RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption
Rajasthan Board RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Important Questions and Answers.
Rajasthan Board RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology in Hindi Medium & English Medium are part of RBSE Solutions for Class 11. Students can also read RBSE Class 11 Biology Important Questions for exam preparation. Students can also go through RBSE Class 11 Biology Notes to understand and remember the concepts easily.
RBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 16 Important Questions Digestion and Absorption
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
In man the primary dentition differs from permanent dentition in the sense that primary dentition lacks which type of teeth?
(a) Canines
(b) Premolars
(c) Molars
(d) Incisors
Answer:
(b) Premolars

Question 2.
In which organ of mammals Glisson’s capsule is found?
(a) Stomach
(b) Kidney
(c) Testes
(d) Liver
Answer:
(d) Liver
Question 3.
The enzyme which is not present in succus entericus:
(a) Maltase
(b) Nuclease
(c) Nucleosidase
(d) Lipase
Answer:
(b) Nuclease
Question 4.
Gastric juice contains the following enzymes:
(a) Pepsin, lipase, rennin
(b) Trypsin, lipase, rennin
(c) Trypsin, pepsin, lipase
(d) Trypsin, pepsin, rennin
Answer:
(a) Pepsin, lipase, rennin
Question 5.
Which help to converting trypsinogen to trypsin?
(a) HCl
(b) Enterokinase
(c) Pepsin
(d) Gastrin
Answer:
(b) Enterokinase
Question 6.
Where from is rennin secreted?
(a) Small intestine
(b) Kidney
(c) Liver
(d) Stomach
Answer:
(d) Stomach
Question 7.
Which enzymes are protein digesting?
(a) Ptyalin, pepsin, erepsin
(b) Trypsin, amylase
(c) Trypsin, pepsin, erepsin
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Trypsin, pepsin, erepsin
Question 8.
Pancreatic juice is:
(a) Acidic
(b) Alkaline
(c) Enzymatic
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Alkaline
Question 9.
Where emulsification of fat takes place by bile?
(a) In duodenum
(b) In intestine
(c) In stomach
(d) In liver
Answer:
(b) In intestine
Question 10.
What is chymotrypsin?
(a) Protein digestive enzyme
(b) Vitamin
(c) Fat digestive enzyme
(d) Hormone
Answer:
(a) Protein digestive enzyme

Question 11.
Which enzyme is present in saliva?
(a) Amylase
(b) Ptyalin
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 12.
Where starch is digested?
(a) In stomach
(b) In stomach and duodenum
(c) In buccal cavity and oesophagus
(d) Buccal cavity and duodenum
Answer:
(d) Buccal cavity and duodenum
Question 13.
Trypsinogen is secreted by:
(a) Stomach
(b) Duodenum
(c) Pancreas
(d) Liver
Answer:
(c) Pancreas
Question 14.
The main function of intestinal villi is:
(a) Assimilation of digested food
(b) Ultra filtration
(c) Increase in absorptive surface
(d) Secretion of enzyme
Answer:
(c) Increase in absorptive surface
Question 15.
Where bilirubin and biliverdin found?
(a) In bile
(b) In blood
(c) In saliva
(d) In lymph
Answer:
(a) In bile
Question 16.
Glycogen is synthesised in liver by:
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Glycogenesis
(c) Glyconeogenesis
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Glycogenesis
Question 17.
Deficiency of which vitamin causes pellagra?
(a) B1 (Thiamin)
(b) B12 (Cobalamin)
(c) Niacin (Nicotinic acid)
(d) D (Calciferol)
Answer:
(c) Niacin (Nicotinic acid)
Question 18.
Where Glisson’s capsule is found?
(a) In liver
(b) In lung
(c) In kidney
(d) In stomach
Answer:
(a) In liver
Question 19.
Riboflavin is:
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B2
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin B12
Answer:
(b) Vitamin B2
Question 20.
Which portion of tooth is covered by enamel?
(a) Crown
(b) Root
(c) Dentine
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Crown
Question 21.
Hunger centre is present in:
(a) Stomach
(b) Cerebrum
(c) Hypothalamus
(d) Cerebrum and hypothalamus
Answer:
(d) Cerebrum and hypothalamus
Question 22.
Which type of teeth found in human?
(a) Acrodont
(b) Thecodont
(c) Polydont
(d) Monophyodont
Answer:
(b) Thecodont
Question 23.
