RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 4 Air
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 4 Air Important Questions
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 7. Students can also read RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 7 Social Science Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily. Go through these प्लेट क्यों घूमती है and get deep explanations provided by our experts.
RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 4 Air
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which is the most plentiful gas in the air?
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Argon
(d) Carbon Dioxide
Answer:
(b) Nitrogen
Question 2.
Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from the space:
(a) Thermosphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) Biosphere
Answer:
(c) Mesosphere

Question 3.
It shows the direction of wind:
(a) Rain Gauge
(b) Wind Vane
(c) Barometer
(d) Thermometer
Answer:
(b) Wind Vane
Question 4.
What changes from day to night but also from season to season?
(a) Temperature
(b) Wind
(c) Sim
(d) Clouds
Answer:
(a) Temperature
Question 5.
It is a form of precipitation:
(a) Rain
(b) Hail
(c) Snow
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
Green plants produce oxygen during the process of ...............
Answer:
Photosynthesis,
Question 2.
Above the mesosphere, lies the ............... layer.
Answer:
Thermosphere
Question 3.
The amount of ............... decreases from the equator towards the ...............
Answer:
Insolation, Poles,
Question 4.
Temperature is measured in ...............
Answer:
Degree Celsius
Question 5.
Air in motion is termed as ...............
Answer:
Wind
True/False
Question 1.
Atmospheric pressure is not the same everywhere.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Increased volume of carbon dioxide is affecting the earth’s weather and climate.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Water freezes at 100° C and boils at 0°C.
Answer:
False

Question 4.
Air presses us from all directions and our body exerts a counter pressure.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
With the increase in temperature the air becomes lighter and moves upwards.
Answer:
True
Match the column
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
1. Green plants |
(a) 0.93% |
|
2. Carbon dioxide |
(b) 80 km |
|
3. Argon |
(c)13 km |
|
4. Troposphere |
(d) 0.03% |
|
5. Mesosphere |
(e) photosynthesis |
Answer:
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
1. Green plants |
(e) photosynthesis |
|
2. Carbon dioxide |
(d) 0.03% |
|
3. Argon |
(a) 0.93% |
|
4. Troposphere |
(c)13 km |
|
5. Mesosphere |
(b) 80 km |
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which gas is called as the Green House Gas?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is called as the Green House Gas.
Question 2.
What is the percentages of nitrogen and oxygen in air?
Answer:
Nitrogen is 78% and oxygen is 21% in Air.
Question 3.
Due to which gas the balance of earth’s weather and climate is adversely affected?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide helps to make the balance of earth’s weather and climate.
Question 4.
What is average height of troposphere?
Answer:
The average height of troposphere is 13 km.
Question 5.
Who invented the unit to measure temperature?
Answer: Anders Celsius invented the unit to measure temperature.
Question 6.
What is the direction of the airflow?
Answer:
Air always moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
Question 7.
What are the other forms of precipitation?
Answer:
Rain, snow, sleet and hail.
Question 8.
What is insolation?
Answer:
Insolation is exposure to the sun’s rays. It is the amount of solar radiation reaching at given area.
Question 9.
What is released in the air from the burning of fuels?
Answer:
When these fuels burn, the carbon and hydrogen atoms combine with oxygen atoms to produce carbon dioxide and water vapour.

