leaf.
- They suck the cell sap from various parts of the plant.
- They bore into stem and fruits.
Question 15.
What are the new varieties obtained by cross breeding of Indian and exotic breeds of poultry?
Answer:
The new variety/traits obtained by cross breeding of Indian and exotic breeds of poultry are :
- Number and quality of chicks
- Dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production
- Summer adaptation capacity/tolerance to high temperature
- Low maintenance requirements
- Reduction in the size of the egg-laying bird with ability to utilise more fibrous and cheaper diet, formulated using agricultural byproducts
Question 16.
State the difference between egg-layers and broilers.
Answer:
|
Egg-layers |
Broilers |
|
1. Layers are egg laying birds. They are maintained for getting eggs. |
1. Broilers are maintained for getting meat. |
|
2. Layers start producing eggs at the age of 20 weeks. |
2. Broilers are raised upto 6-8 weeks in poultry farms and then sent to market for sale. |
|
3. Layer need feed rich in vitamins, minerals and micronutrients. |
3. Broilers require feed rich in proteins, fats and vitamin A and K. |
|
4. Layers require enough space and adequate lighting for proper growth. |
4. Broilers require conditions to grow fast with low mortality. |

Question 17.
Distinguish between a mullet and a prawn.
Answer:
Mullet is a type of fish while prawn is a crustacean. Both live in water and serve as a food supplement worldwide. Prawn belongs to group arthropoda whereas mullet belongs to group Pisces.
Question 18.
Name two breeds of cows selected for long lactation period.
Answer:
After giving the birth of a calf, a cow secretes milk. The duration of milk secretion of a cow that is the period of time till which the cow secretes milk is known as lactation period. Brown Swiss and jersey are selected for their long lactation period.
Question 19.
What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage? Also mention any two preventive measures to control loss of grains during storage.
Answer:
Factors responsible for losses are:
Biotic: Insects, rodents, fungi, mites and bacteria.
Abiotic: Inappropriate moisture and temperatures in the place of storage. Cleaning of the produce before storage, proper drying of the produce first in sunlight and then in shade, and fumigation are preventive measures to control loss of grains during storage.
Question 20.
Name any three methods of irrigation and briefly describe them.
Answer:
- Drip irrigation: In this kind of irrigation, water is supplied drop by drop near the roots of the crops or plants. It is generally used in the areas where there is a scarcity of water. However, it is very expensive.
- Sprinkler system: In this system, the water escapes from the revolving nozzles and is sprinkled like rain on the crops. This system is used for sandy soils and uneven land.
- Surface irrigation: Method to supply water to agricultural lands from well, river, dam, etc.
Question 21.
What is the advantage of crop rotation?
Answer:
Rotation of crops helps in saving on nitrogenous fertilisers, because leguminous plants grown during the rotation of crops can fix atmospheric nitrogen in the soil with the help of nitrogen fixing bacteria.

Question 22.
What are the three advantages of shorter duration of the crop in between sowing and harvesting?
Answer:
Short durations allow farmers to grow multiple rounds of crops in a year. Short duration also reduces the cost of crop production. Uniform maturity makes the harvesting process easy and reduces losses during harvesting.
Question 23.
Which method is commonly used for improving cattle breeds and why?
Answer:
Cross breeding between a two good variety crops is called hybridization that also results in a new improved variety. Another way of improving the crop is by introducing a gene that would provide the desired characteristic. This results in genetically modified crops.
Question 24.
What are the types of food requirements of dairy animals? Why external and internal parasites live on and in the cattle can be fatal?
Answer:
Roughage and concentrates are the types of food requirements of dairy animals. The external parasites live on the skin and mainly cause skin diseases. The internal parasites like worms, affect stomach and intestine while flukes damage the liver.
Question 25.
What is composite fish culture system? Mention one merit and one demerit of this system.
Answer:
The composite fish culture system is a technology to grow both local and imported fish species in the water in the paddy field. One problem with such composite fish culture is that many of these fish breed only during monsoon. One of the advantages is that fish do not compete for food.
Question 26.
What is meant by bee-keeping? Name : (a) the variety commonly used for commercial honey production, (b) the variety having high honey collection capacity. State how pasturage is related to honey production.
Answer:
Beekeeping is the practice of rearing bee for making honey (a) Indian bee (Apis ceranaindica), (b) The Italian (Apis mellifera) bees have high honey collection capacity. Pasturage is the availability of flowers to the bees for nectar and pollen collection. Pasturage is related to honey production because it determines the taste of honey and the quantity of honey.

