RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Light
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 16 Light Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 8. Students can also read RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 8 Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Browsing through class 8 science chapter 14 extra questions that includes all questions presented in the textbook.
RBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Important Questions Light
Objective Questions
Question 1.
When an incident ray of light falls perpendiculary on the surface of mirror, the reflected ray:
(a) After reflection, it returns through the same path.
(b) After reflection it goes away from normal.
(c) After reflection it doesnot go away from normal.
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) After reflection, it returns through the same path.

Question 2.
Image formed after reflection from the plane mirror is:
(a) only virtual
(b) only real
(c) may be real or vitural
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) only virtual
Question 3.
What will be the angle of reflection for an incident ray which is normal to the mirror,
(a) 90°
(b) 0°
(c) 45°
(d) 180°
Answer:
(b) 0°
Question 4.
Night blindness is caused due to:
(a) Deficiency of Vitamin A
(b) Deficiency of Vitamin B
(c) Excess of Vitamin A
(d) Excess of Vitamin D
Answer:
(a) Deficiency of Vitamin A
Question 5.
Intensity of light entering our eye is controlled by:
(a) Iris
(b) Ciliary muscles
(c) Cornea
(d) Lens
Answer:
(a) Iris
Fill in the blanks
1. Diffused reflection takes place on ........................... surface.
Answer:
rough
2. Sun light is made of ...........................
Answer:
seven colours
3. Separation of light into its constituent colours is called ...........................
Answer:
dispersion

4. Angle of incidence and angle of reflection are ...........................
Answer:
equal.
True/False
Write ‘T’ for the correct and ‘F’ for incorrect in the given statements:
1. Light is not reflected from every surface.
Answer:
False
2. Regular reflection is caused by irregular/ rough surface.
Answer:
False
3. Angle of incidence and angle of reflection are equal.
Answer:
True
4. Sun light is composed of seven colours.
Answer:
True
5. Separation of light into its constituent colours is called dispersion.
Answer:
True

6. Image formed by a mirror is not laterally inverted.
Answer:
False
Match the words given in 'Column-A’ with 'Cohimn-B'
Question 1.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Incident ray |
(a) Angle between the reflected ray and the normal |
|
(ii) Reflected ray |
(b) The ray falling on the surface |
|
(iii) Angle of incidence |
(c) The ray coming from the surface after reflection |
|
(iv) Angle of reflection |
(d) The angle between the normal and the incident ray |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Incident ray |
(b) The ray falling on the surface |
|
(ii) Reflected ray |
(c) The ray coming from the surface after reflection |
|
(iii) Angle of incidence |
(d) The angle between the normal and the incident ray |
|
(iv) Angle of reflection |
(a) Angle between the reflected ray and the normal |
Question 2.
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Iris |
(a) Colour sensitive |
|
(ii) Cornea |
(b) Light sensitive |
|
(iii) Cone |
(c) Transparent front part of eye |
|
(iv) Rods |
(d) Control the amount of light entering into the eye |
Answer:
|
Column-A |
Column-B |
|
(i) Iris |
(d) Control the amount of light entering into the eye |
|
(ii) Cornea |
(c) Transparent front part of eye |
|
(iii) Cone |
(a) Colour sensitive |
|
(iv) Rods |
(b) Light sensitive |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why do we see objects?
Answer:
When light from the objects enters our eyes, we see objects.
Question 2.
What is the nature of the image formed by a plane mirror?
Answer:
Image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect.
Question 3.
What is reflection of light?
Answer:
When a light ray is incident on a reflecting surface, if it return into the same medium, it is called reflection of light.
Question 4.
What is lateral inversion?
Answer:
Image formed by a plane mirror has right side of object as its left and left side of object as its right, this is called lateral inversion.