Question 10.
What is condensation?
Answer:
Condensation is the change of physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase.
Question 11.
What is evaporation?
Answer:
Evaporation is the process in which a substance in a liquid state changing to a gaseous state due to an increase in temperature or pressure.
Question 12.
Name the instrument which measures air pressure.
Answer:
A barometer is a scientific instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure.
Question 13.
In which areas the convectional rainfall is common?
Answer:
Convectional rainfall is very common in areas where the ground is heated by the hot sun, such as the Tropics.
Question 14.
What is global warming?
Answer:
Global warming is the rise in the average temperature of the earth’s climate and its related effects.
Question 15.
Define dew point.
Answer:
The dew point is the temperature at which air is saturated with water vapour, which is the gaseous state of water.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain composition of air? Show it with diagram
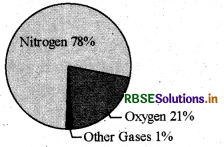
Answer:
Earth’s atmosphere is composed of air. Air is a mixture of gases, 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. The remaining 1% is made up of argon(0.93%), carbon dioxide (0.03%) and other trace gases (0.04%). Water vapour (water in its gaseous state) is also present in the atmosphere in varying amounts.
Question 2.
What is Ozone layer? How ozone is an important layer of atmosphere?
Answer:
Ozone layer is a gas in the atmosphere that protects every living being on the earth from harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays of the sun. Without the layer of ozone in the atmosphere, it would be very difficult for anything to survive on the surface. It protects us by absorbing harmful radiations (UV rays) that cause a variety of health problems in humans, plants and animals, as well as damage to the ecosystem. The ozone layer in the stratosphere is thin but powerful.
Question 3.
How does air circulation take place?
Answer:
When air is heated, it expands, becomes lighter and goes up. Cold air is denser and heavy. Thus, it tends to sink down: When hot air rises, cold air from surrounding area rushes there to fill the gap. This is how air circulation takes place.
Question 4.
Name the layers of atmosphere in sequence from earth surface. Which is the most important layer and why?
Answer:
The layers of atmosphere are:
- Troposphere
- Stratosphere
- Mesosphere
- Thermosphere
- Exosphere.
Troposphere is the most important layer of the atmosphere. Starting at ground level, it extends upward to about 13 km above sea level. We humans live in the troposphere, and nearly all weather phenomenon occurs in this lowest layer.
Question 5.
Why is the temperature of cities higher?
Answer:
In cities we find high rise buildings of concrete and metals. The tar of roads get heated up during the day. This heat is released during the night. Other reason is highly crowded buildings trap the warm air and raise the temperature of cities.
Question 6.
Write a short note on air pressure?
Answer:
Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. As we go up in the layers of atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly. The air pressure is the highest at sea level and decreases with height,
- In areas where temperature is high, the air gets heated and rises. This creates low pressure area and there is cloudy sky and wet weather,
- In areas with high pressure, air is cold and becomes heavy. Heavy air sinks and is associated with clear and sunny skies. The air always moves from high to low pressure areas.
Question 7.
State the difference between weather and climate.
Answer:
Weather is-the day-to-day state of the atmosphere, and it varies in short-term i.e., within minutes to hours or days to weeks. People generally think of weather as the combination of temperature, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, visibility, and wind. We talk about changes in weather in terms of the near future. Climate is the weather of a place averaged over a period of time, often more than 10 years. Climate information includes the statistical data that tells us about the normal weather, as well as the range of weather changes for a location.