Question 27.
Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer:
Continuous plantation of crops in a field affects soil fertility. Plants utilise all the nutrients from soil which leads to depletion of nutrients in the soil. As a result, soil fertility reduces drastically.
Question 28.
Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
Answer:
Sending crop to sugar factory → Irrigation → Harvesting → Sowing → Preparation of soil → Ploughing the field → Manuring
Preparation of soil → Ploughing the field → Manuring → Sowing → Irrigation → Harvesting → Sending crop to sugar factory.
Question 29.
Explain different types of fisheries.
Answer:
The different types of fisheries are marine fisheries, inland fisheries, capture fishing, mariculture and aquaculture.
- Marine fisheries: Marine fish are caught using fishing nets.
- Mariculture: Marine fish are cultured in seawater.
- Inland fisheries: The fisheries done in freshwater resources like canals, ponds, reservoirs and rivers.
- Capture fishing: It is done in sea-water, estuaries and lagoons.
- Aquaculture: Culture of fish done in different water bodies is called aquaculture.
Question 30.
What are the practices used for dairy industry?
Answer:
The practices used for dairy industry to get the optimum yield are:
(i) Shelter, (ii) feeding, (iii) rearing of animals, (iv) breeding.
(i) Shelter: The shelter should be clean, spacious and airy.
(ii) Feeding: Proper food at proper time is essential for dairy animals.
(iii) Rearing of animals: Providing them proper health care and protection from pathogens, diseases and proper vaccination.
(iv) Breeding: The crossing of different variety of milch animals to obtain a . breed that can produce more yield of milk.
Question 31.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer:
The crop of wheat needs mild to moderate temperature and frost free days; along with irrigation but no water logging. Winters are suitable for growing wheat. In the kharif season; which coincides with the peak summer months in India, temperature is at its peak which is not suitable for wheat. Moreover, during rainy season lot of water accumulates in fields which would be harmful for wheat crop. Hence, if wheat is sown in the kharif season; the productivity would be minuscule and would not be profitable for the farmers.

Question 32.
List-out some useful traits in improved crop.
Answer:
- Yield is improved to a high level.
- Resistance developed from biotic and abiotic stresses.
- Disease resistance is developed.
- Enhanced nutritional qualities.
- Adaptabilities were improved in the crop.
- Desired agronomic characteristics were developed, e.g. improved shelf life, more pulpiness, seedless, etc.
Question 33.
Why is organic matter important for crop production?
Answer:
The importance of organic matter for crop production are :
- Soil fertility will be improved.
- It enhances soil structure and porosity in soil.
- It also helps in improving water holding capabilities in sand cultivation.
- Organic matter also helps in improving drainage.
- Water logging problems in day soil will also be improved.
Question 34.
Differentiate between compost and vermicompost.
Answer:
Compost formation is the process in which decomposition of the organic wastes takes place to produce manures.
Vermi-compost is the degradation of organic matter present in waste to produce manui-es with the help of earthworms.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the various methods of irrigation in India?
Answer:
Most of agriculture in India is rain-fed, several different kinds of irrigation system are adopted to supply water to agricultural lands. The resources are- wells, canals, rivers and tanks.
- Wells: Dug wells and tube wells. In dug wells water is collected from water- bearing strata.
- Tubewells: Water from deeper strata.
- Canals: Most extensive irrigation system. Canals receive water from reservoirs or rivers. The main canal is divided into branch canals having further distributaries to irrigate fields.
- River lift system: Water is directly drawn from the river for supplementing irrigation in areas close to rivers.
- Tanks: These are small storage reservoirs, which intercept and store the run-off of smaller catchment areas.