Question 5.
What is a unique quality of Kalieidoscope?
Answer:
Any pattern once seen in it cannot be seen again.
Question 6.
Which property of light is responsible for separating white light into seven colours?
Answer:
Dispersion of light.
Question 7.
To which part of light cone responds?
Answer:
Cons responds to the constituent colours of light.
Question 8.
Which sensory cells work in dim light?
Answer:
Rod cells.
Question 9.
What is blind spot?
Answer:
At the junction of the optic nerve and the retina, there are no sensory cells, so no vision is possible at that spot. This is called
blind spot.
Question 10.
What is cataract?
Answer:
In old age, eye lens become foggy and ability of vision decreases. This is called cataract. It can be corrected by surgery.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
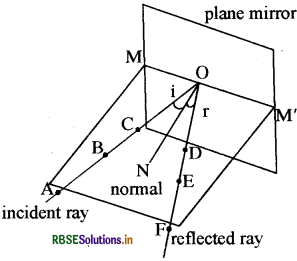
Write two laws of reflection and draw a diagram to show that.
Answer:
- Angle of incidence is equal to angle of reflection.
- Incident ray, reflected ray and normal lie on the same plane.
Question 2.
Write the process of image formation by a plane mirror. Write the qualities of that image.
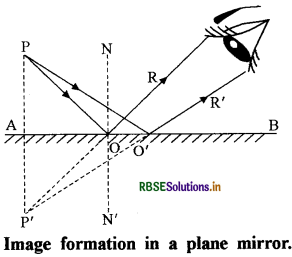
Answer:
Here ‘P’ is an object kept in front of the plane mirror AB. The light rays PO and PO' from this object are incident on the mirror and get reflected in the direction of OR and O'R'. These reflected rays of light when reach our eyes appear to be coming from P'. Hence P' is the image of object P.
Qualities of this image:
- The distance of image from the mirror is same as the distance of object from the mirror.
- Image is always virtual.
- Size of image is same as that of object but it is laterally inverted.
Question 3.
How many types of reflection of light are present? Explain.
Or
What is reflection? How many types of it are there? Explain the types with diagram.
Answer:
Reflection:
When a light ray is incident on a reflecting surface, if it returns into the same medium, it is called reflection of light.
Reflection of light is of two types:
1. Regular reflection: When a light is incident on a plane smooth surface like plane mirror, then all the reflected ray travel in a particular fixed direction, this is called regular reflection.
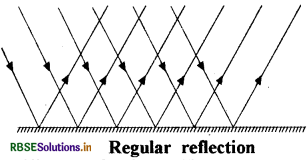
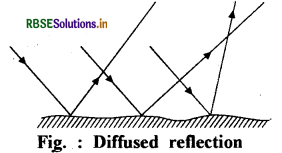
2. Diffused reflection: When a light ray is incident on a rough surface, the rays get reflected in different directions, this is called irregular diffused reflection.