Kupffer cells are found:
(a) In liver
(b) In small intestine
(c) In pancreas
(d) In thyroid
Answer:
(a) In liver
Question 24.
The largest gland in adult human is:
(a) Thymus
(b) Liver
(c) Pancreas
(d) Thyroid
Answer:
(b) Liver
Question 25.
Islets of Langerhans are found in:
(a) Liver
(b) Kidney
(c) Thyroid
(d) Pancreas
Answer:
(d) Pancreas
Question 26.
Crypts of Lieberkuhn are related to:
(a) Secretion of succus entericus
(b) Secretion of rennin
(c) Secretion of ptyalin
(d) Digestion of fat
Answer:
(a) Secretion of succus entericus
Question 27.
The hardest substance in human body is:
(a) Bone
(b) Hair
(c) Dentine
(d) Enamel
Answer:
(d) Enamel
Question 28.
Lacteal is concerned with:
(a) Secretion of lactic acid
(b) Absorption of long chain fatty acids
(c) Absorption of small chain fatty acids
(d) Production of lymph
Answer:
(b) Absorption of long chain fatty acids
Question 29.
Pancreatic juice from pancreas is secreted by stimulation of:
(a) Rennin
(b) Gastrin
(c) Secretin
(d) Trypsin
Answer:
(c) Secretin
Question 30.
Synthesis of carbohydrates from amino is called:
(a) Glycolysis
(b) Glycogenesis
(c) Gluconeogenesis
(d) Glycogenolysis
Answer:
(c) Gluconeogenesis
Question 31.
Folds of the empty stomach are called:
(a) Rugae
(b) Taeniae
(c) Foveole
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Rugae

Question 32.
Brunner’s glands are found in:
(a) Oesophagus
(b) Stomach
(c) Duodenum
(d) Rectum
Answer:
(c) Duodenum
Question 33.
HCl is secreted by:
(a) Oxyntic cells
(b) Pancreatic cells
(c) Renal cells
(d) Cells of Bolani
Answer:
(a) Oxyntic cells
Question 34.
What is produced in Peyer’s patches?
(a) RBCs
(b) Lymphocytes
(c) Hormones
(d) Mucous
Answer:
(b) Lymphocytes
Question 35.
Enzyme amylase acts on:
(a) Starch
(b) protein
(c) Fat
(d) Sugar
Answer:
(a) Starch
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name two types of digestion.
Answer:
- Intra cellular digestion,
- Extra cellular digestion.
Question 2.
Give two examples of animals in which intracellular digestion is found.
Answer:
- Amoeba
- Yeast.
Question 3.
What is rugae?
Answer:
The mucous membrane of hard palate has many transverse ridges called rugae.
Question 4.
Name the four types of teeth in human beings.
Answer:
- Incisors
- Canines
- Premolars
- Molars.
Question 5.
Write names of three parts of stomach.
Answer:
Three parts of stomach are:
- Cardiac part
- Fundic part and
- Pyloric part.
Question 6.
Name three parts of small intestine.
Answer:
- Duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum.
Question 7.
Name three parts of large intestine.
Answer:
- Caecum
- Colon
- Rectum.
Question 8.
Name four layers present in histology of alimentary canal.
Answer:
- Serosa
- Muscularis
- Sub - mucosa
- Mucosa.
Question 9.
Name enzymatic components of pancreatic juice.
Answer:
- Trypsin and chymotrypsin
- Amylase or amylopsin
- Steapsin or lipase.
Question 10.
Where are islets of Langerhans found? Name chemicals produced by them.
Answer:
Islets of langerhans are found in pancreas. These secretes -
- Insulin and
- Glucagon hormone.
Question 11.
What is muscle contriction of stomach called?
Answer:
The muscle contriction of stomach is called peristalsis.
Question 12.
Name two enzymes and their functions secreted from gastric glands of human.
Answer:
- Trypsin: It converts proteins into peptones and proteoses.
- Rennin: It converts casein protein of milk into para casein.
Question 13.
What happens, if peristalsis would be stopped in alimentary canal?
Answer:
The food would not be move forward as a result the digestion of food is stopped.

Question 14.
Name the hormones which control digestive processes.
Answer:
Hormones which control digestive processes:
- Gastrin
- Enterogastrin
- Cholecystokinin
- Secretin
- Pancreozymin and
- Enterocrinin.