Question 2.
What are the different patterns of cropping?
Or
What are the different cropping systems?
Answer:
Different systems of growing crop:
(a) Mixed cropping
(b) Inter-cropping
(c) Crop rotation.
(i) Mixed cropping : Two or more crops grow simultaneously on the jame piece of land, is called mixed cropping.
Example: Wheat + grain, wheat + mustard.
(ii) Inter-cropping: It is a method of growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite pattern. A few rows of one crop alternate with a few rows of second crop.
Example: Soyabean + Maize or Bajra + Lobia.
(iii) Crop rotation: The growing of different crops on a piece of land in a succession is known as crop rotation.
Question 3.
Large amount of food grains get spoiled every year in India due to improper storage of food grains. How can this be avoided?
Answer:
Food grains get spoiled by insects, fungi, rodents, bacteria, moisture at the place of storage.
Storage losses can be reduced by taking some preventive and control measures.
- The seeds that are to be stored should be dry.
- The grains should be cleaned.
- The grains should be fumigated using chemicals that kills pest.
- The storage houses should be waterproof.
- The grains should be stored in sealed gunny bags.
- The bags should be kept few centimetres away fiom the wall.
- The walls and the floor should be water-proof with no holes in it, to avoid rodents, pests.
Question 4.
Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Preparation of soil:
Preparation of soil is the first step of farming. Soil is loosened and turned over. This helps in making the soil more airy so that roots can breathe in air. Moreover, loosening of soil also facilitates better penetration of roots into the soil. Seeds can be easily sown in loosened soil.
(b) Sowing:
The method of putting the seeds into soil is called sowing. Traditionally, seed is sown manually by spreading the seeds by hands. This process is called broadcasting. Seed drills are used when sowing needs to be done on a large scale.
(c) Weeding:
Removal of weeds is called weeding. Unwanted plants which grow along with the crops are called weeds. They compete for resources; like sunlight, water and air; with the main crop. So, it is necessary to remove weeds for proper growth of crops. Weeding is usually done manually by using hands and sickles. Sometimes weediddes are also sprayed.
(d) Threshing:
Separation of grains from harvested stems is called threshing. For smaller quantity, threshing is done by hands. For somewhat bigger quantity, threshing is done using animal; especially bullocks. Animals are made to trample over the harvested stock which helps in separation of grains. Threshing machines are used for bigger quantities.

Question 5.
Give brief sketch on advantages and disadvantages on manure and fertilisers.
Answer:
Advantages of manure:
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
- It improves the texture of soil by adding organic matter (humus).
- It increases soil fertility, water holding capacity and aeration.
- It reduces soil erosion.
- It is cheap.
Disadvantages of manure:
- They have fewer amounts of nutrients as compared to fertilisers.
- Manures are bulky and not easy to store and transport.
Advantages of fertilisers:
- They are nutrient specific and required in small amounts.
- They are water soluble and absorbed by the plant easily.
- They are easy to store and transport.
Disadvantages of fertilisers:
- Fertilisers can change the soil structure by killing the soil microbes.
- Fertilisers can change the chemical composition of soil.
- Accumulation of fertilisers in water bodies causes eutrophication.
Question 6.
What are weeds? How can we control them? Give different methods of weed control.
Answer:
Unwanted plants which grow along with crops are called weeds. Weeds compete with crops for natural resources; like sunlight, water and nutrients. Thus, weeds hamper the growth of crops. Weeds are usually removed manually by hands and by sickles. This process is called weeding. Sometimes, weedicides are also sprayed to kills weeds.
Weeds can be controlled by different methods :
(a) Weedicides: These are the chemicals sprayed on the weeds to kill them. Excessive use is poisonous and causes environmental pollution.
(b) Mechanical removal: In this method weeds are uprooted by removing manually or by machines.
(c) Preventive methods: Proper seed bed preparation, timely sowing of crops, intercropping and crop rotation helps in weed control.

Question 7.
Define:
(i) Vermicompost
(ii) Green manure
(iii) Bio-fertiliser
Answer:
(i) Vermicomposts: These are the products obtained by the process of composting using various earthworms to create a heterogeneous mixture of decomposed vegetables.

(ii) Green manures: These are referred to those fast growing plants which could be sown to cover bare lands to transform them into fertile soil for cultivation. Such manures also prevent soil erosion and add valuable nutrients to the soil which enhance soil quality. For example: sun hemp.
(iii) Bio-fertilisers: Substances which utilise microorganisms to enhance plant growth and nutrient absorption from soil (e.g. blue green algae are effective for nitrogen fixation in soil and rice fields).
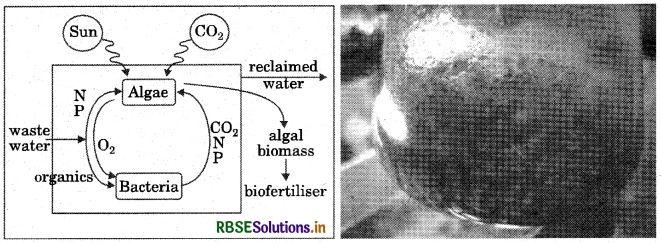
These methods are highly beneficial for productivity and are environment friendly in nature.
Question 8.
Differentiate between the following:
(i) Capture fishery and Culture fishery
(ii) Mixed cropping and Inter cropping
(iii) Bee-keeping and Poultry farming
Answer:
(i) Capture fishery is the method used to obtain fishes from natural resources whereas culture fishery is the method by which fishes can be obtained through fish farming.
(ii) Mixed cropping is the method of growing two or more crops simultaneously within the same land piece whereas the inter-cropping is a method of growing two or more crops in the same land but with definite division of growing area, i.e. divided into equal rows.

