RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 14 Movements of Ocean Water
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 14 Movements of Ocean Water Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Geography Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 14 Movements of Ocean Water
Multiple Choice Questions
1. Which of the following seas has the highest salinity?
(A) Red Sea
(B) Baltic Sea
(C) Rome Sea
(D) Dead Sea.
Answer:
(D) Dead Sea.

2. Name a part where ships enter with the help of tides?
(A) Kolkata
(B) Mumbai
(C) Gujarat
(D) Odisha.
Answer:
(A) Kolkata
3. The earth reaches its perihelion in
(A) October
(B) September
(C) July
(D) January.
Answer:
(D) January.
4. In which ocean, flows Gulf stream?
(A) Atlantic Ocean
(B) Indian Ocean
(C) Pacific Ocean
(D) Arabic Ocean.
Answer:
(A) Atlantic Ocean
5. The gravitational pull of sun is less than that of moon-
(A) 3/11
(B) 4/11
(C) 5/11
(D) 7/11.
Answer:
(C) 5/11
6. Which is the cold current?
(A) Gulf Stream
(B) Labrador Current
(C) Brazil Current
(D) Kuroshio Current.
Answer:
(B) Labrador Current
7. Which is a tidal port?
(A) Mumbai
(B) Kolkata
(C) Cochi
(D) Vishakapatnam.
Answer:
(B) Kolkata
8. Which desert is located near canary current?
(A) Kalahari
(B) Sahara
(C) Thar
(D) Gobi.
Answer:
(B) Sahara
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are ice floes?
Answer:
The drifting ice fields.
Question 2.
What are icebergs?
Answer:
Large masses of floating ice.
Question 3.
Where are icebergs generally found?
Answer:
Near Greenland.
Question 4.
What is upwelling of water?
Answer:
When the cooler water from below comes up.
Question 5.
Name three types of Sea-waves.
Answer:
Sea, Swell and Surf.

Question 6.
What is an ocean current?
Answer:
General movement of mass of water in a regular direction.
Question 7.
Name two warm ocean currents of Atlantic ocean.
Answer:
Gulf Stream and Brazilian Current.
Question 8.
Name a cold current of Atlantic ocean.
Answer:
Labrador current.
Question 9.
Which two currents meet to create Fog near new foundland?
Answer:
Labrador and Gulf Stream.
Question 10.
Which current is called Black Stream?
Answer:
Kuroshio current.
Question 11.
Which current flows along coast of Sahara?
Answer:
Canary current.
Question 12.
Which current is a common current of three oceans?
Answer:
Antarctic Drift.
Question 13.
Where is the highest tidal range found?
Answer:
20 metres near Bay of Fundy.
Question 14.
Name two types of tides.
Answer:
Flood tide and Ebb tide.
Question 15.
Name a port where ships enter with help of tides?
Answer:
Kolkata.
Question 16.
What is tidal bore?
Answer:
A wall of water in deltas of a river.
Question 17.
What is the interval between two high tides?
Answer:
12 hrs. 25 minutes.
Question 18.
When does spring tide occur?
Answer:
On new moon and full moon.
Question 19.
When does neap tide occur?
Answer:
On first and the third Quarter of the moon.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are ocean currents?
Answer:
The ocean current is the general movement of a mass of water in a defined and fixed direction over great distance.
Question 2.
How can the velocity of a wave be determined?
Answer:
The velocity of a moving wave can be determined as follows :
Velocity of wave (v) \(=\frac{\text { Wave length }(\mathrm{L})}{\text { Wave Period }(\mathrm{T})}\)
The distance between two crests or or two successive troughs is the wave length. The time taken by a wave length to pass a fixed point is known as the wave period.
Question 3.
Distinguish between a cold and warm current.
Answer:
Ocean currents are broadly of two types :
Warm and cold currents. The warm currents flow from the low latitudes in tropical zones towards the high latitudes in polar areas. The cold currents flow from high latitudes to low latitudes.