Question 15.
Name the absorbing unit of digested food.
Answer:
Villi.
Question 16.
What is deamination?
Answer:
Liver cells break down surplus amino acids into pyruvic acid and ammonia. This process is called deamination.
Question 17.
What is main place of action of gastrin?
Answer:
Stomach.
Question 18.
Where digested fat is absorbed?
Answer:
Digested fat is absorbed in lymph vessels called lacteals.
Question 19.
In which part of alimentary canal villi are found. What is their function?
Answer:
Villi are found in small intestine of alimentary canal. They absorb digested food.
Question 20.
Which enzyme is present in saliva? Mention its function.
Answer:
Saliva contains ptyalin enzyme. It converts starch into maltose.
Question 21.
In which form pepsin is secreted?
Answer:
Pepsin is secreted in the form of pepsinogen.
Question 22.
What is most important function of bile juice?
Answer:
Bile juice emulsifies the fat due to which it is absorbed easily.
Question 23.
What is assimilation?
Answer:
The utilization of absorbed susbstances by cells is known as assimilation.
Question 24.
What is glycogenesis?
Answer:
Assimilated glucose is used as primary source of chemical energy. Excess of glucose is converted into glycogen. This process is called glycogenesis.
Question 25.
What is glyconeogenesis?
Answer:
Conversion of stored glycogen into glucose as required is called gluconeogenesis.
Question 26.
Write the reaction of steapsin.
Answer:
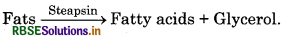
Question 27.
Name the hormone secreted by ß - cells of pancreas.
Answer:
Insulin.
Question 28.
Where is the thirst centre situated?
Answer:
Thirst centre is situated in the cerebral cortex and hypothalamus.
Question 29.
What are Peyer’s patches?
Answer:
Lymph nodes are found at various places in intestine. These nodes are called Peyer’s patches.
Question 30.
What is the chemical nature of vitamin - C?
Answer:
It is ascorbic acid.
Short Answer Type Questions - I
Question 1.
What is micelles?
Answer:
Micelles: During the process of digestion the fats are not digested completely and give mono and diglycerides on hydrolysis. These end products of fat digestion form small globules with bile salts. These globules are called micelles.
Question 2.
Write the name of digestive enzymes secreted from pancreas.
Answer:
Digestive enzymes secreted from pancreas:
- Amylase
- Trypsin
- Carboxydase
- Lipase
- Esterase
- Nuclease.

Question 3.
Write the action of trypsinogen enzyme.
Answer:
Trypsinogen is an inactive endopeptidase enzyme which is converted into an active trypsin in the presence of enterokinase enzyme secreted by mucous membrane of duodenum. This trypsin causes autocatalysis of inactive forms of trypsinogen and chymotrypsinogen into their active forms. Trypsin converts peptones and proteoses into polypeptides.
Question 4.
Name two enzymes and their functions found in intestinal juice.
Answer:
- Peptidase (Erepsin): It degrades pentose sugar, proteoses and polypeptide into amino acids.
- Maltase: It converts maltose sugar into glucose.
Question 5.
Name the fundic glands of stomach and their secretions.
Answer:
Fundic glands of stomach and their secretions:
- Mucous cells: Mucous.
- Chief or zymogen cells: Pepsinogen and prorennin.
- Oxyntic or parietal cells: HCl.
- Argentaffin cells: Serotonin and gastrin.
Question 6.
What is lactose intolerance?
Answer:
In some people the absorptive cells of the small intestine fail to produce enough lactase which is essential for the digestion of lactose. This condition is called as lactose intolerance. Due to undigested lactose in chyme, fluid is retained in faeces and the bacterial fermentation of the undigested lactose results in production of gases.
Short Answer Type Question - II
Question 1.
Write the functions of liver.
Answer:
Functions of Liver:
- Deamination: Liver cells receiving surplus amino acids from blood to degrade them into pyruvic acid and ammonia. Pyruvic acid either used in energy production or glucose synthesis under gluconeogenesis.
- Synthesis of urea: Liver cells synthesise urea with the help of urease enzyme taking ammonia formed from deamination and protein metabolism and CO2. Kidney excrete it with urine taking from blood.