Question 4.
What do you mean by illuminated objects? Explain.
Answer:
The objects which shine by the light of other objects are called illuminated objects.
For example:
Moon shines due to light of sun. Therefore it is an illumitated objects. Objects which shine on their own are called luminous objects.
Question 5.
How can the focal distance of our eye lens change?
Answer:
The shape and size of eye lens is controlled by ciliary muscles by which its focal length also changes. When muscles are relaxed, focal length increases and therefore far away objects can be seen clearly. For some nearby objects, muscles contract and so focal length decreases so nearby objects can be seen clearly.
Question 6.
What is the reason that we cannot see the original colours in dim light?
Answer:
In dim lights, rod cells are very active but cone cells are less active and cone cells are involved in the identification of appropriate colours.
Question 7.
Do the cone cells of retina equally sensory for all the colours of primary light?
Answer:
No, cone cells are differently active for the primary colours, red, green and blue. When red light falls on retina, the cone cells receptive for red colour will get active and sensory and the others won’t.
Question 8.
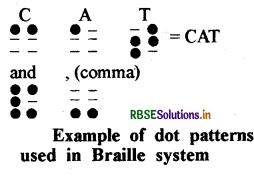
What is Braille system? Represent it with a dotted pattern.
Answer:
The most popular resource for visually challenged persons is known as Braille system. Braille system has 63 dot patterns or characters. Each character represents a letter, a combination of letters, a common word or a grammatical sign.
Dots are arranged in cells of two vertical rows of 3 dots each. These patterns when embossed on Braille sheets help visually challenged to recognise words by touching. To make them easier to touch, the dots are raised slightly.
Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What is reflection? What are the laws of reflection ? Explain the angle of incidence and angle of reflection and write a relation between them.
Answer:
The light returns back after colliding with a surface that separates two medium. This phenomena is called reflection. In this, light doesnot change its medium, it changes its path after reflection.
Laws of reflection:
- Reflected ray, incident ray and normal, all lie in the same plane.
- Angle of incidence (i) is equal to angle of reflection (r).
Angle of incidence i is the angle between incident ray and the normal at the point of incidence.
∠AON = ∠i
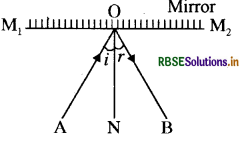
Angle of reflection r is the angle between reflected ray and the normal at the point of reflection.
∠BON = ∠r
Relation: ∠i = ∠r
Question 2.
Explain the parts and working of human eye.
Or
Explain the structure of human eye with labelled diagram.
Answer:
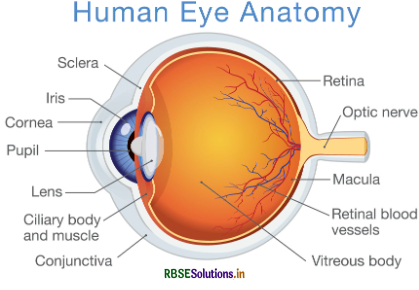
Structure of eye has the following parts:
1. Sclera:
This is the upper layer the eye ball that is thick, solid, white and opaque. This helps maintain the structure of eye ball and to protect eye from external injuries.
2. Cornea:
This is a small bulged out part in front of sclera. This can also be said as transparent layer that joins upper and lower part of sclera.
3. Iris:
It is an opaque membrane behind the cornea. There is a hole in middle of the iris. It is mostly black in colour.
4. Pupil:
The hole in the iris is called pupil. It has a quality that by the help of muscles, its size decreses on more light intensity and its size increases in dim light conditions. Its diameter increases to 1cm. in darkness while it decreases to the size of pin head in sun light.
5. Eye lens:
There is a thick convex lens behind iris called Eye lens. This lens is soft and made up of transparent material and remains at a fixed place with the help of muscles. Generally, the outer surface of convex lens has a radius of 1cm. and the radius of the other inner Surface is 6mm. By changing the stress in muscles, the radius of curvature of the lens can be altered. A small, inverted and real irtiagc is formed of an object is seen through this lens.
6. Choroid:
On the inner side, it is a black coloured film present beneath the sclera. Because it is black, it absorbs all the light so that no reflection takes place within the eye. It has a lot of blood capillaries and veins on its surface which provides nourishment to the eye.
7. Retina:
It is the innermost layer beneath the choroid. This layer is called Retina. Retina is composed of many nerve fibres. The stimulus experienced by nerve cells reaches brain through optic nerve.
Nerve cells are of two types:
1. Cones:
Sensitive for bright light intensity.
2. Rods:
Sensitive for dim light intensity. Besides this, cones also transfer informations about colours. At the point of connection of optic nerve with retina, no nerve cells are present there. This point is called blind spot. If image of an object is formed at blind spot, it will not be seen.

Question 3.
Explain the power of accomodation and vision range of eye. How are the eye defects developed in human. How can these be treated?
Answer:
Accommodation Power of an eye:
Muscles associated with eye lens can easily change the focal length of the eye. This process of changing focal length of eye lens by muscles is called power of accommodation of eye.
Vision Range:
For a healthy human eye, the nearest vision limit is 25cm. and farthest is infinity (∝). The distance between these two points is vision range.
Eye defects:
Due to age or some other factors, eye defects are developed in eye. For example some people can see nearby objects clearly but not those which are kept far away. This is called near sightedness while some can see distant objects but not nearby, this is called forsightedness. We can use appropriate optical lenses to treat this. With the use of lenses eye can be corrected for vision.
Cataract:
This is a common disease in old people. In this, the crystal clear lens become foggy and opaque due to a formation of opaque membrane. Due to this vision becomes weak. This can only be treated by a surgery in which this defective lens are replaced by artificial lens.

- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Class 8 Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 16 Light
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and Plastics
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 4 Materials: Metals and Non-Metals
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 5 Coal and Petroleum
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 6 Combustion and Flame