Question 4.
How can the velocity of the ocean currents be measured?
Answer:
Air flowing over the water surface exerts a dragging force upon the surface setting the surface, water in motion. This drag produces currents :
The velocity of the ocean currents can be determined by wind velocity and dragging force.
Question 5.
If there were no ocean currents, what would have happened?
Answer:
Due to absence of ocean currents, the climate, trade and marine life would not have been the same. The continent of Europe could not have pleasant climate. The temperate region would have got less rainfall. The deserts would not have been located in western margins of continents. The European ports would not have been free for trade throughout the year. Fisheries would now have been found in some areas.
Question 6.
Name the main types of wind produced waves.
Answer:
According to their origin, the ocean currents are of three types :
- Longshore Currents. When the waves break against the shore and move parallel to the shore.
- Undertow. Seaward movement of water is known as undertow.
- Rip Currents. Rip currents are localised streaks of returning water.
Question 7.
Describe the main characteristics of ocean currents.
Answer:
Main Characteristics of Ocean Currents :
- According to Ferral’s law, ocean currents move to their right in the northern hemisphere and to their left in the southern hemisphere.
- Warm currents move towards cold seas and cold currents move towards the warm seas.
- In the lower latitudes, warm currents flow on the eastern shores and cold on the western shores.
- In the higher latitudes, warm currents move along the western shores and cold currents along eastern shores.
- Cold and warm currents meet along the convergence and move out along divergence.
- Cold currents move as sub-surface currents and warm currents move as surface currents.
Question 8.
What are icebergs? Describe the sources of icebergs.
Answer:
Huge masses of floating ice are known as icebergs. These break from the ice-sheets and reach the oceans were l/10th of the iceberg remains above seawater. There are numerous icebergs in the North Atlantic. These originate from the glaciers of Greenland. Icebergs in the southern hemisphere, originate from the Atlantic ice barrier. Alaska is also one of the sources for icebergs. These are dangerous for navigation and many accidents take place.
Question 9.
Why does Southampton (Southern Coast of England) experiences tides four times a day?
Answer:
Generally tides occur twice a day. But Southampton gets tides four times a day. This area connects North Sea with Atlantic Ocean through English Channel. Tides come twice from the Atlantic Ocean and twice from the North Sea. In total, tide comes four times a day.
Question 10.
Explain the importance of tides in Hoogly river.
Answer:
At the time of high tides, the water increases at the mouth of rivers. The rivers become navigable and big vessels can enter the river port. Kolkata is located along Hoogly river at a distance of 120 kms, but ships can enter the port due to tides.
Question 11.
What is a tidal bore?
Answer:
The vertical wall of water in the deltas of a river is called a tidal bore. When tide enters the narrow and shallow estuary of a river, it forces the river water in the opposite direction. When the height of tidal wave increases, the flow of water rushes upstream and acts like a wall. Tidal bore is common in Hoogly river.
Question 12.
Describe the Tides of Bay of Fundy (Canada).
Answer:
Tides of Bay of Fundy, Canada. The highest tides in the world occur in the Bay of Fundy in Nova Scotia, Canada. The tidal range is 15-16 metres (approximately 45-50 feet). Because there are 2 high tides and 2 low tides every day (roughly a 24 hour period); then a tide must come in within about a 6 hour period. As a rough estimate, the tide rises about 8 feet (or 96 inches) an hour (48 feet divided by 6 hours). This translates to a tide which rises at more than one inch per minute. If you have walked down a beach with a steep cliff along side (which is common there), be sure to watch the tides.
Question 13.
What is the interval between two tides?
Or
Tides are delayed every day by 50 minutes.
Explain.
Answer:
Tides do not occur regularly every twelve hours. They occur at an interval of 12 hours and 25 minutes.
Reasons. The moon revolves around the earth from west to east and completes one revolution in 29 days. The moon shifts away and moves a little eastward from its position in 24 hrs. Therefore, it takes an extra time (more than 24 hrs.) for the earth to bring the same point in line of the moon everyday.
Extra time = \(\frac{24 \mathrm{hrs} . \times 60 \text { minutes }}{29}=50\)
minutes.
So the tides are delayed by 50 minutes every day. As the tide occurs twice a day, each tide is delayed by 25 minutes. Hence high tides follow an interval of 12 hrs. 25 minutes.