2NH3 + CO2 → CO(NH2)2 + H2O - Removal of excretory substances: Some excretory substances reach to duodenum with bile and then eliminated with faeces.
- Detoxification: The toxic substances produced by bacteria present in intestine reach to liver by hepatic portal vein. The liver cells destroy them into harmless substances.
- Formation and destruction of blood corpuscles: In embryonal stages RBCs are formed in liver cells. In adult stage, kupffer cells of liver eat dead RBCs and bacteria.
- Storage of inorganic substances: Liver cells store iron, copper etc., inorganic substances.
- Synthesis of blood protein: Liver cells synthesise prothrombin and fibrinogen proteins which form blood clot during injury.
- Secretion of Heparin: Liver cells secrete heparin which prevents clotting of blood in vessels.
- Phagocytosis of bacteria: Liver cells eat harmful bacteria present in blood.
- Production and storage of lymph: Lymph is formed in liver and it is stored in blood sinusoids of liver.
Question 2.
What is emulsification?
Answer:
Emulsification: The breakdown of fat globules in the duodenum into tiny droplets which provides a larger surface area for enzyme action. This process is called emulsification. Bile salts and lacethin molecules acted on fat present in food. They have a polar end and a non - polar end. Non polar part dissolves in surface of fat globules and polar part remain in water. Due to this process, the surface tension of fat globules reduces, as a result large fat globules change into small droplets.The enzymes acts rapidly on emulsified fat.
Fat + Bile juice → Emulsified fat
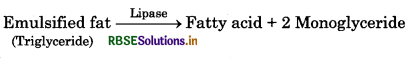
Question 3.
What are chylomicrons?
Answer:
During the process of digestion the fats are not digested completely and give mono and diglycerides on hydrolysis. These end products of fat digestion from small globules with bile salts. These globules are called micelles. Fat soluble vitamins also join these micelles. Through these micelles end product of fat digestion and fat soluble vitamins Teach absorptive cells through facilitated diffusion leaving bile salts aside. In these cells triglycerides are resynthesised from monoglycerides, diglycerides and fatty acids. Some triglycerides form phospholipids by combining with phosphate. Apart from this cholesterol is also esterified in these cells. All these fatty materials mix to form globules called chylomicrons.
Question 4.
What is difference between digestion and nutrition? Write the names of any two digestive juice found in human.
Answer:
Digestion: Breaking of organic food into smaller units by mechanical and chemical action for absorption is called digestion. While the nutrition is the process in which organism taking food materials which is usable for body. The digestive juice found in human:
- Gastric juice, secreted from stomach and
- pancreatic juice, secreted from pancreas.
Question 5.
Mention the chemical composition and functions of bile.
Answer:
Chemical composition of Bile: Bile contains 92% water the following other substances are found in bile:
1. Bile acids: These are formed from cholesterol. For example, cholic acid, deoxycholic acid etc.
2. Bile salts: Bile acids formed in liver combine with glycine or thiamine before their excretion into bile. In alkaline medium they are found as glycocholates and taurocholates of sodium and potassium. Sodium glycocholate and potassium glycocholate are the main bile salts of human beings.
3. Bile pigments: Bile pigments are formed by the break down of haemoglobin. There are two types of bile pigments in bile - bilirubin and biliverdin.
Function of bile:
- Bile turns the acidic medium of food to alkaline medium.
- Organic salts of the bile like sodium glycolate and sodium taurocholate reduce the surface tension of Tats and convert them into small globule. This process increases the surface area of fat for the action of lipase enzyme and is called emulsification of the fat.
- It protects food from decay destroying bacteria.
- Bile helps in the absorption of fat soluble vitamins like A, D, E and K.
- Bile acts as an excretory medium for the removal of many unwanted and toxic substances from the body. Bile pigments, medicines, toxic substances, copper, zinc and nickel etc., are excreted through bile only.
- It activates trypsin present in pancreatic juice.
- Bile salts are absorbed through the intestine and reach liver through entero - hepatic circulation, where they stimulate the secretion of bile. This is called cholagogue action.

Question 6.
How carbohydrates are digested in human alimentary canal? Explain.
Answer:
Digestion of Carbohydrates in alimentary canal of Human:
- The digestion of carbohydrates in human alimentary canal begins from buccal cavity. Saliva is mixed in it on chewing. The ptyalin enzyme present in saliva hydrolyses starch to converts it into maltose and dextrin.