Question 8.
Cyclone Nature’s Fury.” Write a short note.
Answer:
Cyclone is a storm or strong wind that rotates about a centre of low atmospheric pressure with high speed and often brings heavy rains and cause disaster and damage. The damages caused are mainly due to wind velocity, rain and tides. The winds blow up to 260 km per hour. These high velocity winds uproot trees, damage kutcha houses. Power supply, electricity and other supplies are affected by heavy rains occurring with cyclonic winds causing tidal waves.
Question 9.
Write a note on Precipitation.
Answer:
Precipitation is the process by which condensed water vapour falls on the earth in the form of rain, snowfall, hail etc. Most precipitation falls as. rain. A rain gauge is an instrument used to gather and measure the amount of liquid precipitation over a set period of time.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the structure of the atmosphere with diagram.
Answer:
Our atmosphere is divided into five layers. They are:
(i) Troposphere,
(ii) Stratosphere,
(iii) Mesosphere,
(iv) Thermosphere,
(v) Exosphere.
(i) Troposphere:
This is the most important layer of atmosphere. Its average height is 13 km. The air we breathe exists here and almost all weather phenomena qepur in this layer like rainfall, fog, hail storm, etc.
(ii) Stratosphere:
It lies above troposphere and extends up to 50 kins. This layer is free from weather phenomenon and makes ideal conditions for flying aeroplanes. This layer contains layer of ozone gas which protects us from the harmful effects of sun’s rays.
(iii) Mesosphere:
This is the third layer of atmosphere. It extends up to 80 km. Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from the space.
(iv) Thermosphere:
This is the fourth layer where temperature rises very rapidly with increasing height. Ionosphere is a part of this layer which extends to 80-400 km. It helps in radio transmission.
(v) Exosphere:
This is upper most layer with very thin gases like helium and hydrogen which float into the space from here.
Question 2.
Define wind and its types. Draw the diagram showing the wind system of the earth and pressure belts.
Answer:
The movement of air from high pressure area to low pressure areas is called wind. They are named after the direction they blow from. Types of winds are: Permanent Winds, Seasonal Winds and Local Winds.
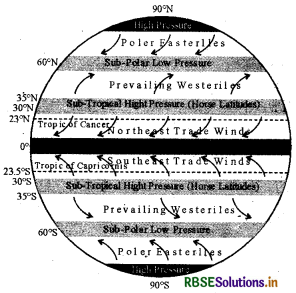
- Permanent Winds: The trade winds, westerlies and easterlies are the Permanent Winds. These blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction. Winds blowing from west are called Westerlies and from East are called Easterlies.
- Seasonal Winds: These winds change their direction in different seasons.For example: Monsoon winds in India.
- Local Winds: These blow only during a particular period of the day or year in a small area. For example: Land and sea breeze. The hot and dry local winds of northern plains are called “Loo”.
Question 3.
Give reasons:
(i) Places near the equator are very hot and places near the poles are very cold.
Answer:
Our earth is a sphere and the amount of sunshine received at various places on the earth is different. The places near the equator are the warmest because the sun’s rays hit it more directly whereas the places near the poles receive slanting rays of the sun making these places the coldest as they receive' very less sunshine.
(ii) We see a white line following a jet rocket.
Answer:
The white lines following jet rockets or planes left behind are actually artificial clouds. As hot exhaust gases escape from a plane, the water vapour in the fumes hits the air. The cold air causes the water vapour to condense. This means the water vapour turns into tiny water droplets or even freeze into tiny ice crystals.This condensed water vapour and mixture of ice crystals make up the cloud-like trails we see in the sky.
(iii) A high pressure on land and low pressure on sea is created during the night.
Answer:
At night, the land is cooled down much more quickly than the sea (which is heated up by sun during daytime). Hence, the air above the sea expands and rises causing low pressure and moves towards the land causing high pressure on it.

Question 4.
Describe the fury of cyclone taking example of ‘Super cyclone’ of Odisha.
Answer:
Odisha on eastern sea coast of India is prone to cyclones originating in Bay of Bengal.
- Odisha was hit by cyclone on 17th- 18th October, 1999 and again on 29th October.
- Cyclone originated as a ‘depression’ in the Gulf of Thailand near Port Blair.
- It moved in northwest direction on 25th October and intensified into super cyclone and hit Odisha.
- Wind speed was upto 260 km/hr which lasted for 36 horns.
- Trees were uprooted kutcha houses, roof tops industrial sheds etc. blown away.
- Power supply and communication lines damaged.
- Continues rains flooded the major rivers. Tidal waves swept 20 km of inland areas including cities of Bhubaneshwar and Cuttack and destructed 28 coastal towns.
- 7-10 m high tidal waves caused damage to paddy crops, vegetables fruits and agricultural land turned infertile due to salination.
- 13 million people were affected. Livestock was killed.
- Plantations of teak, sal, bamboo, mangrove forests of Paradeep and Konark disappeared.

- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Notes in Hindi & English Medium Pdf Download
- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science in Hindi Medium & English Medium
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 8 बाज़ार में एक कमीज़
- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 9 समानता के लिए संघर्ष
- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 8 बाज़ार में एक कमीज़
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 9 समानता के लिए संघर्ष
- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 7 हमारे आस-पास के बाज़ार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 7 हमारे आस-पास के बाज़ार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 6 संचार माध्यमों को समझना
- RBSE Class 7 Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 6 संचार माध्यमों को समझना