Question 14.
Describe the geographical effects of tides.
Answer:
Advantages :
- Tides keep the coasts clear of all the waste and refuse of ports.
- Tides keep the water in motion and so ocean water does not freeze.
- Tides help some of the rivers in making navigable such as St. Lawrence, Hoogly and Hudson.
- Tidal force may be used as a source of electricity such as in France and Japan.
- Tides bring many shells, animals and other things from the oceans were:
- Tides help many big ships to reach the ports located in shallow waters. At high tides, ships can enter the harbour such as at Kolkata, London etc.
Disadvantages :
- Tides are sometimes harmful for ships and boats.
- Tides check the formation of the Deltas.
- Marshes are formed due to accumulation of tidal water.
- Tides also hinder fishing.
Comparison Questions
Question 1.
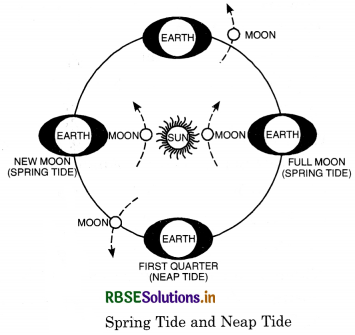
Distinguish between Spring tides and Neap tides.
|
Spring Tides |
Neap Tides |
|
1. The highest high tides are known as spring tides. |
1. The lowest high tides are known as neap tides. |
|
2. This occurs at new moon and full moon. |
2. Thisoccursatthefirstand the third quarter of the moon. |
|
3. On these days, the sun, the moon are almost in a line with the earth. Due to their combined pull, very high tides are produced. |
3. Onthesedays,thesunand the moon make a right angle at the earth’s centre. The pulls of the moon and the sun cancel each other out With the result, low tides are produced. |
|
4. Spring tide is the sum total of solar and lunar tides. |
4. Neap tide is the difference of solar and lunar tides. |
|
5. Spring tide is 20% higher than ordinary tides. |
5. Neap tide is 20% lower than that of ordinary tides. |
|
6. On these days high tide is higher and the low tide is lower than the usual. |
6. On these days the high tide is less higher and the low tide is less lower than usual. |
Question 2.
Distinguish between swell and surf.
Answer:
|
Swell |
surf |
|
1. The regular waves are called swells. |
1. The breaking waves near coast are called surf. |
|
2. Near coasts, the height of swells increases. |
2. Surf strikes the coast with a big noise. |
Question 3.
Distinguish between Swash and Back wash.
Answer:
|
Swash |
Back wash |
|
1. The broken masses of water dashing along the coast are called swash. |
1. The waves descending seaward from the coast are called back wash. |
|
2. The crest of these waves erodes this coast with a strong force. |
2. The under currents carry the sediments from coast to seaveards. |

Essay Type Questions
Question 1.
What are tides? How are these formed?
Answer:
Tides. The sea level is always changing. The water of the sea rises and falls twice a day. These are called tides. ‘The regular rise and fall of sea water is called tides’. When the sea water rises, it is known as flood or high tide or incoming tide. When the sea water falls, it is known as ebb or low tide or outgoing tide. In open seas, the height of the tide is about one metre, but the highest tidal range is found upto a height of 20 metres in the Bay of Fundy (North America).
Characteristics of Tides :
- The height of tides varies at different places.
- The period of high tide or low tide varies at different places.
- The seawater rises for 6 hours 13 minutes and falls also for the same period.
- Tides do not occur regularly at a place.
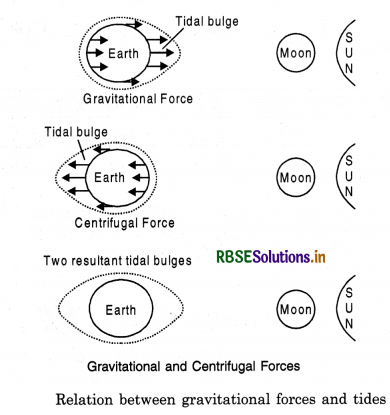
Causes of origin. According to Newton, tides are caused due to gravitational pull of the moon and of the sun on the earth. Due to gravitational pull, waters of the ocean are attracted towards moon. Water being liquid rises higher than the solid crust of the earth. This is known as high tide. Where the level of the water falls, it is known as low tide. Due to the rotation of the earth tides occur twice a day at a place. One tide occurs in the waters of the earth facing the moon; the other tide occurs at diametrically opposite side of the earth. This is due to the centrifugal force of the earth. The moon is very close to the earth and its gravitational pull is 5/11 times greater than that of the sun. The sun, owing to its greater distance from the earth, does not exert much influence.
Question 2.
Describe the different types of Tides.
Answer:
Types of Tides. Tides vary in their frequency, direction and movement spatially from place to place and also from time to time. Tides may be grouped into various types based on based on their frequency in one day or 24 hours or based on height.
(A) Tides based on Frequency
- Semi-diurnal Tide. The most common tidal pattern, featuring two high tides and two low tides each day. Successive high or low tides are approximately the same height.
- Diurnal Tide. There is only one high tide and one low tide during each day. Successive high and low tides are approximately the same height.
- Mixed Tide. Tides having variations in height are known as mixed tides. These tides generally occur along the west coast of North America and on many islands of the Pacific Ocean.
(B) Tides based on height.
The height of rising water (high tide) varies appreciably over space and time. Besides attraction of the Sun and the Moon, the narrowness of bays, and depth of water also influence the height of tides. Spring tides and neap tides come under this category.
1. Spring Tides. Tides at certain periods of time are unusually lower or higher than normal height. The position of both the sun and the moon in relation to the Earth has direct bearing on tide height. When all three are in a straight line, the tidal range will be higher. These are called spring tides and they occur twice a month, one on full moon period and another during new moon period.
2. Neap Tides result in less extreme tidal conditions. Normally there is a seven day interval between spring tides and neap tides. At this time the forces of the Sun and Moon tend to counteract one another. The Moon’s attraction, though more than twice as strong as the Sun’s, is diminished by the counteracting force of the Sun’s gravitational pull.
Source Based Questions
1. Read the following paragraph and answer the questions given below:
Tides vary in their frequency, direction and movement spatially from place to place and also from time to time. Tides may be grouped into various types based on their frequency in one day or 24 hours or based on height. The most common tide pattern features two high tides and two low tides each day. Successive high or low tides are approximately the same height. Diurnal tide is the only one high tide and one low tide during each day. Mixed tides have variations in height. These tides generally occur mainly along the west coast of North America.
(i) Upward and downward movement of ocean water is known as the-
(a) Tide
(b) Current
(c) Wave
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Tide
(ii) Which of the following tides occur along the west coast of North America?
(a) Semi-Diurnal
(b) Diurnal
(c) Mixed
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Mixed