- The next digestion of carbohydrates takes place in duodenum. The amylase enzyme present in pancreatic juice converts starch and glycogen into maltose sugar in alkaline medium.

- After this the digestion of carbohydrates occurs in small intestine as follows:
- The maltase enzyme of intestinal juice converts maltose sugar into glucose.

- Lactase enzyme converts milk lactose into glucose and galactose.

- Sucrase enzyme converts sucrose sugar into glucose and fructose.
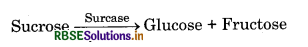
- The maltase enzyme of intestinal juice converts maltose sugar into glucose.
Such a way digestion of carbohydrates completed in small intestine.
Question 7.
Explain in brief main digestive glands takes part in digestion in human.
Answer:
Digestive glands in man:
1. Salivary Glands: There are three pairs of salivary glands found in human:
- parotid
- submaxillary and
- sublingual glands.
An alkaline fluid is secreted by these glands. It contains water ptyalin, α - amylase, lysozyme, mucous, sodium chloride, potassium, bicarbonates etc. The ptyalin present in saliva is a digestive enzyme which acts on starch of food. It makes food wet. Lysozyme kills the bacteria.
2. Liver: Liver is the largest gland of body. It is situated in the right upper side of the abdominal cavity just below the diaphragm. It is bilobed and the right lobe, is much bigger than the left lobe. There is an oval blue coloured sac like structure, attached to the lower surface of the right lobe, through mesentery. This sac is called gall bladder. The bile juice secreted by liver is stored in gall bladder. Which helps in digestion.
3. Pancreas: Pancreas is second largest gland of the body. It is irregular shaped leaf like, pinkish- coloured gland which situated between ‘U’ part of duodenum, attached by mesentery. It secretes pancreatic juice mainly. Many islets of Langerhans are found in interstitial tissue at many places in pancreas. These islets have α - cell, ß - cell and γ - cells. These cells secrete glucagon, insulin and somatostatin hormones respectively.
Question 8.
Write sources and functions of ptyalin and pepsin.
Answer:
- Ptyalin: Ptyalin is present in saliva secreted by salivary glands. It is an enzyme which converts starch into maltose in mouth.
- Pepsin: Inactive pepsinogen is secreted by gastric glands of stomach which is turned into active pepsin by the action of HCl. It degrades food proteins into peptones and polypeptides.
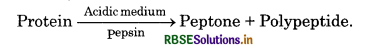
Question 9.
Why chapati seem sweet by chewing it more?
Answer:
Chapati has a polysaccharide carbohydrate starch in insoluble condition. When chapaties are chewed for a time, the saliva gets mix in it. The ptyalin enzyme present in it converts about 5% insoluble starch into soluble sugar called maltose. Maltose is sweet in taste. Due to this chapati seems sweet on chewing it more.
Question 10.
What would happen if pancreas stops their functions?
Answer:
1. There shall be no pancreatic juice secreted from pancreas. The pancreatic juice contains trypsin, chymotrypsin, amylase, lipase, carboxypeptidase enzymes. They digest protein, starch and fat. In the absence of these enzyme there would be digestion of protein, starch and fat will not takes place.
2. The ß - cells and α - cells of islets of Langerhans of pancreas secrete insulin and glucagon hormones respectively. The insulin causes glycogenesis (the process of conversion of glucose into glycogen in liver) and the glucagon causes glycogenolysis (the process of conversion of glycogen into glucose). Due to lack of insulin and glucagon these process are stopped. The level of glucose in blood will be increases. It may cause diabetes.

Question 11.
Where following are found? Give one function of each.
1. Incisors
2. Amylase
3. Carbohydrates
4. Pancreas
5. Bile.
Answer:
|
Substance |
Source |
Main function |
|
1. Incisors |
1. On the jaws inbuccal cavity in mammals. |
1. Tearing and cutting of food. |
|
2. Amylase |
2. Present in pancreatic juice. |
2. Digestion |
|
3. Carbohydrates |
3. Wheat, rice, potato and fruits. |
3. Provide energy. |
|
4. Pancreas |
4. In abdominal cavity below the diaphragm. |
4. Digestion of food by enzymes. |
|
5. Bile |
5. Secreted from liver. |
5. Emulsification of fats. |
Question 12.