(iii) Bee-keeping is the practice through which yielding of honey is focused, whereas poultry farming is a practice which is done to raise the domestic fowl for the production of eggs and meat.

Question 9.
Give the merits and demerits of fish culture.
Answer:
Merits of Fish Culture:
- Large quantities of desired fishes can be generated.
- Profit earning mode of employment when pain is less than cattle rearing.
- Aquaculture has proved to safe and good source of employment.
- Produces healthy and disease free fishes.
- High yield despite of small area covered.
- The natural food chain is not hampered with the increase in population
Demerits of Fish Culture:
- Only economically valued fishes are cultured.
- Continuous supply of freshwater is required.
- Maintenance of natural habitat is desired.
- Uses of distinct disinfectants are reqiiired for diverse variety of fishes.
- The target is to grow only a few variety of fishes which could be a threat to biodiversity.
Question 10.
Write the modes by which insects affect the crop yield.
Answer:
There are various parts of plant bodies for insects which can be leaves, flowers, fruits and stems. They cause damage to the plant body and even to the fruits. Thus, this leads to heavy loss for farmers and cultivators. The various ways through which insects can damage crops are as follows:
- Cutting off plant parts through biting and chewing of stems and leaves of a plant.
- Cell sap suction through creating a hole and then sucking or entering in the stem.
- Few insects feed on the secondary products deposited on tree trunk or insects living on plant stems creating damage to the surface.
- They could also act as disease vectors transmitting to the plants and further to consumers.
- This will lead to the production of unhealthy crop.
- The presence of insects on plant bodies also attracts population of birds causing damage to agriculture.
- Insects like bees have a tendency to fly surrounding the ripened fruits.
Question 11.
Discuss why pesticides are used in very accurate concentration and in very appropriate manner.
Answer:
Substances used for the destruction of insects or other organisms harmful for the cultivated agricultural fields are known as pesticides. Pesticides should be used in accurate concentration and in an appropriate manner since it is harmfiil for the environment and human beings. As pesticides are highly toxic in nature, it is mainly cancer causing for human beings.
The various environmental impacts are as follows:
(i) Water pollution: The runoff water from the fields through rain or the drainage system of field causes harm to the surrounding. Mixing of this water to the nearby water bodies can affect the aquatic ecosystem and the edible source of water for the society. This could be hazardous for human health.
(ii) Air pollution: When the suspended particles are carried away by wind to other areas it contributes in the contamination of those areas as well. This contamination could lead to air borne diseases.
(iii) Soil pollution: The pesticide works has its adverse effects on the biodiversity of soil as well as in depleting its nourishment capability. The accumulation of chemical substances and the percolated or leached particles inside the soil of distance areas can lead to various diseases affecting the other habitats.
(iv) Biodiversity: The affected species can develop resistance through the repeated application of pesticides. Also, the degree of chemical toxin present in the pesticides can kill other microorganisms and animals (insects, birds, and grazing animals) found in the farmland.
(v) Human health hazards: Wide ranges of impacts were observed including both short term and long term disasters. The type of sufferings depends on the type of pesticide usage. They can be acute dangers (such as skin and eye allergies, headache, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, etc.) and chronic symptoms (such as cancer, reproductive damage, endocrine disruption, etc.).

Question 12.
Name two types of animal feed and write their functions.
Answer:
Livestock feeds are the feeds which provide the basic nutrients required by the animals along with the various nutrient supplements beneficial for their growth and development. These supplements include nutrients like macro, micro, minerals, vitamins, proteins, and amino acids.
The two types of animal feeds are as follows:
Roughage is known as the dietary fibres which are responsible for the production of high energy and is a good source of protein. In industries where milk production and meat production' are focused, the animals are fed with high roughage content. It induces more milk production and helps the animals to gain good weight.
Concentrates are those feeds which includes high density of various important nutrients required for energy generation. These are mainly low in crude fibre content and high digestible contents like that of vitamins, minerals; amino acids and micro and macro-nutrients. These help in healthy production of cattle products.
The only difference in between roughage and concentrates is the feeding quantity. Concentrates being compressed with equivalent source of energy and nutrients, it is provided in a maintained quantity. However, roughages comprising of more indigestible fibrous elements are provided in good amount.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 हमारे आस - पास के पदार्थ
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 Motion
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 9 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 13 Why Do We Fall Ill
- RBSE Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 प्राकृतिक सम्पदा
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 10 गुरुत्वाकर्षण
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 गति
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 9 बल तथा गति के नियम
- RBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions Chapter 13 हम बीमार क्यों होते हैं