(iii) Which of the following is a cycle with only one high tide and one low tide during each day?
(a) Semi Diurnal
(b) Diurnal
(c) Mixed
(d) Spring
Answer:
(b) Diurnal
2. Read the following paragraph and answer the given questions:
The highest tide in the world ocean in the Bay of Fundy in Nova Scotia, Canada. The tidal range is 15-16 metres. Because there are two high tides and two low tides everyday (roughly a 24 hour’s period), a tide must come in within about a 6 hours period. As a rough estimate, the tide rises about 8 feet or (96 inches) an hour (48 feet divided by 6 hours). This translates to a tide which rises at more than one inch per minute. If you have walked down a beach with a steep cliff alongside, be sure to watch the tides.
(i) Where is the highest tide in the world occurs?
(a) BayofFundy
(b) Nova Scotia
(c) Canada
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
(ii) How many tides must come in one day?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
(iii) Within how much period a tide must come?
(a) 4 hours
(b) 5 hours
(c) 6 hours
(d) 7 hours
Answer:
(c) 6 hours
HOTS QUESTIONS.
Question 1
How are waves caused? What are their characteristics?
Answer:
Waves. Waves are actually energy, not the water as such, which move across the ocean surface. Water particles only travel in a small circle as a wave passes. Wind provides the energy to the waves. Wind causes waves to travel in the ocean and the energy is released on shorelines. The motion of the surface water seldom affects the stagnant deep bottom waters of the oceans were As a wave approaches the beach, it slows down.
This is due to the friction occurring between the dynamic water and the beach i.e. sea floor, And, when the depth of water is less than half the wavelength of the wave, wave breaks. The largest waves are found in the open ocean Waves continue to grow larger as they move and absorb energy from the wind. When the wave height becomes one-seventh the size of the wave length, the wave will fall over.

SELF EVALUATION TEST
- What are ocean currents?
- Name three types of waves.
- Name a warm ocean current of Atlantic ocean.
- Name two types of tides.
- What are icebergs?
- What is a tidal bore?
- What is a swash?
- What are advantages of tides?
- Distinguish between cold and warm current.
- Distinguish between spring tide and neap tide.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 12 Geography Chapter 11 अंतर्राष्ट्रीय व्यापार
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भारत - स्थिति
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 3 पृथ्वी की आंतरिक संरचना
- RBSE Solutions for Class 8 Our Rajasthan Chapter 5 उद्योग
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 2 संरचना तथा भूआकृति विज्ञान
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Geography Chapter 1 भूगोल एक विषय के रूप में
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions in Hindi & English Medium
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 6 Soils
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation
- RBSE Class 11 Geography Important Questions Chapter 4 Climate