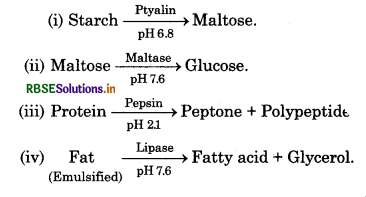
On which component following enzymes acted. Give answer only by chemical equation.
Ptyalin, Maltase, Pepsin, Lipase.
Answer:
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe various parts of alimentary canal of human with labelled diagram.
Answer:
The process of breaking down of large food particles into smaller and water-soluble particles, which can be easily absorbed by the blood plasma is termed as digestion. All parts of the body are involved in the uptake and digestion of food along with the elimination of undigested material. The alimentary canal is mainly referred to as the pathway by which food enters our body and moves out through the anus after digestion. It is a tube - like structure which starts from the mouth and ends in the anus. The alimentary canal plays a primary role in human digestion and is also termed as the digestive tract.
Organs of the Alimentary Canal:
The main organs of the alimentary canal are:
- The Mouth and Oral cavity.
- Oesophagus.
- Stomach.
- Small intestine.
- Large intestine.
The structure and functions of these organs are discussed below.
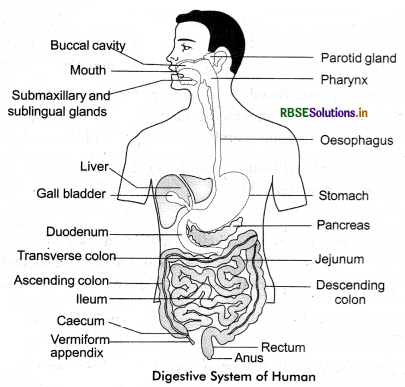
Human digestive system comprises the alimentary canal and various digestive glands. The alimentary canal is a muscular tube, which extends from the mouth to the anus. The human digestive system comprises mouth, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus.
- Mouth: The mouth is the first part of our digestive system. Food is ingested through the mouth.
- Oral cavity: The oral cavity comprises the palate, tongue and teeth.
- Palate: The roof of the oral cavity.
- Tongue: Muscular and glandular structure attached to the base of the oral cavity. The upper surface of the tongue has tiny projections known as lingual papillae. Lingual papillae are of three types: circumvallate, fungiform and filiform.
- Teeth: Humans are diphyodont i.e. they have two sets of teeth - milk or deciduous and permanent teeth. Here is the list of different types of teeth in humans with their functions.
|
Type of teeth |
Function |
|
Incisors |
Used for cutting |
|
Canines |
Used for tearing |
|
Premolars |
Used for Chopping |
|
Molars |
Used for Grinding and Chewing |
The structure of the tooth is made up of three parts- the crown, neck, and root. The exposed part of the tooth is called the crown, the region where it is covered with gums is known as neck and root is embedded in the socket of the jaw bone (Thecodont).
Pharynx: It is the common passage for food and air. Epiglottis prevents the entry of food into the windpipe.
Oesophagus: It is a muscular tube through which small bolus of food passes from the mouth to the stomach. The gastro - oesophageal sphincter controls the movement of food into the stomach.
Stomach: It is a muscular bag, positioned at the upper left part of the abdominal cavity. It has four parts- cardiac, fundus, body and pyloric portion.
Cardiac part: It is present close to the heart. The opening of the oesophagus to the stomach is regulated by the gastro - oesophageal sphincter.
Fundus: It is dome - shaped and is usually filled with air.
Body: This is the main part of the stomach.
Pyloric: It opens in the first part of the small intestine, duodenum. The opening of the stomach into the small intestine is regulated by the pyloric sphincter.
Small Intestine: It is the longest part of the alimentary canal and comprises three parts- Duodenum, Jejunum, and Ileum.
Duodenum: It is C - shaped. The pancreatic, bile and hepatic secretions are added to the food by hepatopancreatic duct.
Jejunum: Middle part of the small intestine.
Ileum: It is highly coiled and opens into the large intestine.
Large Intestine: The small intestine leads into the large intestine. It has three parts- Caecum, Colon, and Rectum.
Caecum: It is a small sac-like structure containing symbiotic microorganisms. The vermiform appendix (vestigial organ) is attached to it.
Colon: It is divided into four regions- ascending, transverse, sigmoid and descending.
Rectum: It opens into the anus.
Question 2.
What do you understand by balanced diet? Write main nutrients of balanced diet.
Answer:
A healthy diet or balanced diet is a diet (what we eat) that contains the right amounts of all the food nutrients (i.e., carbohydrates, proteins, fats, minerals, vitamins and water). It include fruits, vegetables, grains, dairy products and proteins. It does not include too much or too little of any kind of food.
Definition: A diet consisting of a variety of different types of food and providing adequate amounts of the nutrients necessary for good health is called balanced diet.
Eating wrong amounts of a food group, whether it he too much or too little, is called an “unhealthy diet” or an “imbalanced diet”. A healthy diet is one that includes more foods that come from plants and fewer convenience foods. The most primary nutrient of our food is carbohydrate which is the main source of energy, it includes various forms but glucose is common source of energy i.e., other carbohydrates are also converted to glucose. The fat includes necessary fatty acid (like: linolinic acid, linolic acid, aracdonic acid etc.). Though fats also provide energy but their digestion is very hard.
Proteins have essential aminoacids (like: valine, histidine, arginine, tryptophen, lysine etc.). Proteins are building components of our body. It is necessary to includes rough fibres in our diet. Besides in a balanced diet, salt and vitamins are most necessary. Salts and vitamins function as metabolic regulators in our body. The disorders may occur in the abscence of minerals and vitamins. The ratio of amount of nutrients in balanced diet changing accordingly to age, body structure, sex and work, has been given in following tables.
The amount of Energy available in Food Substances:
The amount of energy present in food substances is expressed in kilo calorie. The energy released by complete oxidation of one gram molecule of a food substance in one kilo calorie, is called gross calorie value. The released energy in our body by various food materials is called functional energy.
Question 3.
Explain in detail the intestinal digestion in human.
Answer:
The process of digestion takes place in alimentary canal. This process is completed in following five steps:
- Ingestion.
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Assimilation
- Egestion
I. Ingestion: In take of food into buccal cavity through the mouth is called ingestion. Human is omnivorous and uses his hands for bringing food to mouth and bite the food by incisors or take it in mouth cavity directly depending on the type of the food. Lips do not allow the ingested food to move out and the rugae present on the hard palate hold the food for chewing. The chewing of food is a reflex action. During chewing food mucous and saliva are mixed in the food. The tongue cap sizes the food.
II. Digestion of food: Break down of complex components of the food into simple absorbable molecules is called digestion of food. The digestion is an enzyme based process. The human diet includes carbohydrates, protein, fat, vitamins, mineral salts and water. There is no need to digest minerals, vitamins and water. The remaining parts of food are digested in buccal cavity, stomach and intestine.

Question 4.
Where is the absorption of digested food takes place in human? Explain.
Answer:
Entry of different digested food particles from body cavities into blood capillaries or lymph vessels through biological fnembrane is called absorption. The absorption of food particles takes place by both the inactive and passive methods. In passive absorption, the movement of food particles occurs from higher concentration to lower concentration. By this process, fatty acids, fat soluble substances, and glyceroids and cholesterol are absorbed. Water and salts dissolved in it are absorbed by simple diffusion.
The energy of ATP is required for active absorption. In this absorption takes place against concentration gradient. Such as absorption of amino acids and some ions.
On completing the digestion the food breaks down into its simple components. Carbohydrates, protein, alcohol, water, vitamins etc., are absorbed by simple blood capillaries while fat is absorbed by special lymph vessels called lacteals present in ileum villi.
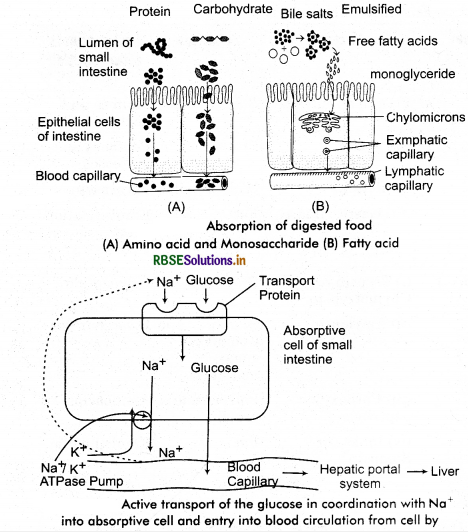
There is no absorption takes place in oesophagus and buccal cavity and in stomach total alcohol and some salts are absorbed. Most of the substances are absorbed through small intestine. About 5-8% of digested food is absorbed in duodenum and about 90% part is absorbed in ileum, because histological structure of ileum is perfectly adopted for the absorption.
1. Absorption of Glucose and Amino acids: Glucose and aminoacids are absorbed into blood through active transport. For this purpose energy is obtained by sodium co-transportation. First of all, in this process Na+ from epithelium of intestine come into intestinal cavity by active transport. ATP energy is used for this. There Na+ being defficient in intestinal epithelium due to movement of them. Na+ions can enter into epithelium by simple diffusion but carrier protein is required for this. When this protein joines with Na+ and glucose or amino acid, then due to electrochemical gradient of Na+, nutrient substances glucose or amino acid along with sodium enter into intestinal epithelium. It is called sodium co - transport.
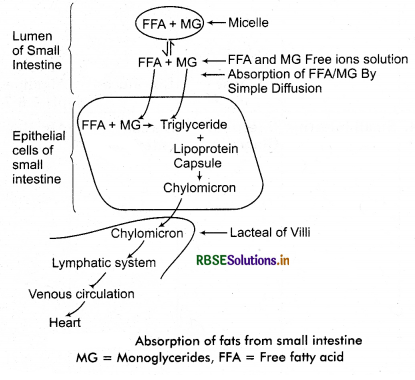
2. Absorption of Fat : During the process of digestion the fats are not digested completely and produce mono and diglycerides on hydrolysis. These end products of fat digestion form small globules with bile salts. These globules are known as micelles. Fat soluble vitamines such as vitamin A, D, E and K also join these micelles. Through these micelles are end products of fat digestion and fat soluble vitamins reach absorptive cells through facilitated diffusion leaving bile salts aside. In these cells triglycerides are resynthesised from monoglycerides, diglycerides and fatty acids.
Some triglycerides form phospholipids by combining with phosphate. Besides cholesterol is also esterified in these cells. All these fatty materials mix to form chylomicron. These chylomicrons reach the lymph vessels present in the villi of absorptive cells. Presence of a lot of chylomicrons in lymph vessels makes the lymph milky in colour. Now it is called chyle and the lymph vessels having chyle are called lacteals. These lacteals open in larger lymph vessels. Larger lymph vessels join each other to form thoracic lymph duct which opens in left sub-clavin vein near the heart.
Question 5.
Tabulate various digestive enzymes related to digestion in human. Give their main functions also.
Answer:
The substances formed as a result of digestion like glucose, amino acids, free fatty acids, glycerol, phospholipids, nitrogenous bases, minerals, vitamins, cholesterol, water etc., finally reach blood circulation after their absorption. They are used in oxidation to produce energy or in the synthesis of complex molecules in cells. In this way, these substances becomes the part of protoplasm. This utilization of substances by cells is known as assimilation and the assimilated substances are called metabolites. In some process of assimilation energy is either required or releases.
The assimilation of main components of food takes place as follows:
1. Assimilation of carbohydrates: After reaching liver, monosaccharides are sent to heart by blood and from heart they are sent to different parts of the body. In tissues they (glucose) are oxidise to produce energy. Excess of glucose is converted into glycogen. This process is called glycogenesis. It is stored in muscles and liver Whenever required, liver cells start converting amino acid and glycerol into glucose.
2. Assimilation of Proteins: Amino acids reach in each cell of body and forms cell and its components. They also take part in the formation of enzymes and different hormones. Surplus amino acids produce ammonia by deamination in liver cells. Ammonia forms urea which is excreted as urine.
3. Assimilation of fat: Fat are used as concentrated source of energy in our body. Apart from this, fat and phospholipids are utilized in the formation or repair of bio membranes. Steroid hormones are also synthesized from fats. Surplus fat is stored as adipose layer beneath skin and functions as insulating layer. Complex fatty acid, triglycerides, phospholipids and cholesterol enclose protein capsule to form chylomicron fat globule and release to lymph. From where central lymph vessel releases them into blood.

- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 10 Cell Cycle and Cell Division
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 9 Biomolecules
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 Cell: The Unit of Life
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 Morphology of Flowering Plants
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 4 Animal Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 3 Plant Kingdom
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 2 Biological Classification
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 1 The Living World
- RBSE Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 5 पुष्पी पादपों की आकारिकी